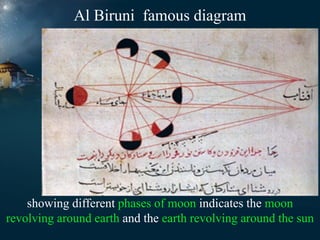
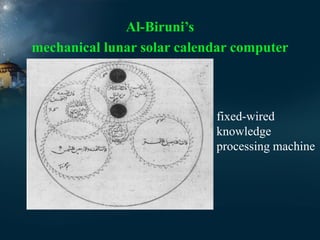
1) During the Abbasid Caliphate from 750-1258 CE, astronomy flourished in the Islamic world with the establishment of observatories and houses of wisdom where scholars studied the field.
2) Key Muslim astronomers and mathematicians like al-Khwarizmi, al-Battani, and al-Biruni made advances in determining the size of the earth, accurately calculating the length of the solar year, and developing early astronomical instruments and models of the solar system.
3) Later astronomers such as al-Zarqali, al-Tusi, and Ulugh Beg established additional observatories where further observations and studies were conducted.