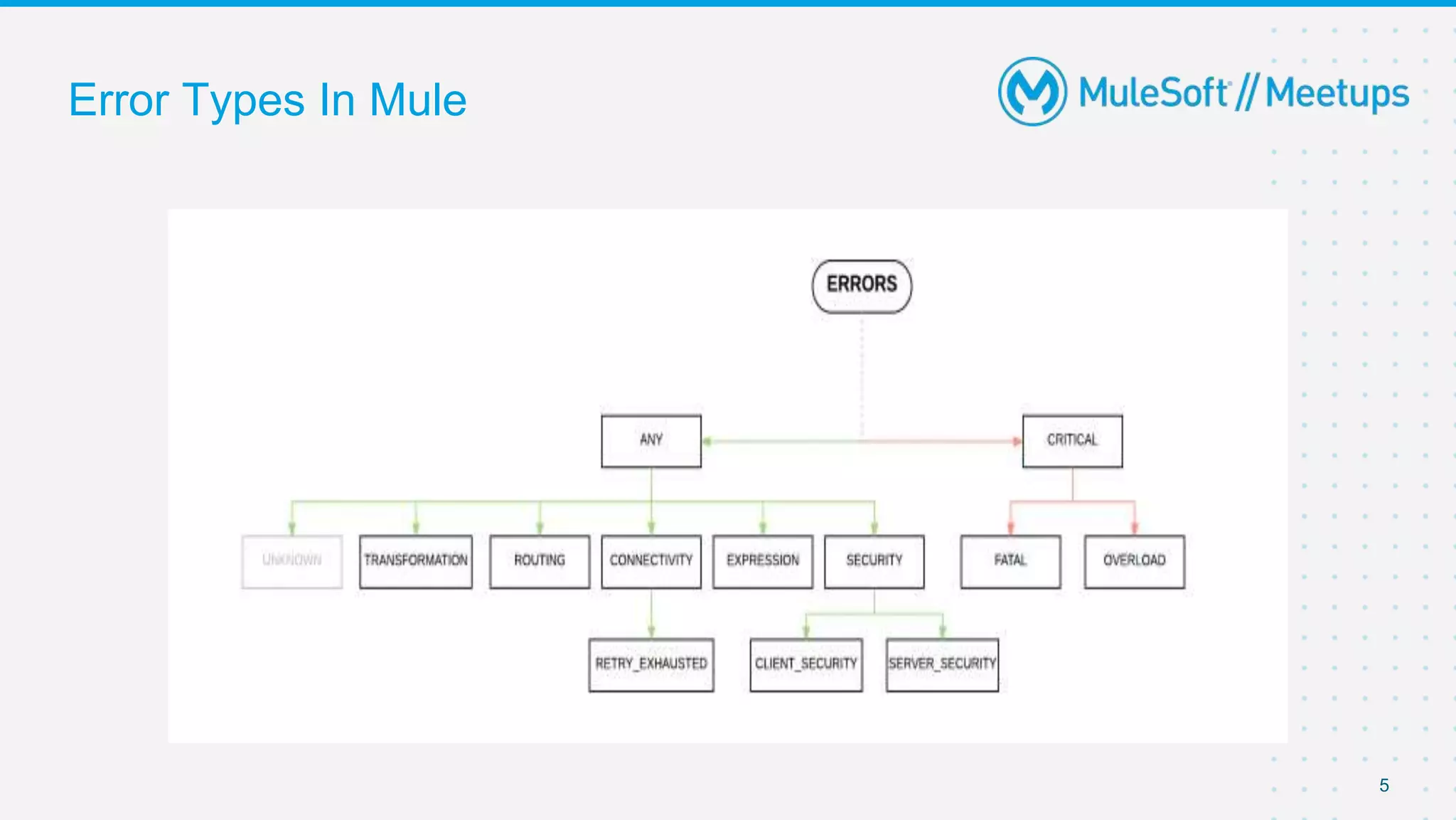
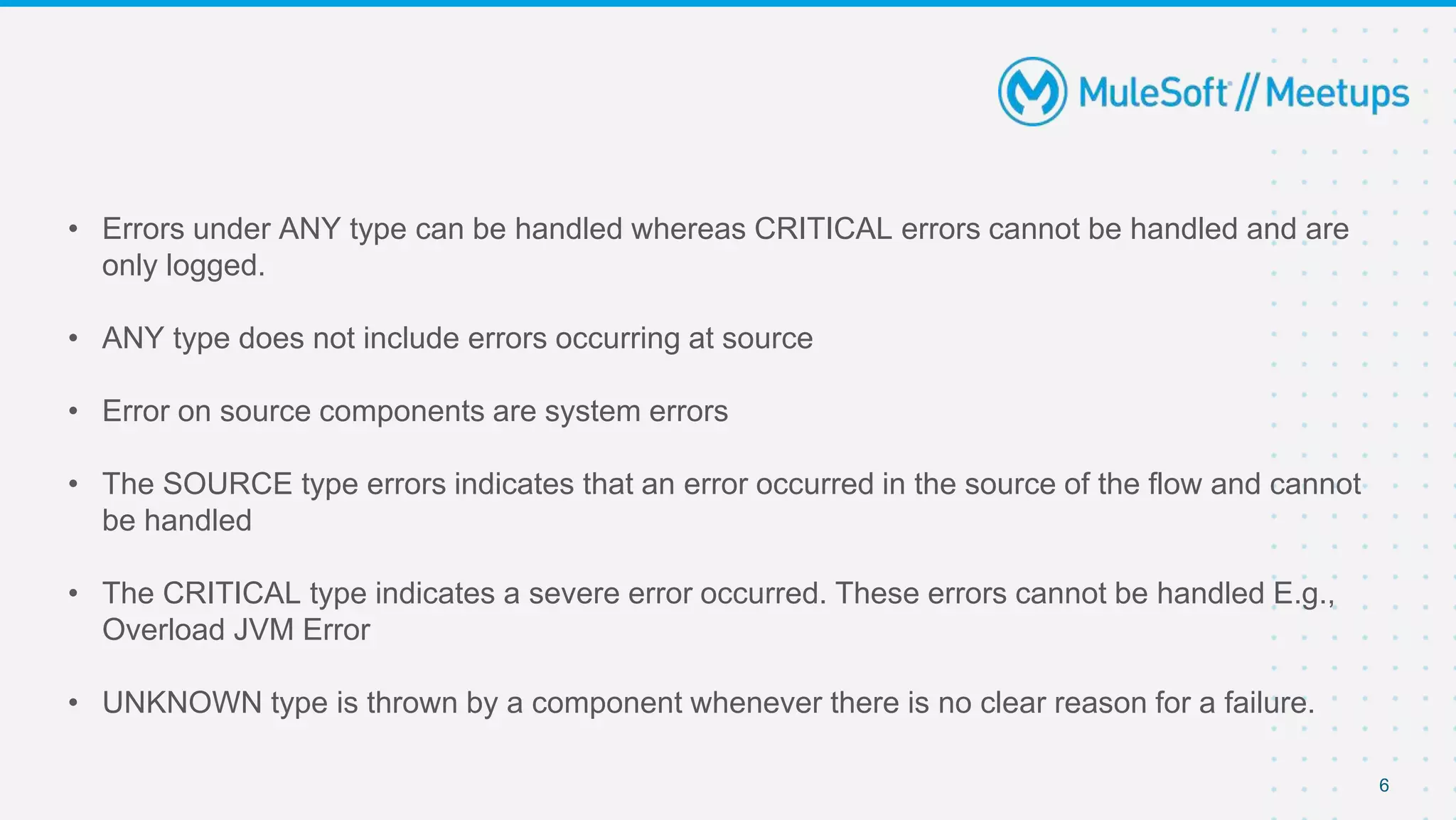
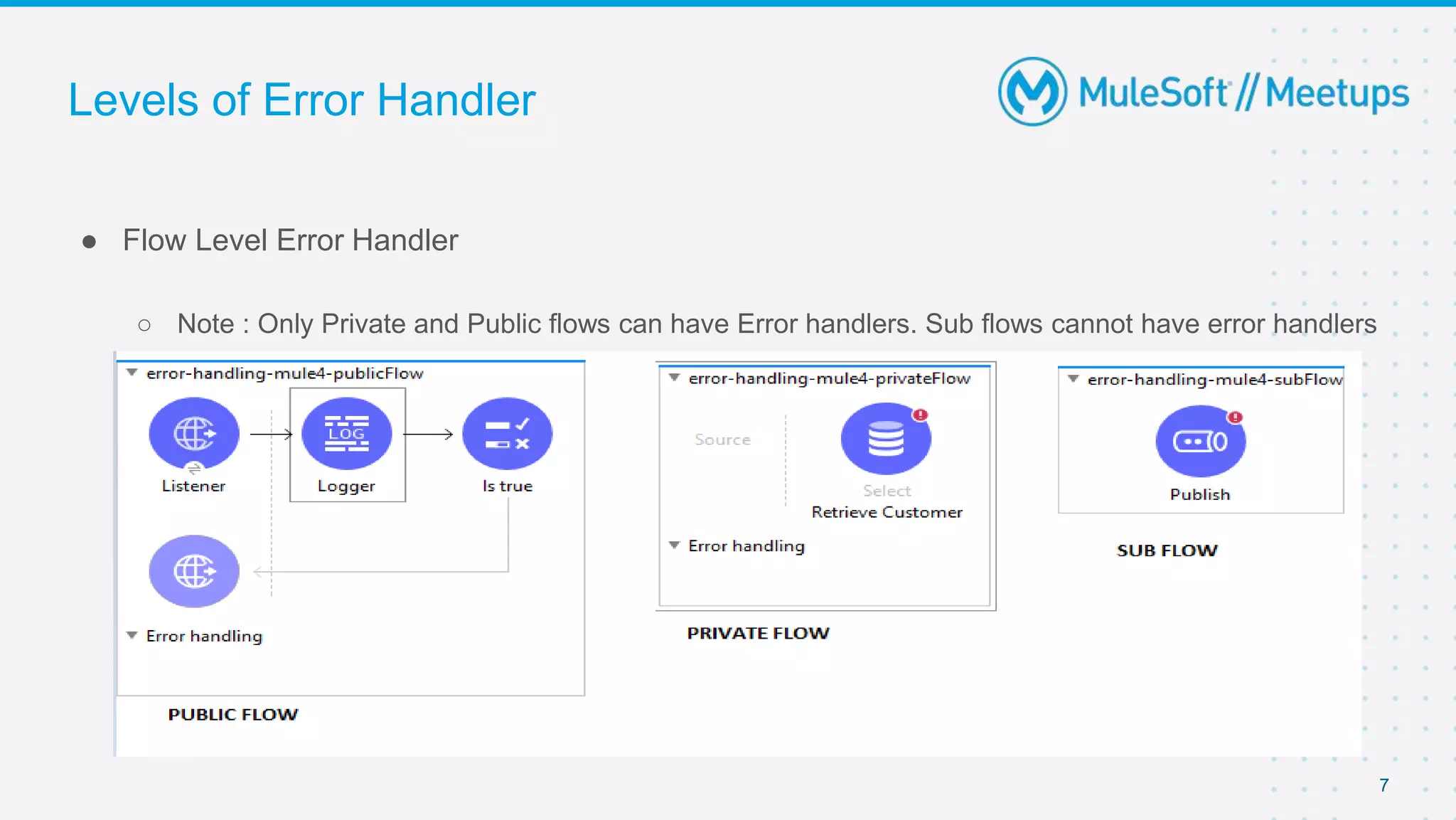
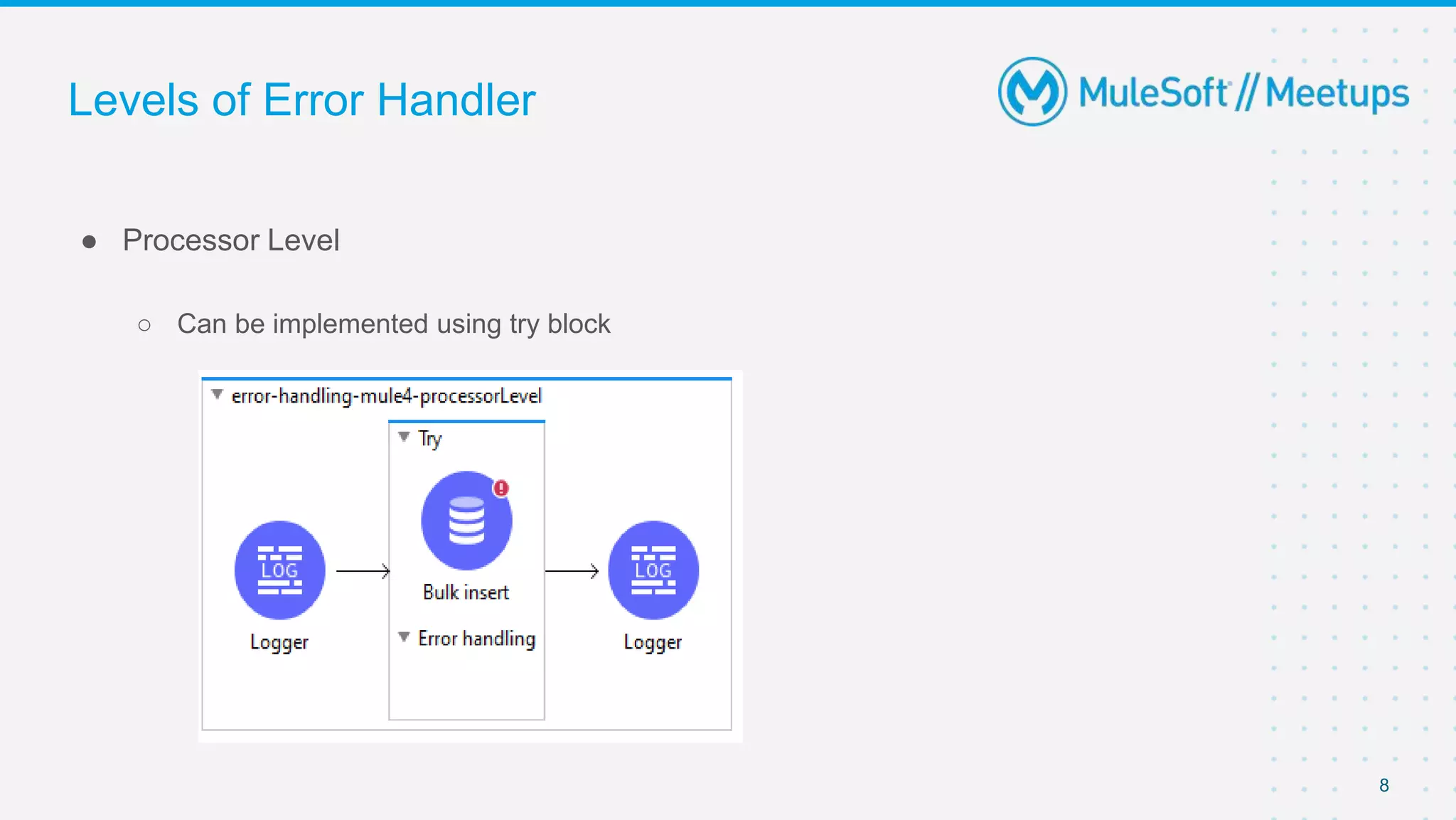
