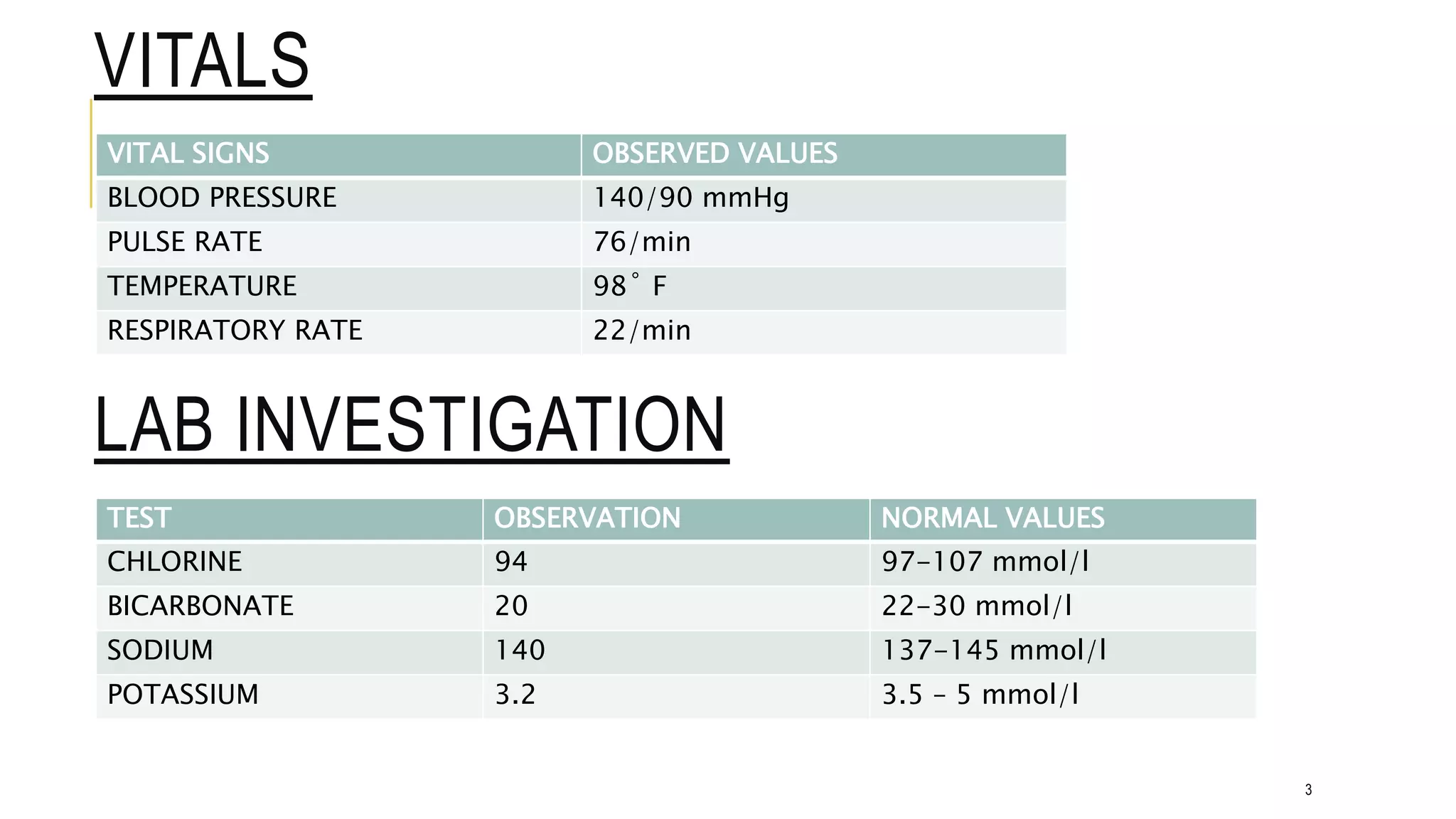
A 45-year old female presented with generalized tiredness, drowsiness, confusion and seizures. Lab tests and CT scan revealed early hydrocephalus, a suspicious lesion in the fourth ventricle, and subarachnoid hemorrhage due to aneurysm rupture. She was admitted to the neuro ICU and started on treatments including dexamethasone, nimodipine, pantoprazole, paracetamol, fosphenytoin, mannitol and ondansetron to relieve symptoms, repair the bleeding vessel, prevent complications and recurrence. The pharmacist provided counseling on disease, drugs, lifestyle modifications and points to the physician regarding monitoring and potential drug interactions.