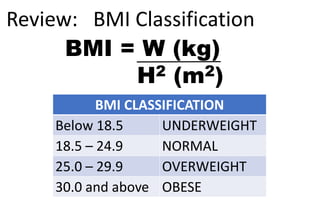
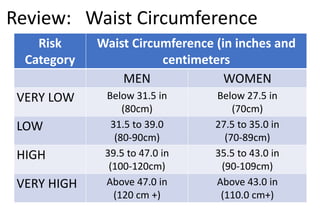
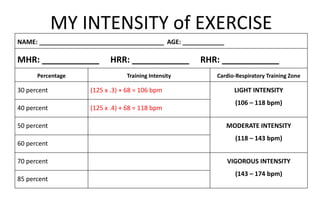
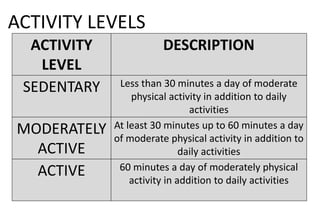
This document provides information about nutrition for better health and fitness. It discusses macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats that should make up a certain percentage of daily caloric intake. It also discusses micronutrients like vitamins and minerals that are essential for various bodily functions. Vitamins discussed include B vitamins, vitamin C, D, E, K, and A. Minerals discussed include calcium, iron, zinc, chromium, magnesium, selenium, and copper. Food sources of these nutrients are also mentioned.