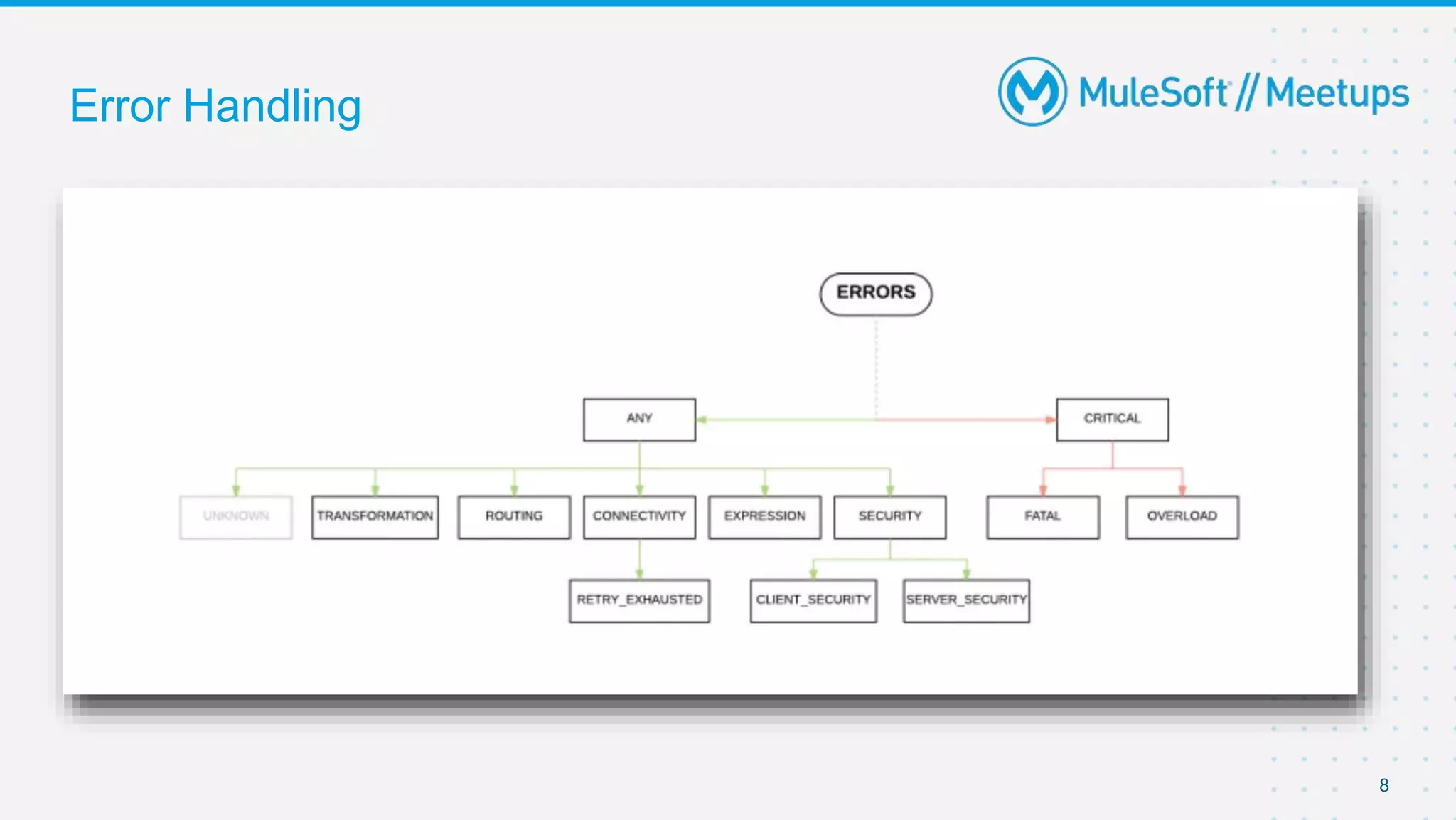
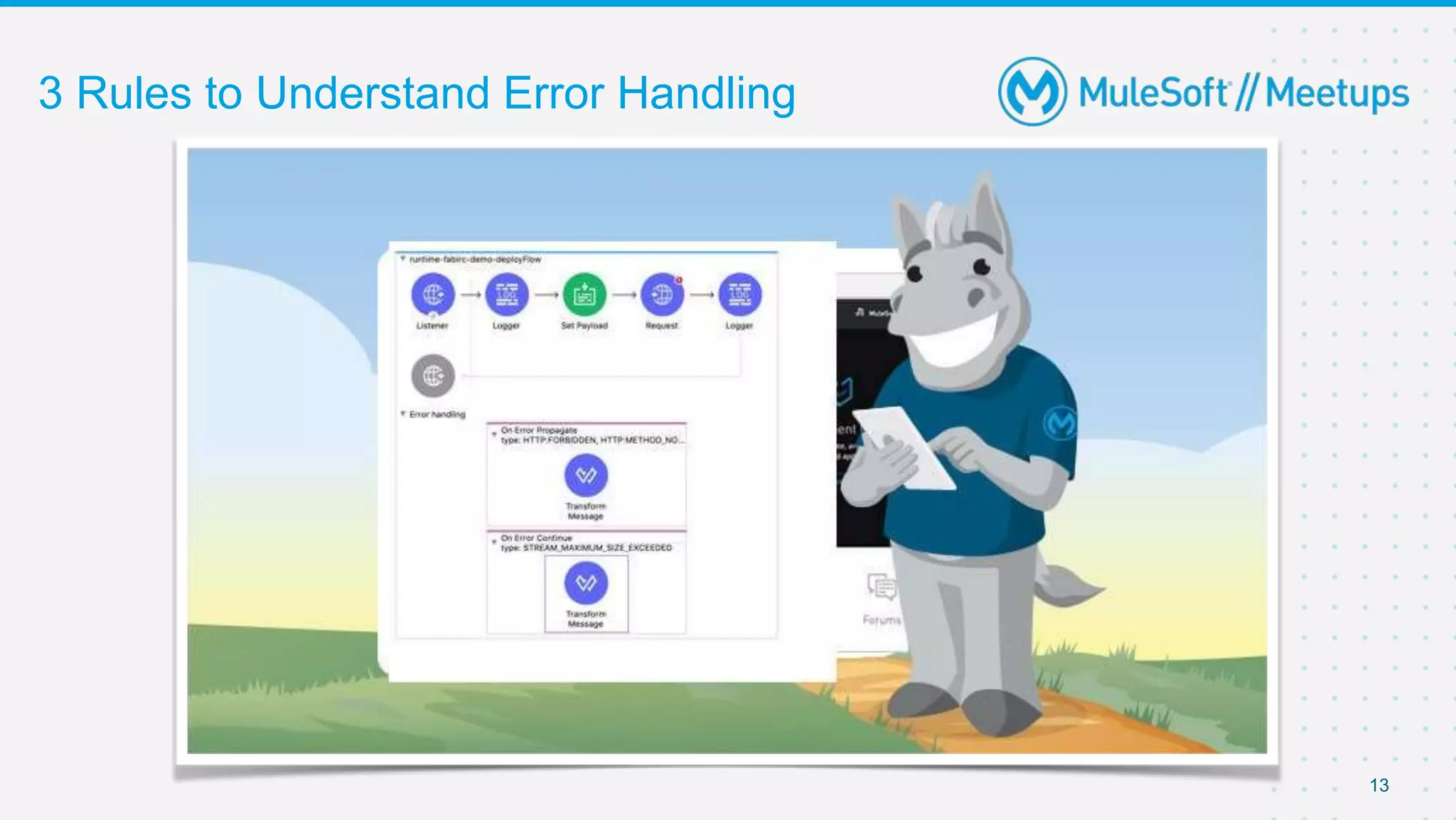
