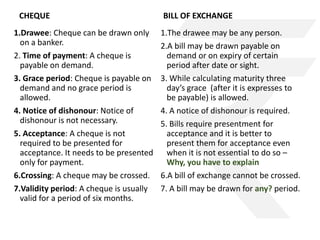
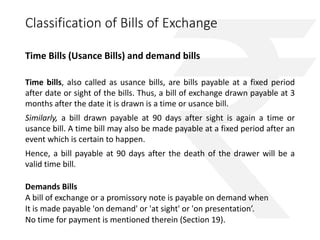
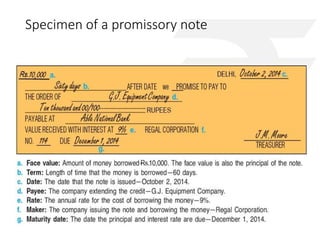
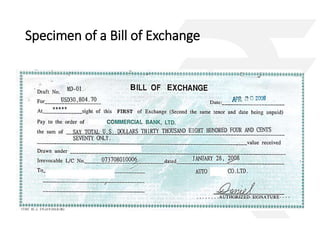
The document outlines the Negotiable Instruments Act of 1881 in India, which governs negotiable instruments such as cheques, promissory notes, and bills of exchange, and describes their characteristics, validity, and legal implications. It highlights the importance of valid signatures, payment conditions, and the rights of holders in due course while detailing the essential elements required for these instruments. Furthermore, the document presents practical case studies to illustrate the application and consequences of these instruments in financial transactions.














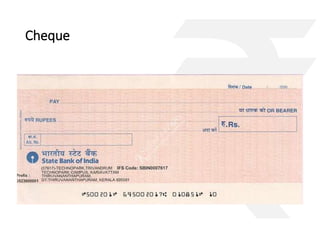








![Case study on Cheque:
In Canara Bank vs. Canara Sales Corporation and Others
[(1987)2 Supreme Court Cases 666]
The company has a current account with the bank which was operated by the
Company’s Managing Director. The Company’s account in whose custody the
cheque book was, forged the signature of the Managing Director in 42 Cheques
totaling Rs.326047.92 over a period of time. This was detected by another
accountant. The company immediately on detected of the fraud demanded the
amount from the bank. The bank refused payment and therefore the company files
a suit against the bank. The bank lost the suit and took the matter up to the
Supreme Court. The Supreme Court dismissed the appeal of the bank and held that
Since the relationship between the customer and the bank is that of a creditor and
debtor, the bank had no authority to make payment of a cheque containing a
forged signature. The bank would be acted against the law in debiting the customer
with the amount of the forged cheque as there would be no mandate on the bank to
pay. The Supreme Court pointed out that the document in the cheque form on
which the customer’s name as drawer was forged was a mere nullity. The bank
would succeed only when it would establish adoption or estoppels. In dealing the
case the Supreme Court relied on its earlier judgment in Bihta Cooperative
Development and Cane Marketing Union Ltd vs. bank of Bihar (AIR 1967 Supreme
Court 389)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group6-141109090244-conversion-gate02/85/negotiable-instruments-only-valid-in-India-27-320.jpg)