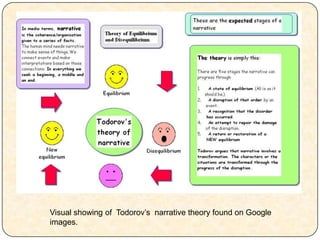
Vladimir Propp examined folk tales and identified eight character roles and thirty-one narrative functions that are commonly found across stories. He found that the character roles of hero, villain, dispatcher, and others along with narrative functions like lack, struggle, and reward are often present in different types of narratives from movies to folk tales. Bordwell and Thompson believed narratives shape events in time and space through techniques like flashbacks and time jumps. Claude Levi-Strauss analyzed narratives based on sets of opposing values or "binary oppositions" like good vs. evil rather than narrative order. Tzvetan Todorov's theory proposed stories begin with equilibrium, are disrupted by an event, and end with restoration of the initial