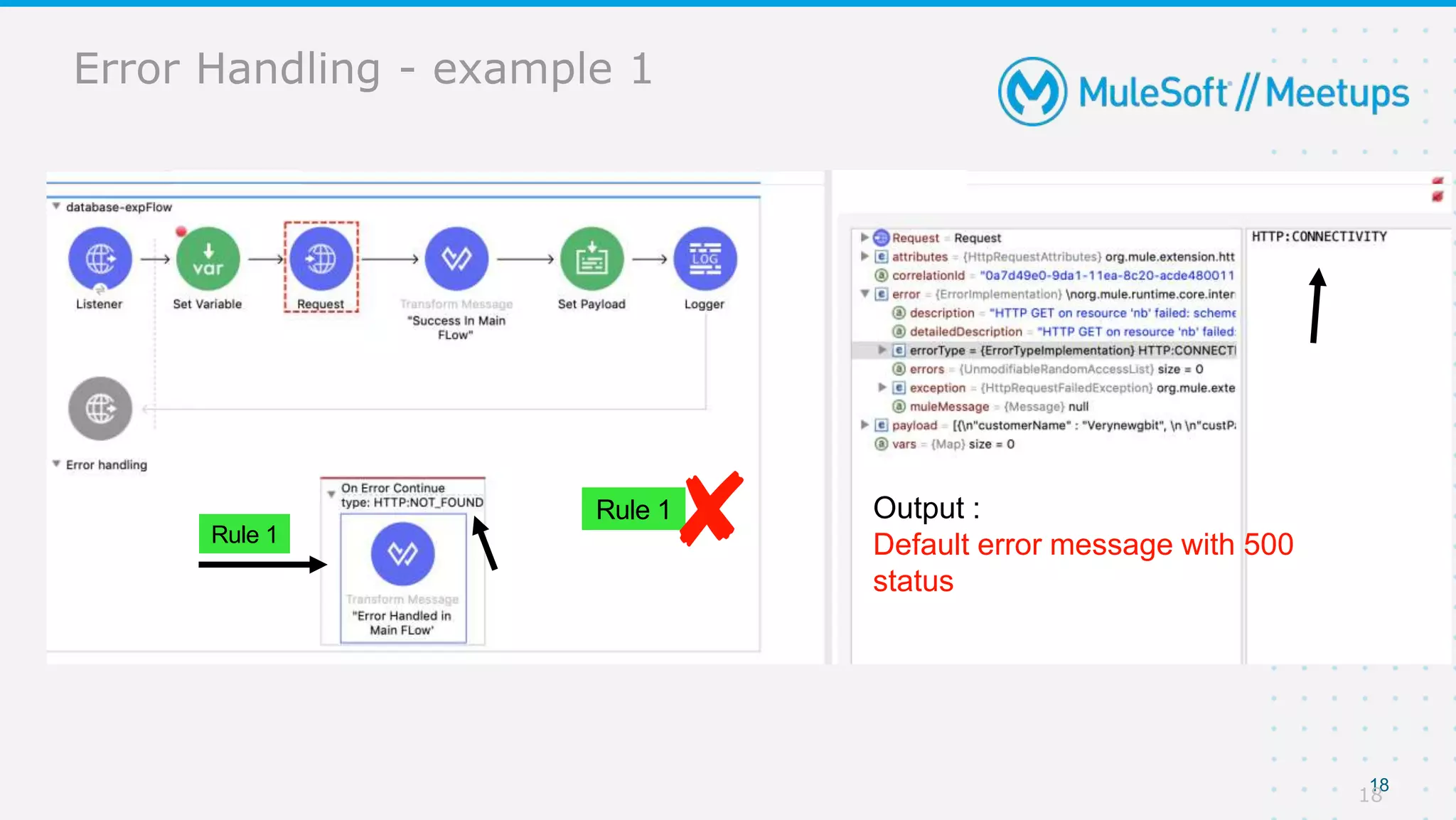
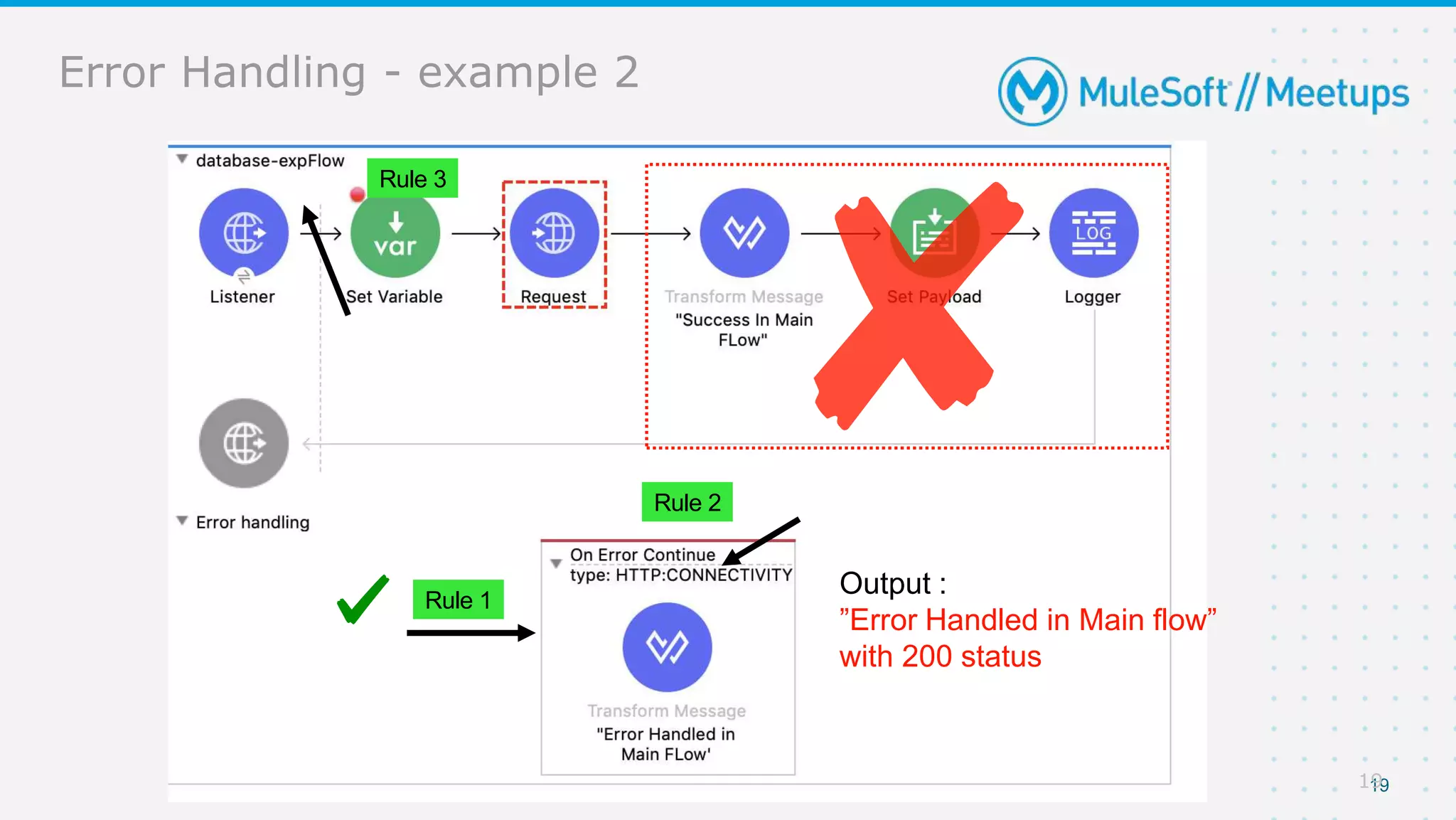
