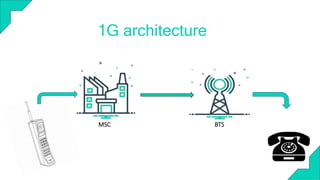
The document outlines the evolution of mobile communication from its inception in 1973, highlighting key milestones such as the introduction of the first handheld mobile phone and the launch of the first commercial cellular network (1G) in 1979. It discusses various generations of mobile networks, culminating in 4G technology, which offers significantly improved speed and connectivity features. The document emphasizes the integral role of mobile technology in enhancing global communication and societal interactions.