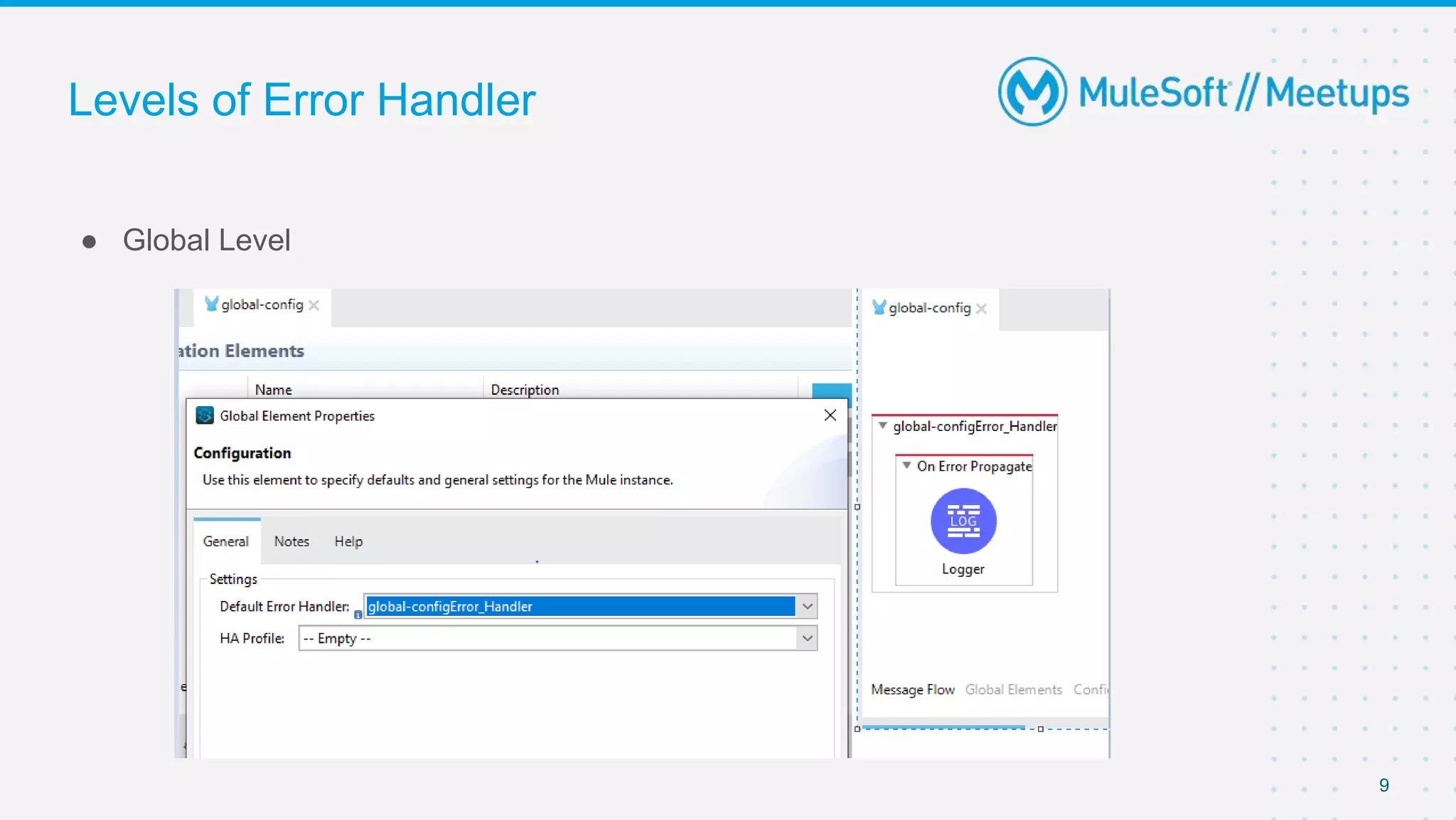
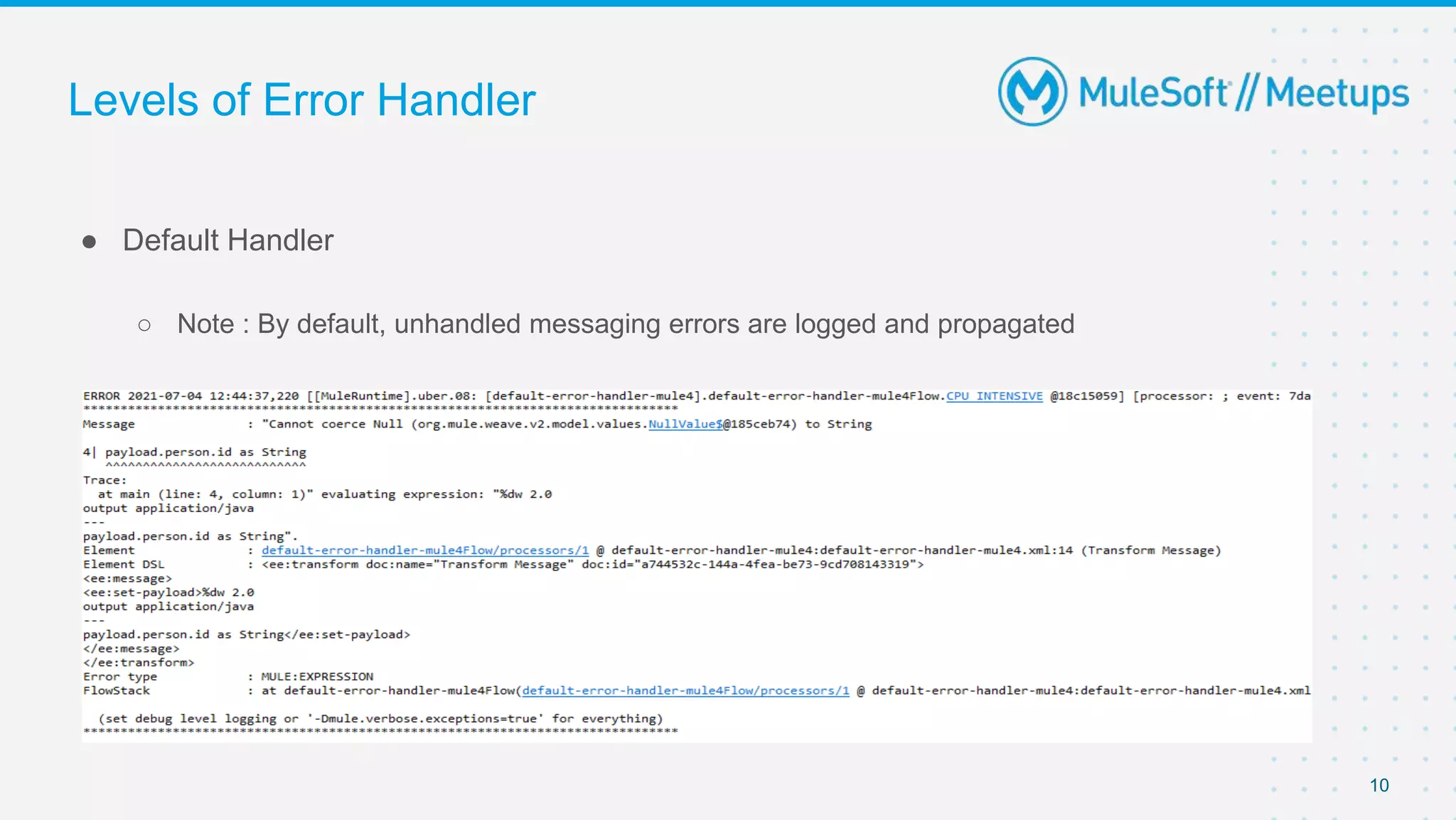
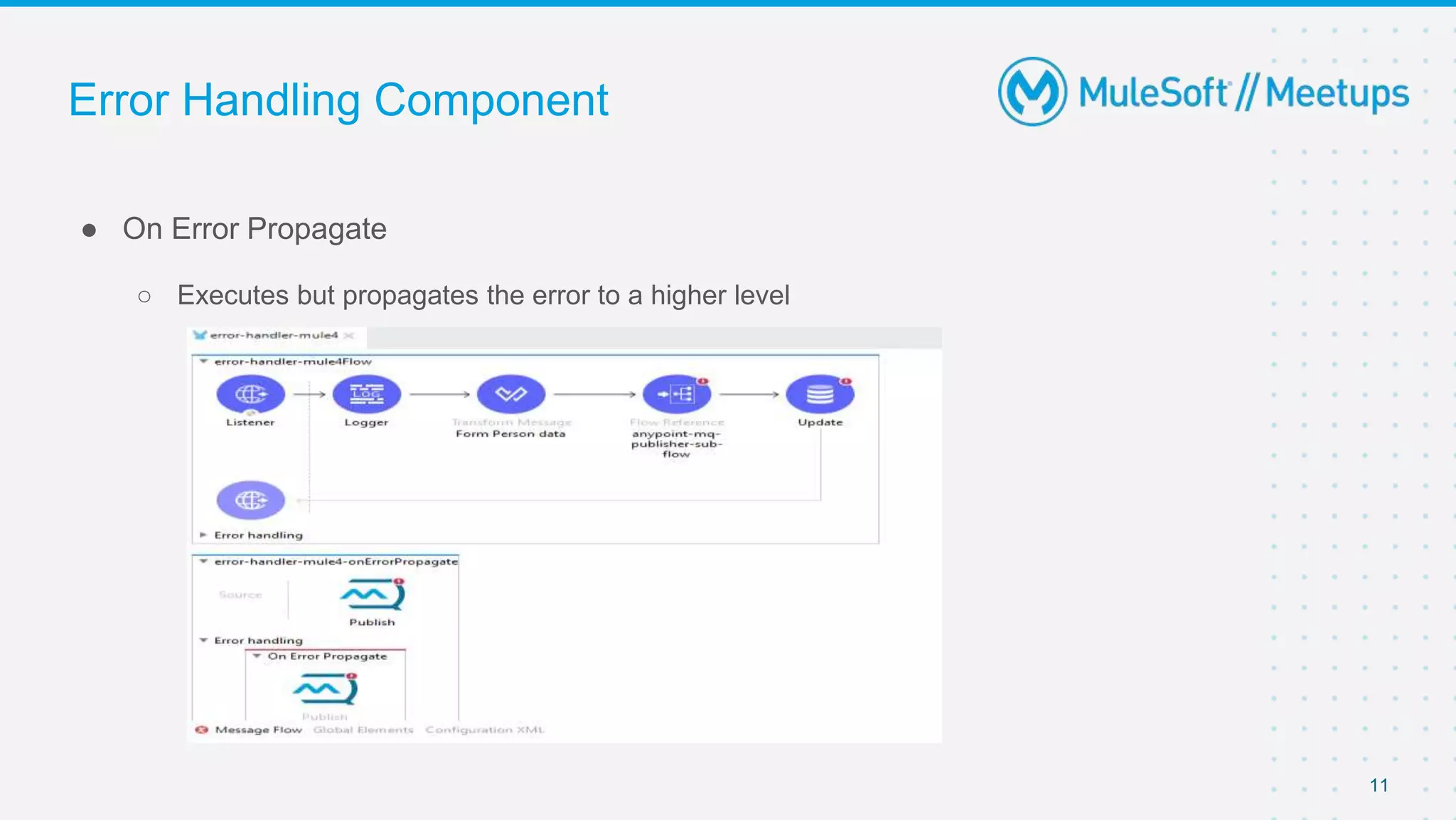
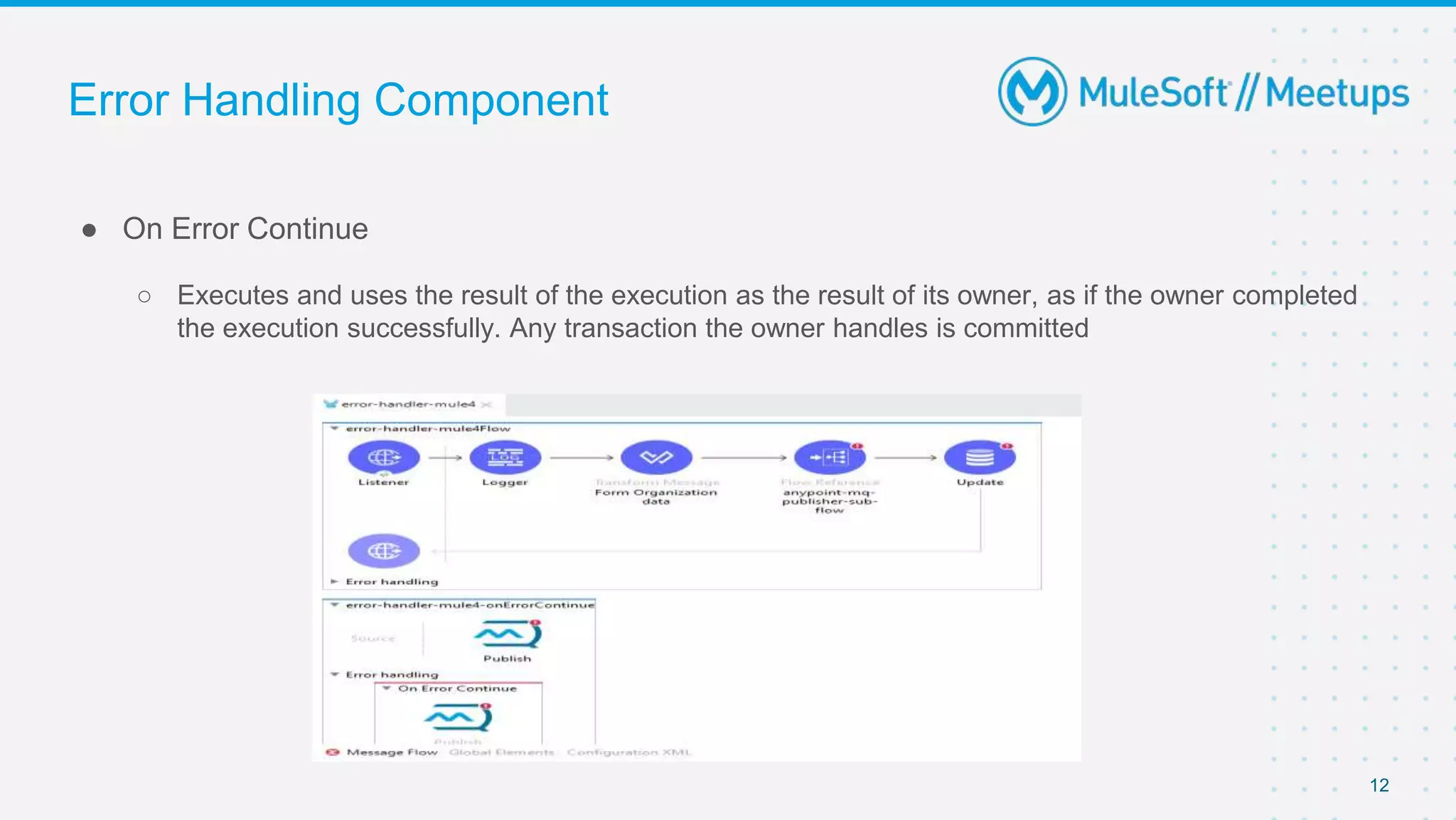
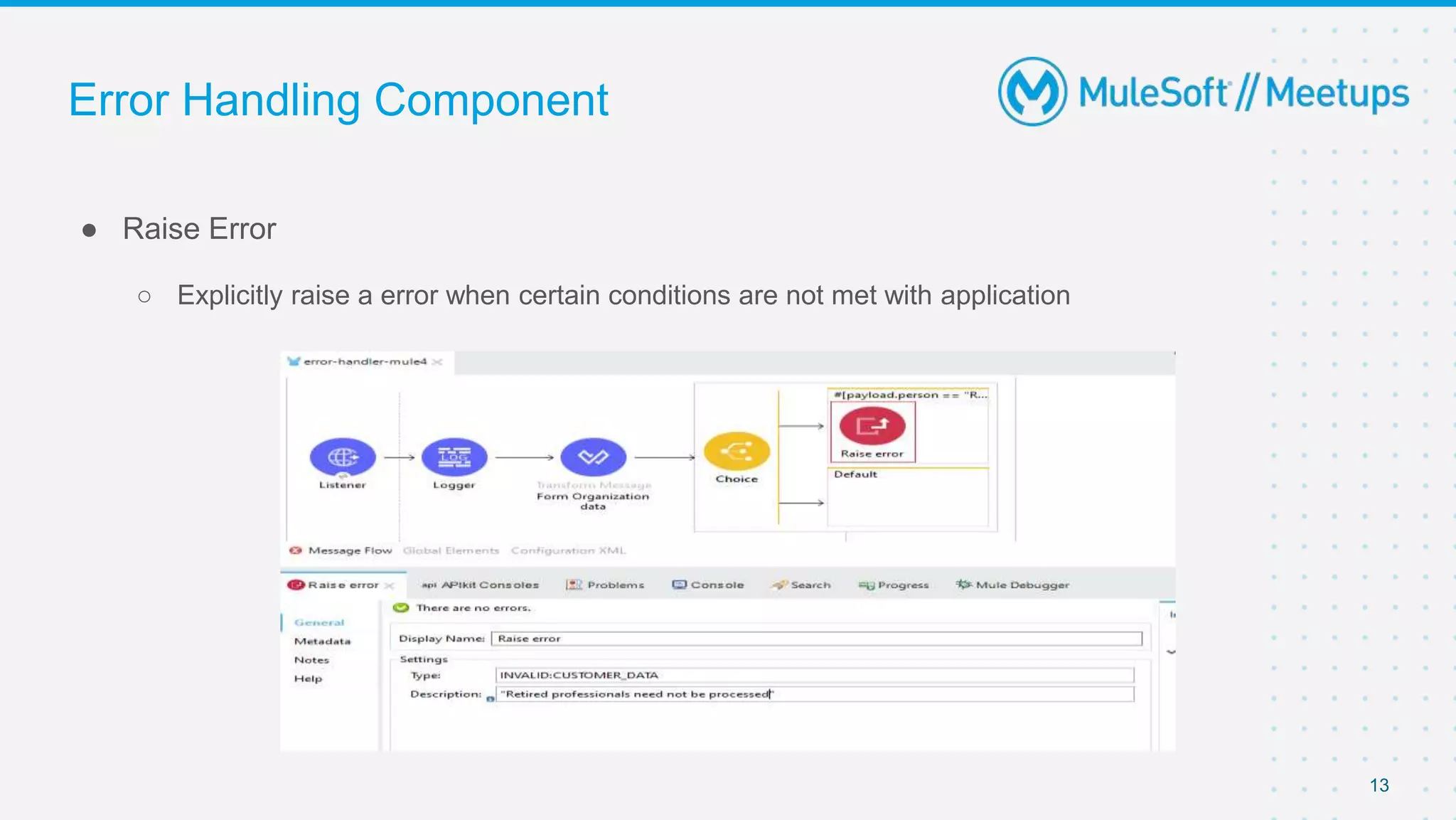