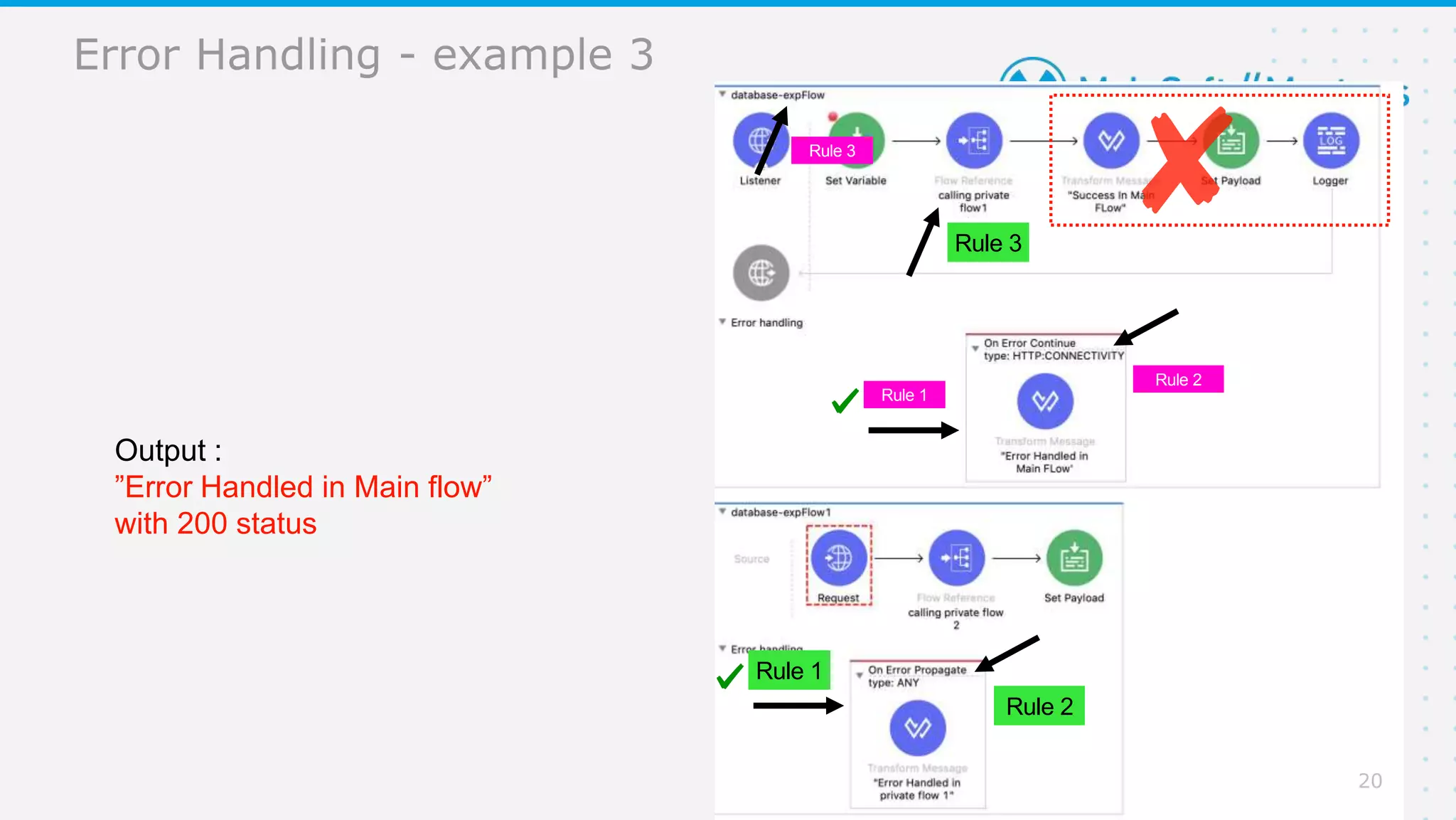
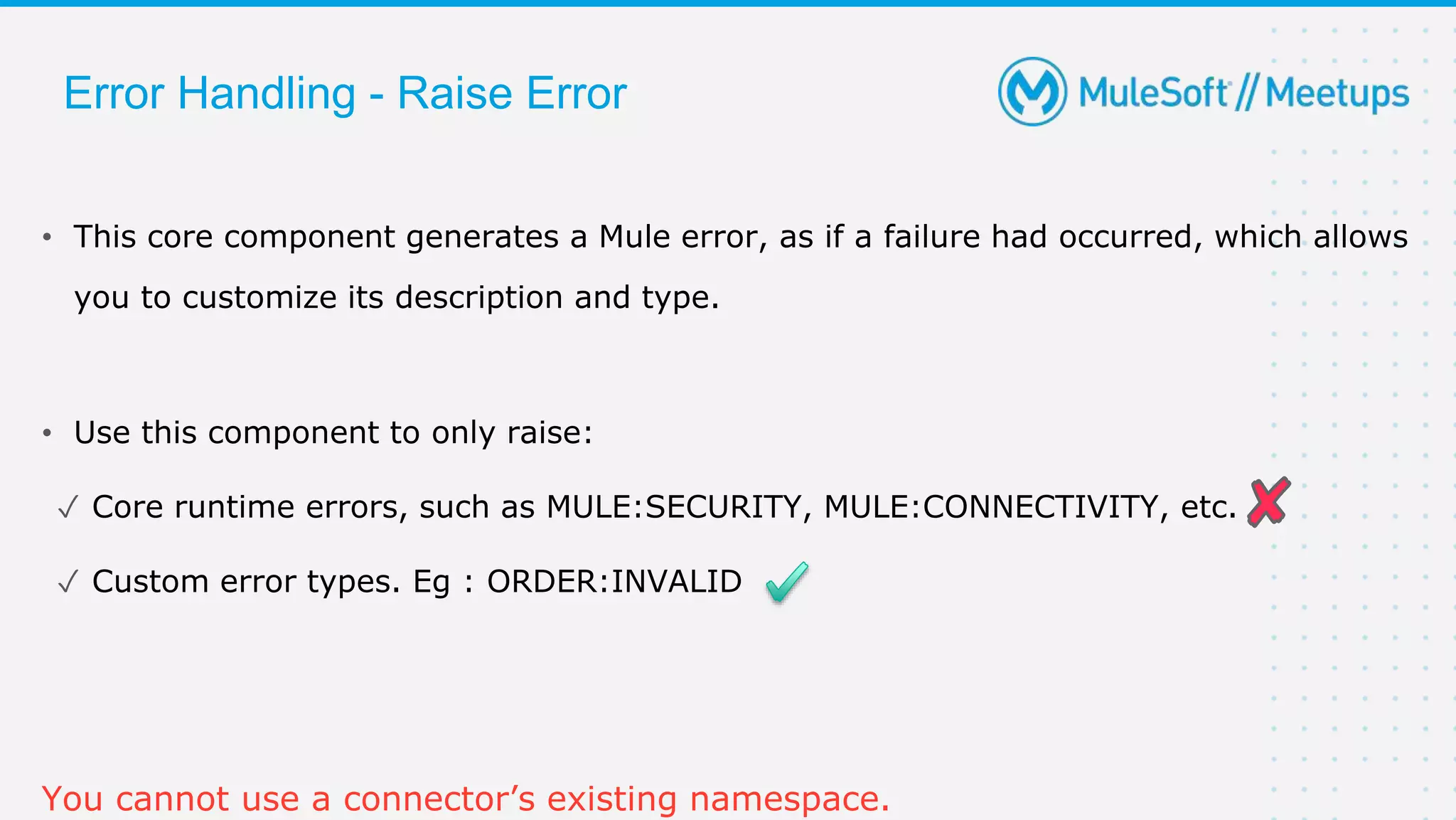
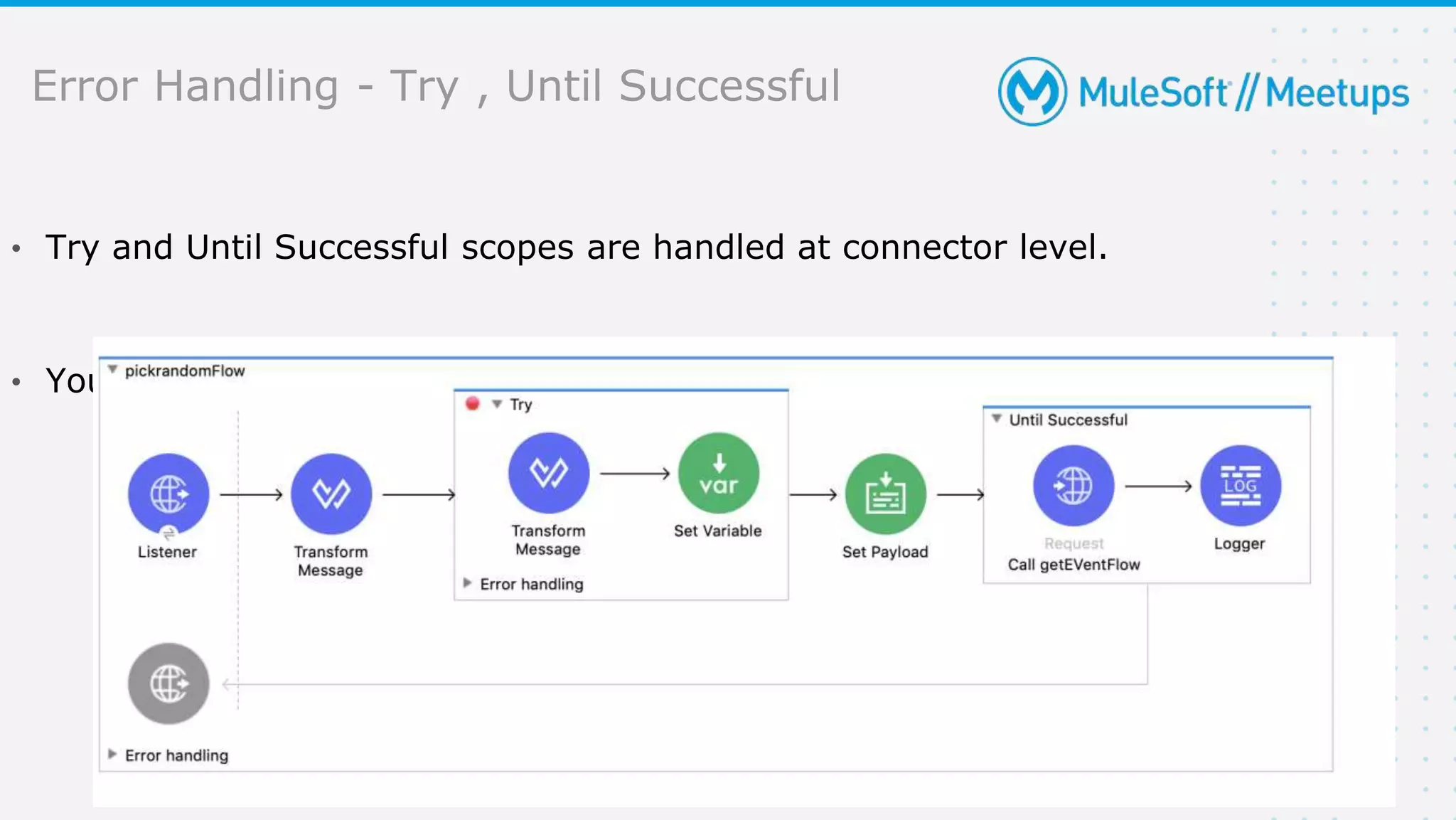
