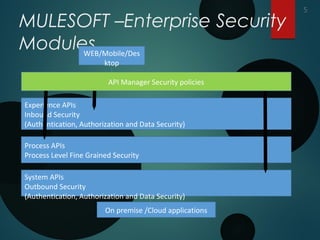
This document discusses security components and modules in MuleSoft's Anypoint platform. It describes Enterprise Security, the API Security Manager, and Virtual Private Cloud. It also explains how MuleSoft's Enterprise Security modules provide OAuth 2.0 authentication, authorization, SAML, WS-Security, and integration with PingFederate. The document outlines how security should be applied at the experience, process, and system connectivity layers of an API approach. It recommends using HTTPS and OAuth 2.0 to secure APIs and describes how MuleSoft implements basic authentication and OAuth 2.0 validation.