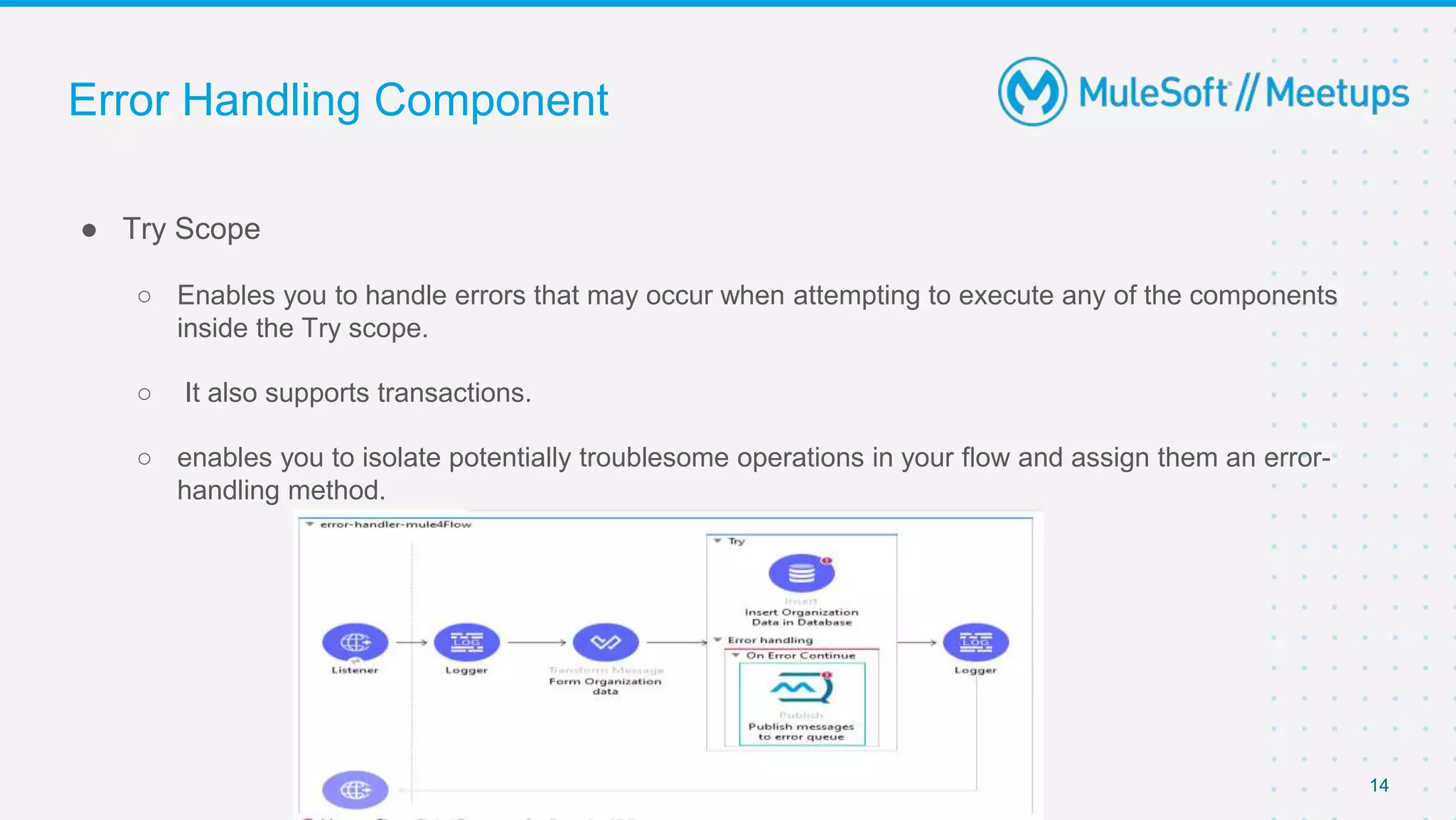
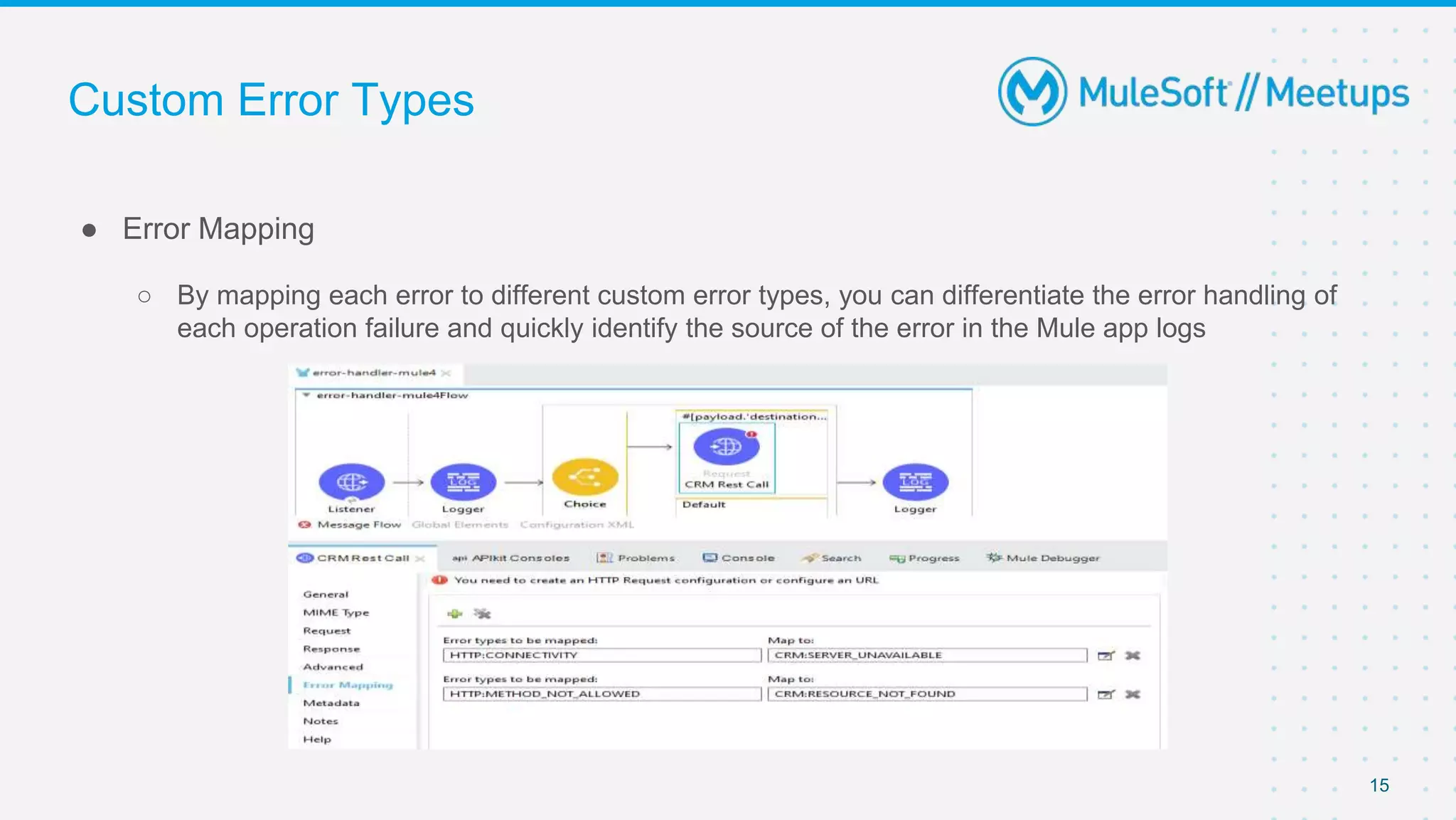
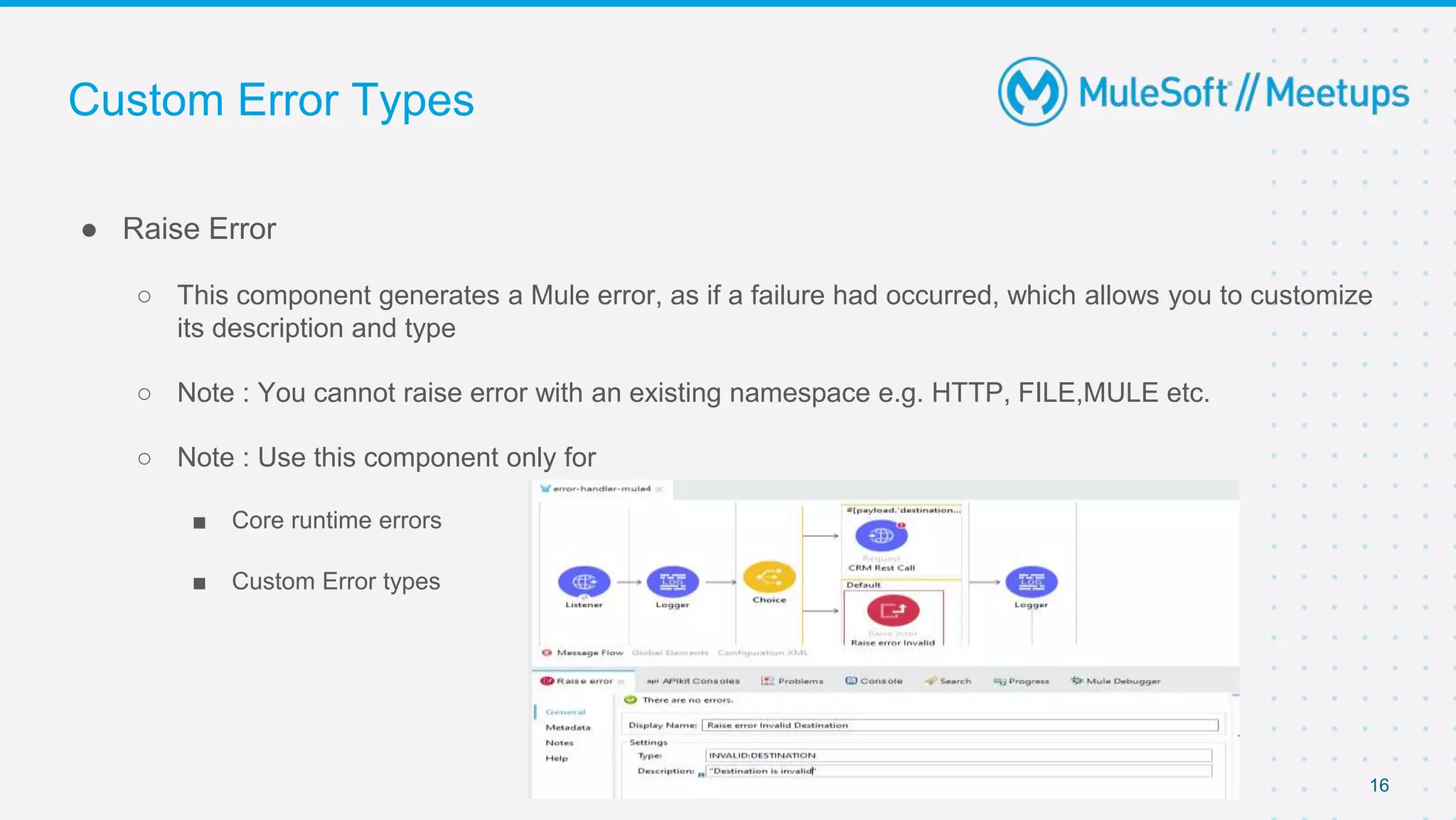
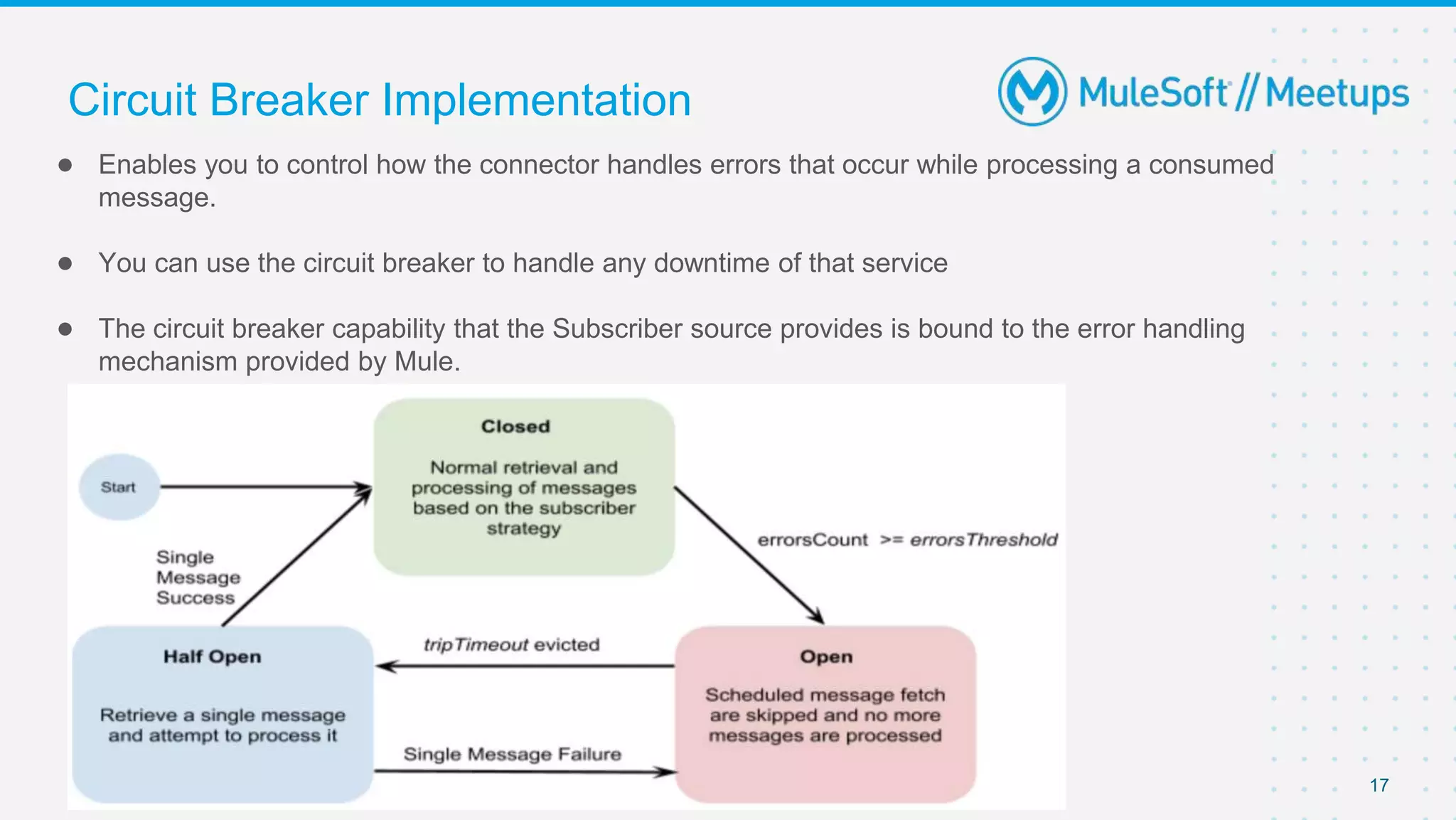