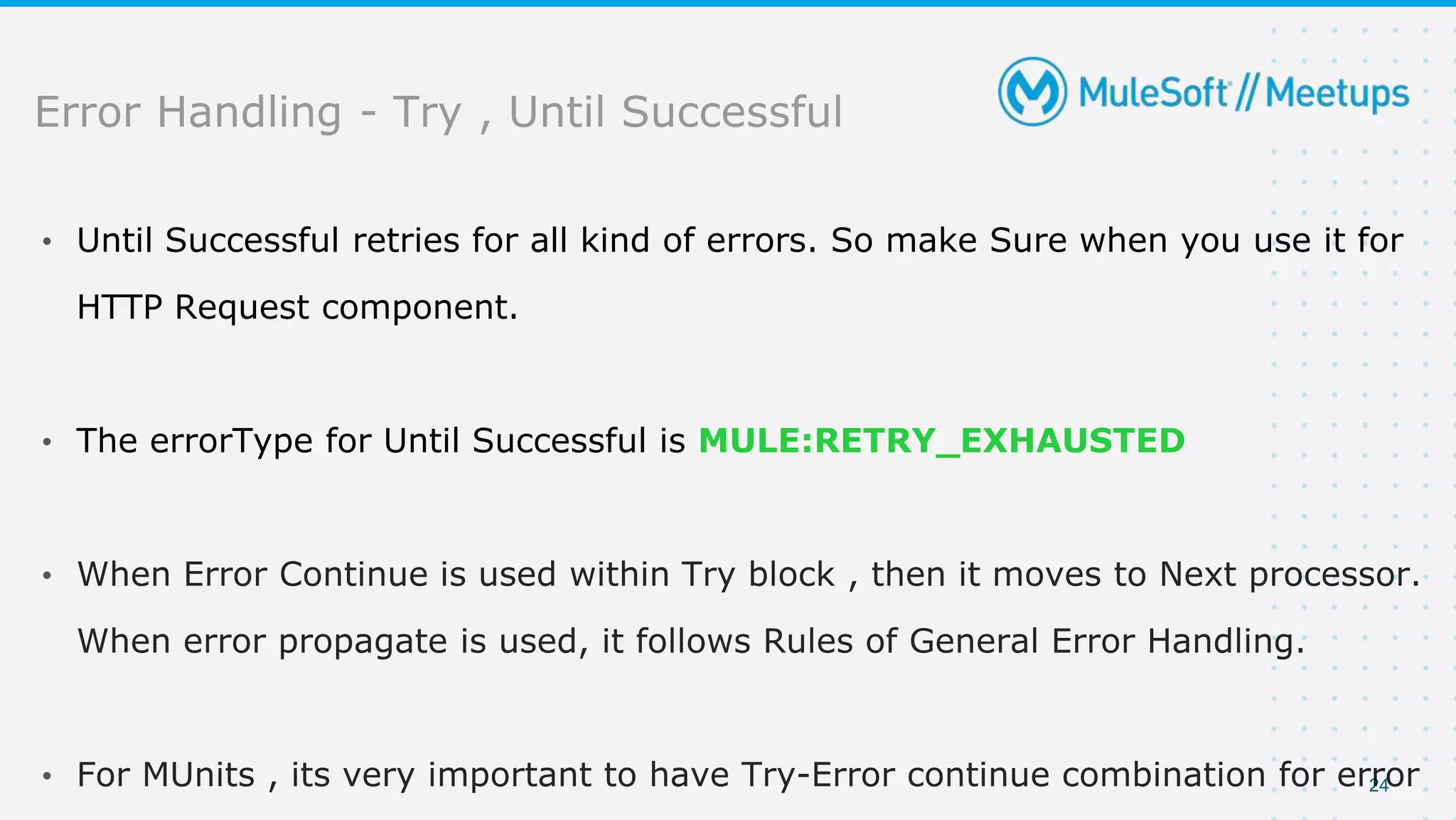
The document provides details about a Mulesoft meetup focused on error handling in Mule 4, scheduled for April 24, 2021. It outlines the responsibilities and expertise of the speaker, Sravan Lingam, and includes a comprehensive overview of error handling techniques and rules within Mule 4. Additionally, it informs attendees about upcoming meetups and encourages feedback for future events.