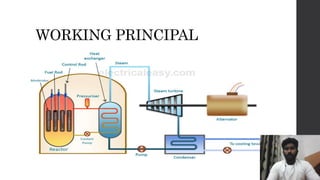
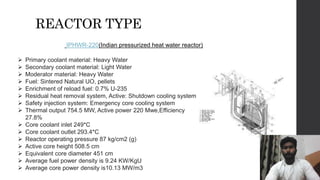
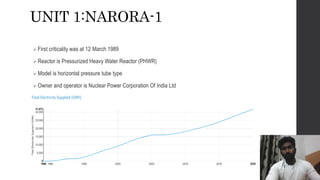
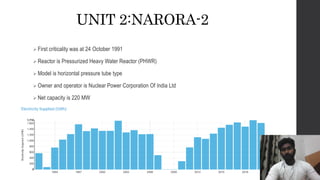
The Narora atomic power plant is located in Uttar Pradesh, India on the banks of the Ganga River. It has two pressurized heavy water reactor units, each with a capacity of producing 220 MW of electricity. The plant uses heat from the nuclear fission of uranium atoms to heat water into steam, which spins turbines that generate electricity. It began operations in 1989 and 1991 for its two units and was India's first standardized pressurized heavy water reactor nuclear power plant.