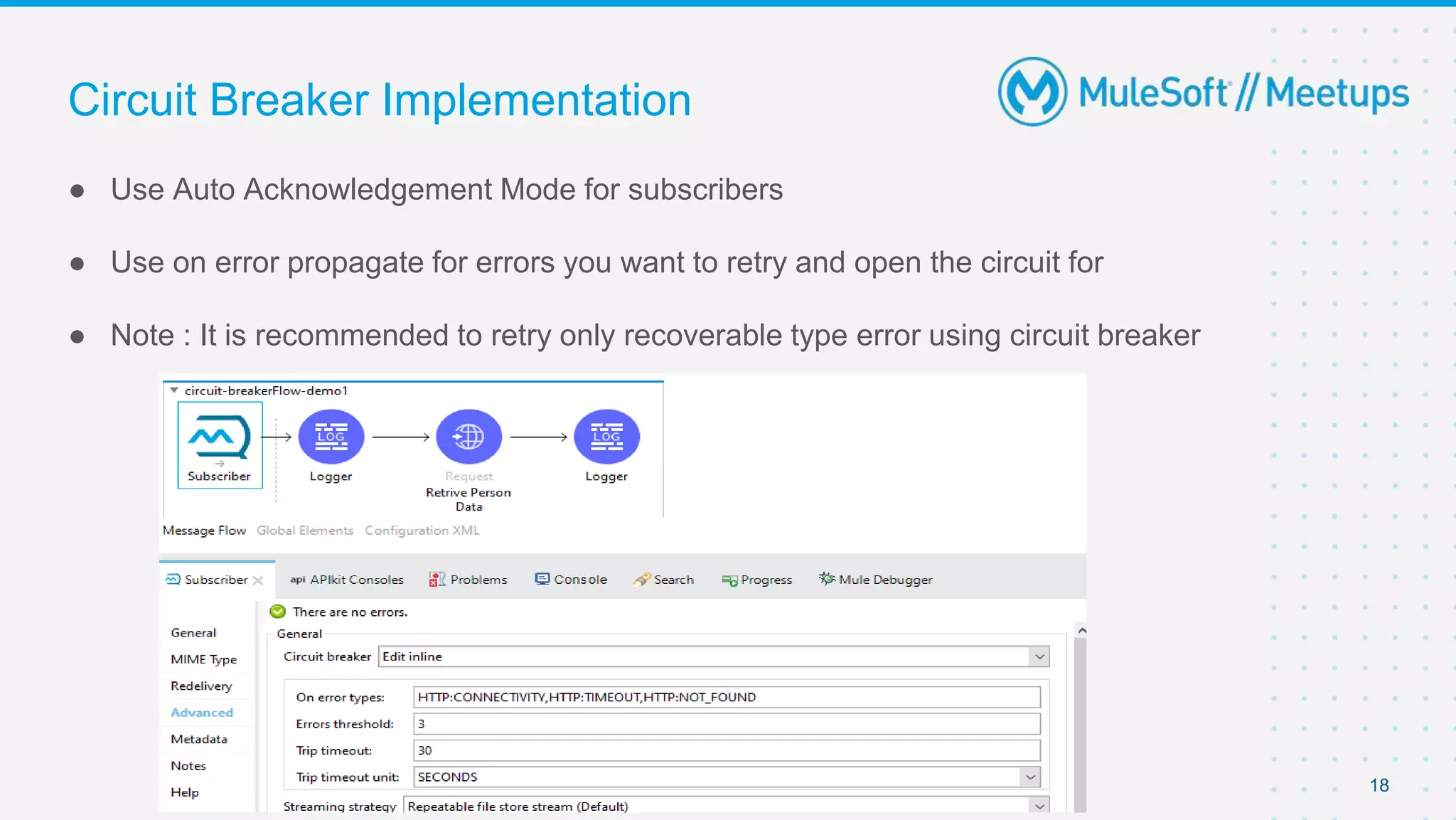
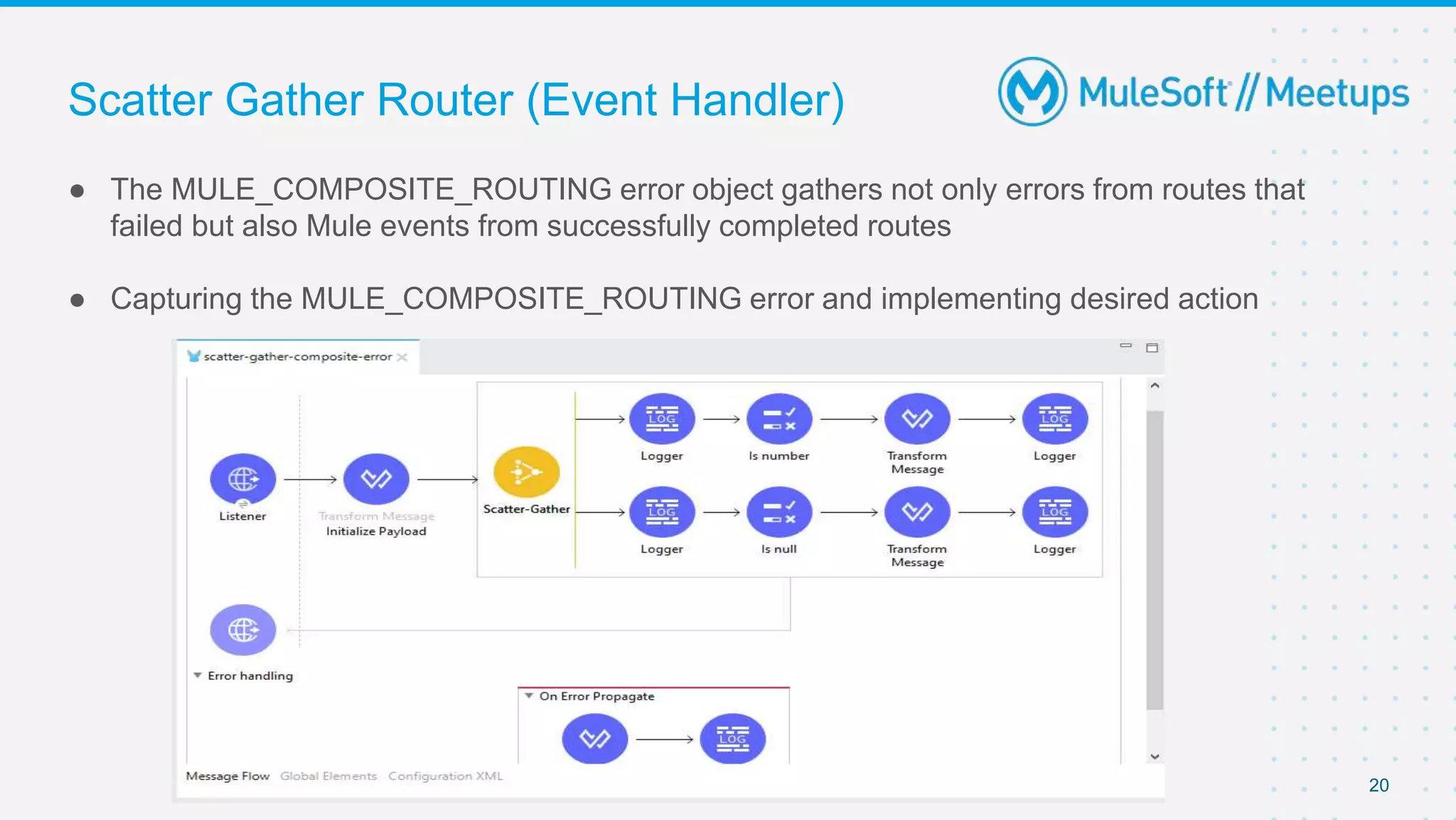
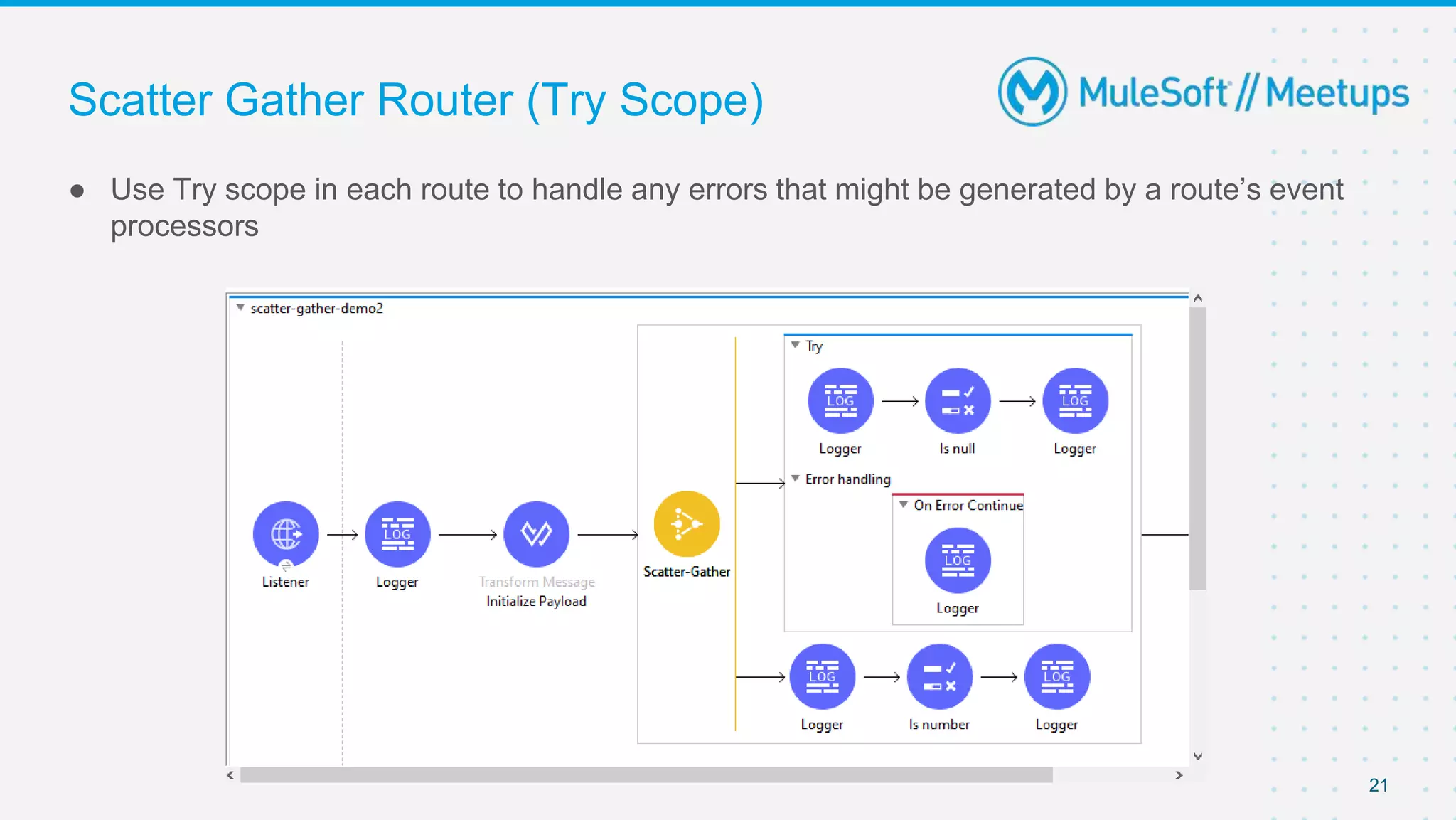
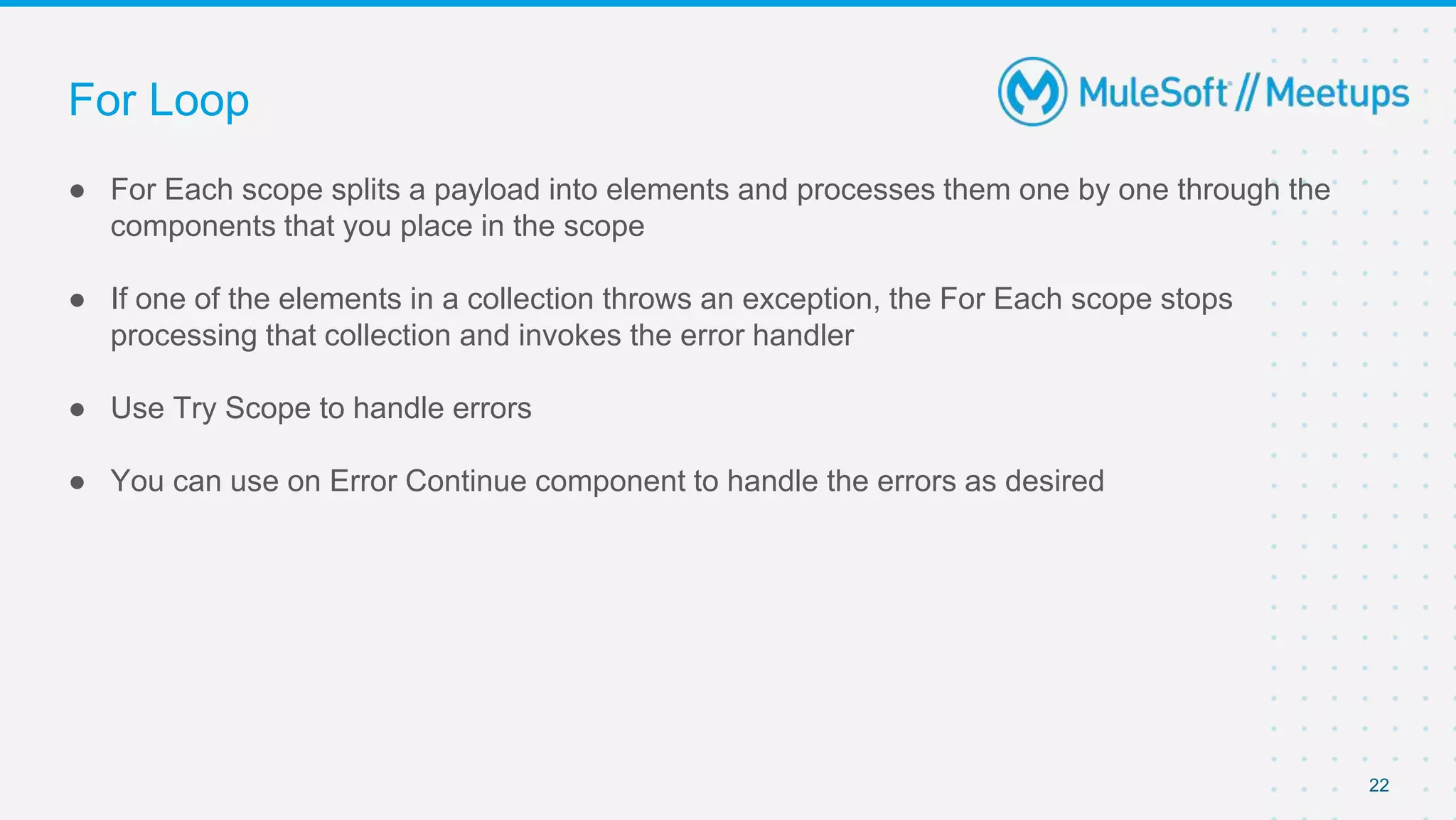
