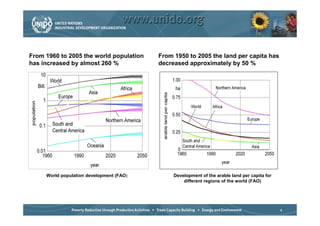
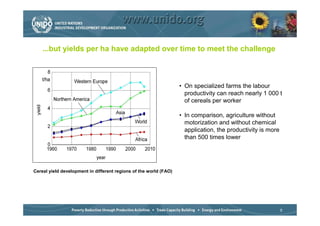
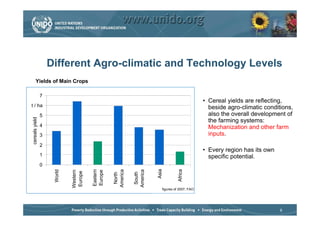
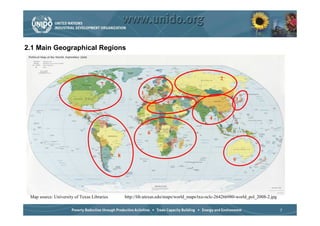
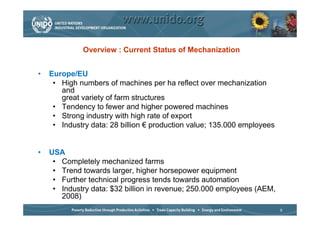
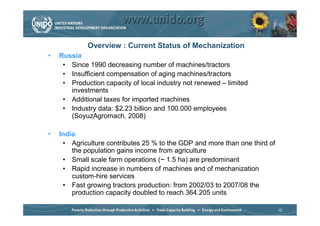
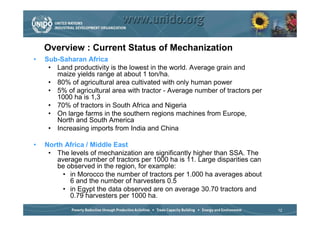
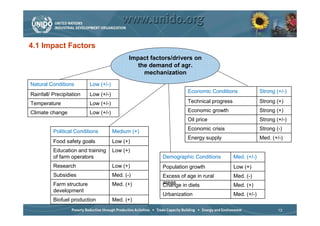
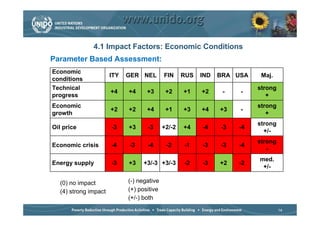
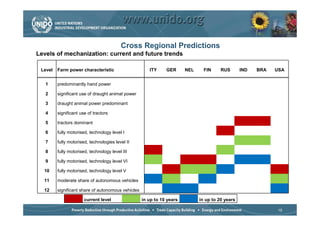
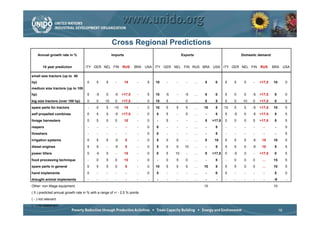
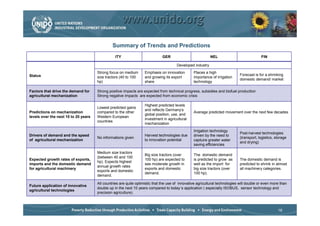
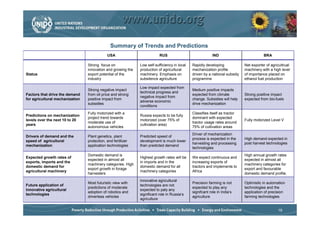
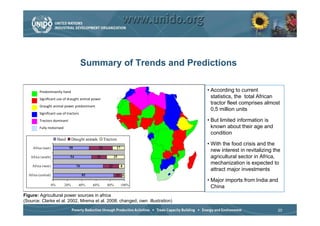
The document discusses world trends in agricultural machinery manufacturing. It outlines the major challenges facing agriculture globally and analyzes the sector by geographical regions. For each region, it provides an overview of the current status of mechanization and predicts future trends over the next 10 to 20 years, such as increasing levels of mechanization and annual growth rates for various machinery exports, imports, and domestic demand. Key drivers of increasing mechanization include technical progress, economic growth, and biofuel production, while economic crises may slow growth.