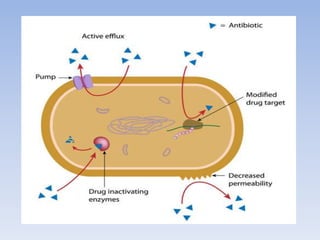
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes become resistant to antimicrobial drugs like antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals. AMR happens through genetic mutations that make microbes impervious to standard drug doses. The overuse and misuse of antimicrobials, including taking leftover drugs and not completing full treatment courses, are major causes of growing AMR. As AMR increases, infections become harder and more expensive to treat, and some "wonder drugs" become obsolete. Public health strategies aim to slow AMR through prudent antimicrobial use, developing new drugs, and limiting over-the-counter drug access.