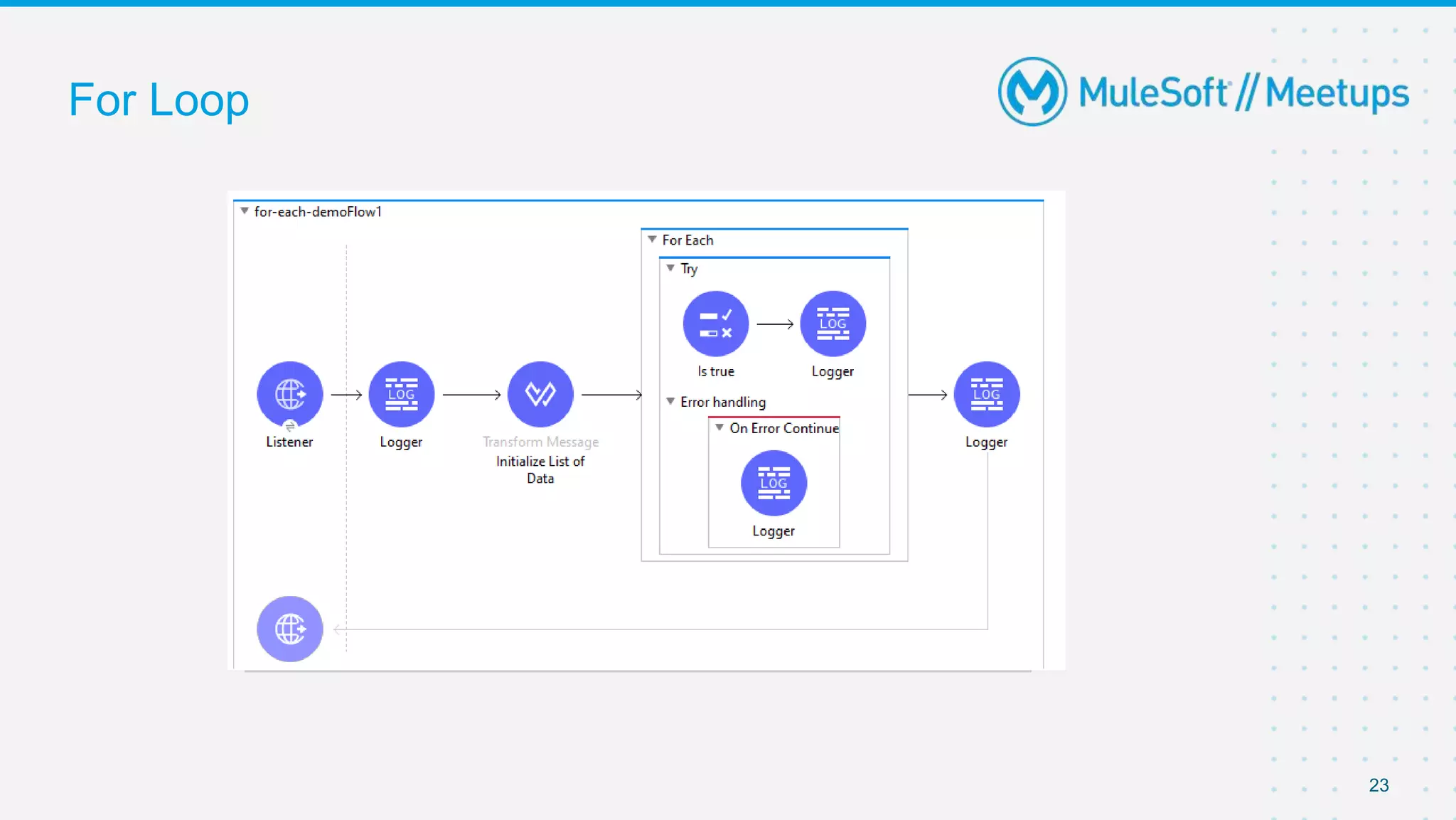
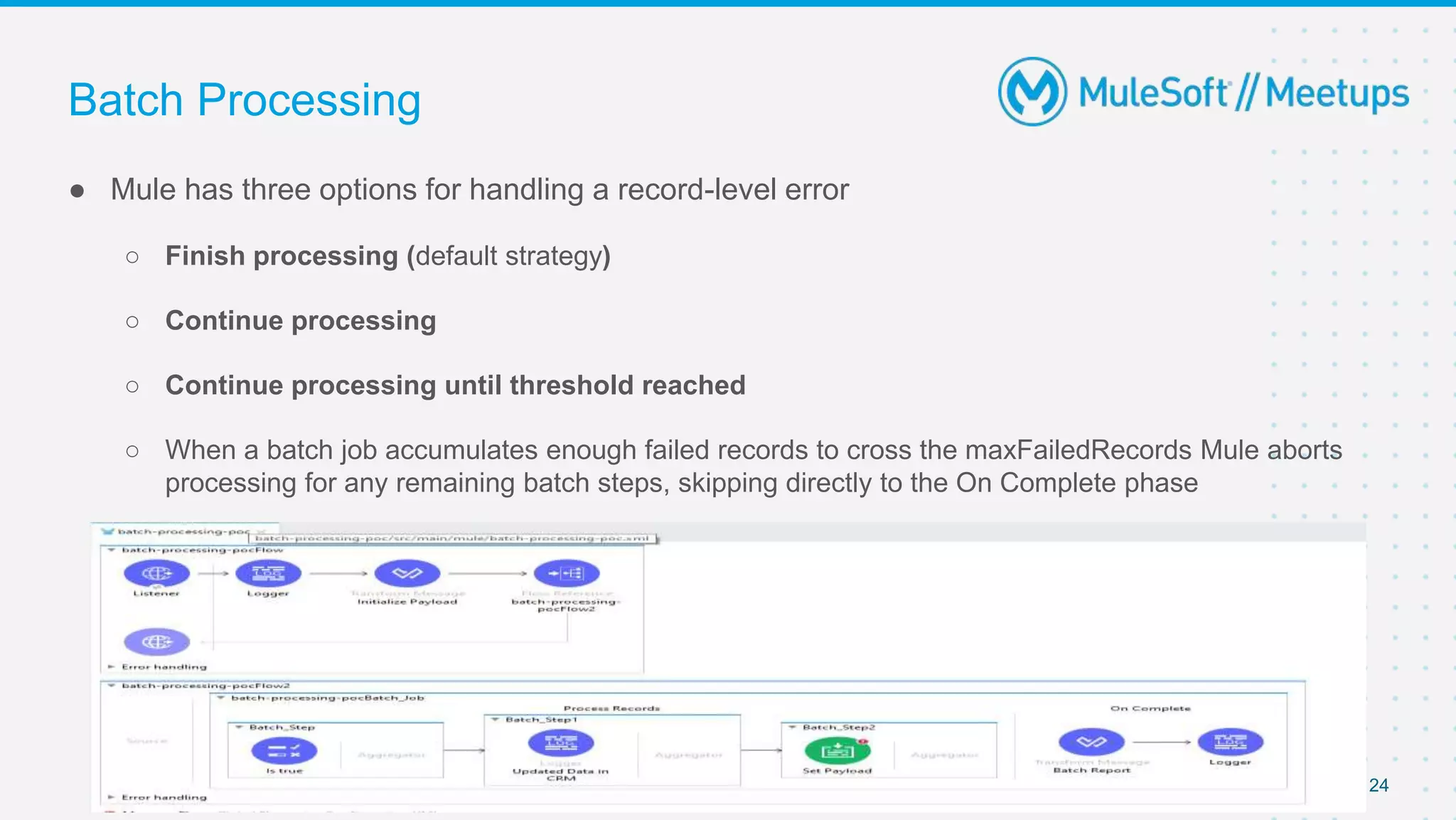
This document outlines the agenda for a MuleSoft meetup on error handling in Mule. The agenda includes an overview of error types in Mule, levels of error handlers, error handling components, creating custom error types, and real-time error handling scenarios with examples like circuit breakers, scatter-gather routing, for loops, and batch processing. The meetup organizers and speakers are also introduced.
![[10-07-2021]
[Kochi] MuleSoft Meetup Group
Error Handling in Mule](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mulesoftmeetupofficialjul2021updated-210710172607/75/MuleSoft-Kochi-Meetup-5-Handling-Mule-Exceptions-1-2048.jpg)