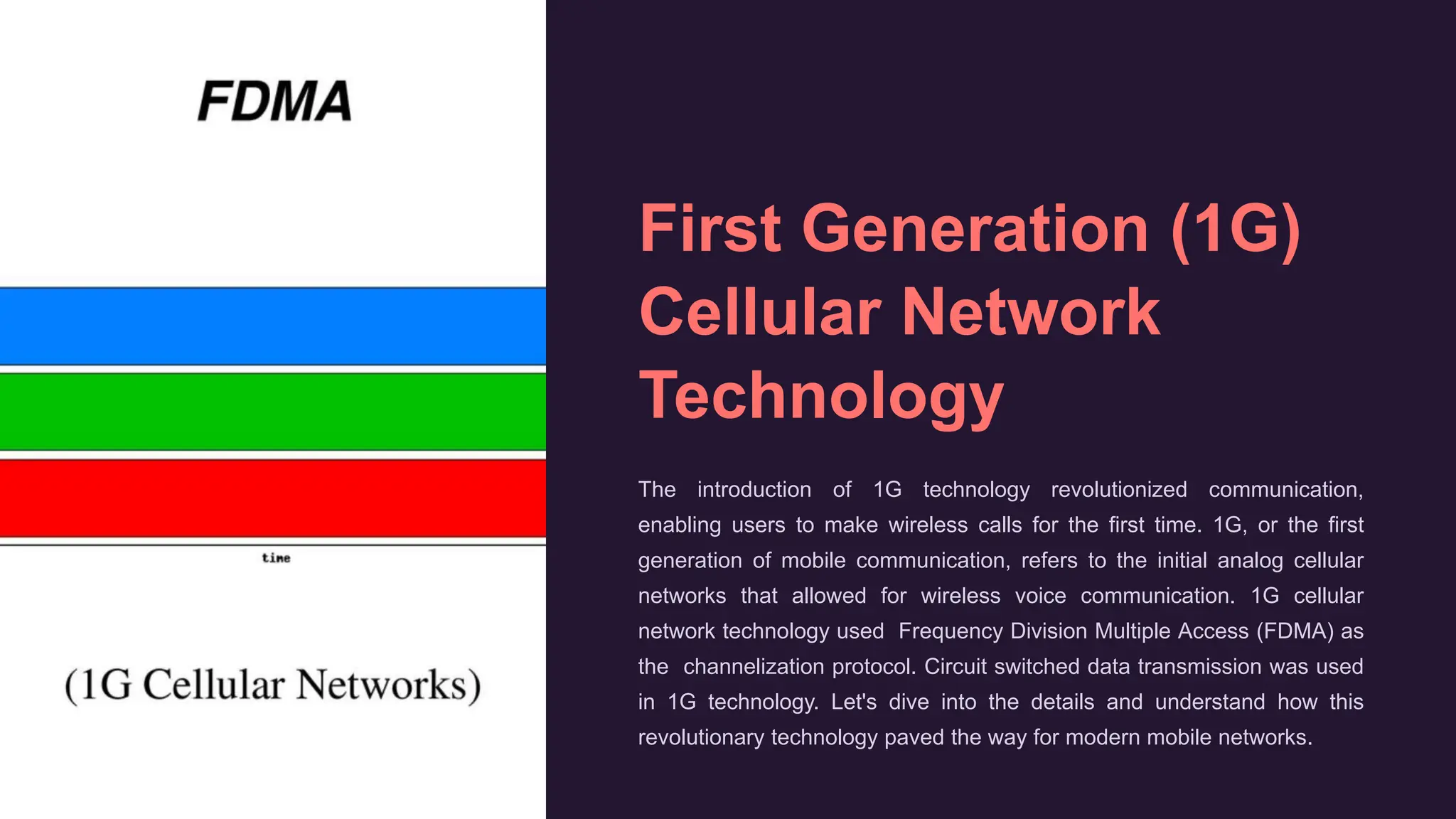
Mobile communication allows for instant wireless communication regardless of location. It uses radio waves between mobile networks and cell phones. Cell towers provide nationwide cellular coverage so cell phones can connect. Mobile communication has become essential by enabling easy communication anywhere.