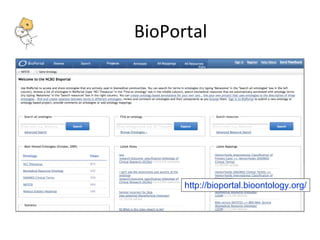
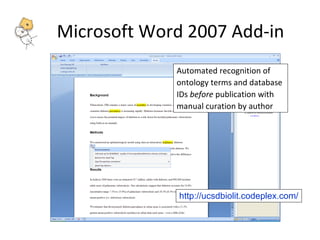
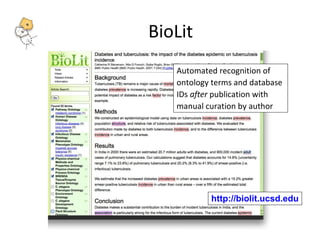
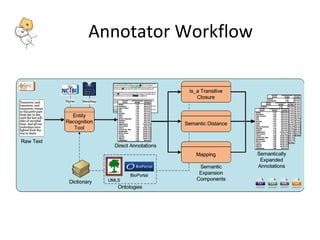
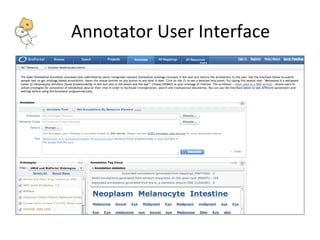
The document describes tools and web services from the National Center for Biomedical Ontology (NCBO) including the Ontology Web Services, Ontology Widgets, NCBO Annotator, NCBO Resource Index, and Ontology Recommender. The NCBO Annotator is an open access web service that annotates text with terms from ontologies in BioPortal and includes a variety of customization parameters. The NCBO Resource Index provides an ontology-based search across publicly available biomedical resources.