Human resource management involves continuous processes concerned with developing employees at all levels of an organization. It covers people-related functions like recruitment, training, compensation and benefits. The goal is to build human capital, align HR policies with business strategies, and help achieve individual, group and organizational goals.
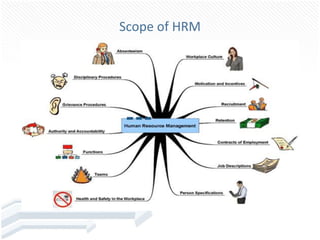
The scope of HRM includes personnel functions from hiring to separation. It also deals with employee welfare like facilities and amenities. Additionally, it covers labor-management relations through activities like collective bargaining and grievance procedures.
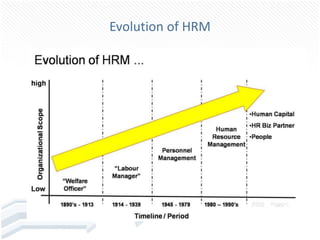
HRM has evolved from early concepts in ancient India and labor commissions to incorporate functions like industrial relations, apprenticeships, and mandatory job vacancy notifications. It has expanded beyond its personnel management origins to place greater emphasis on