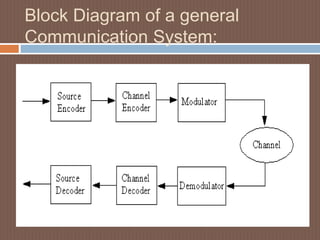
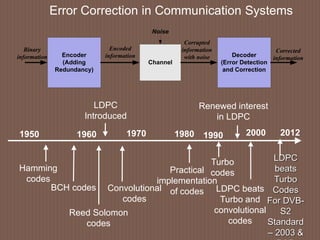
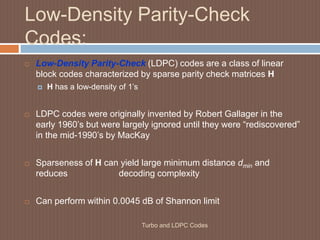
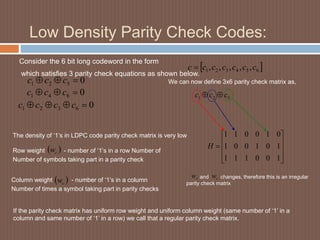
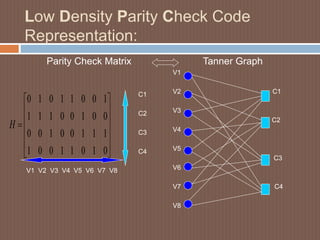
This document discusses low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes. It begins with an overview of LDPC codes, noting they were originally invented in the 1960s but gained renewed interest after turbo codes. It then covers LDPC code performance and construction, including generator and parity check matrices. Various representations of LDPC codes are examined, such as matrix and graphical representations using Tanner graphs. Applications of LDPC codes include wireless, wired, and optical communications. In conclusions, turbo codes achieved theoretical limits with a small gap and led to new codes like LDPC codes, which provide high-speed and high-throughput performance close to the Shannon limit.










![LDPC Code Performance
Example:
]
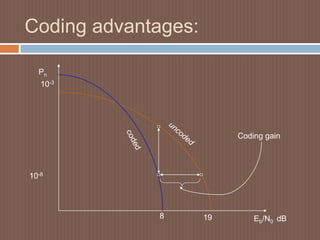
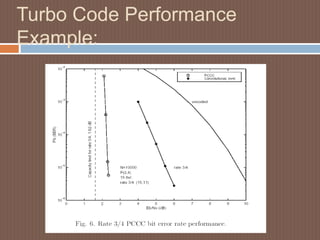
LDPC Performance can
Be very close to capacity.
The closest performance
To the theoretical limit
ever was with an LDPC,
and within 0.0045dB of
capacity.
The code shown here is
a high-rate code and
is operating within a few
tenths of a dB of capacity.
Turbo Codes tend to work
best at low code rates and
not so well at high code
rates.
LDPCs work very well at
high](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myreviewonldpc91-141221204638-conversion-gate02/85/My-review-on-low-density-parity-check-codes-20-320.jpg)