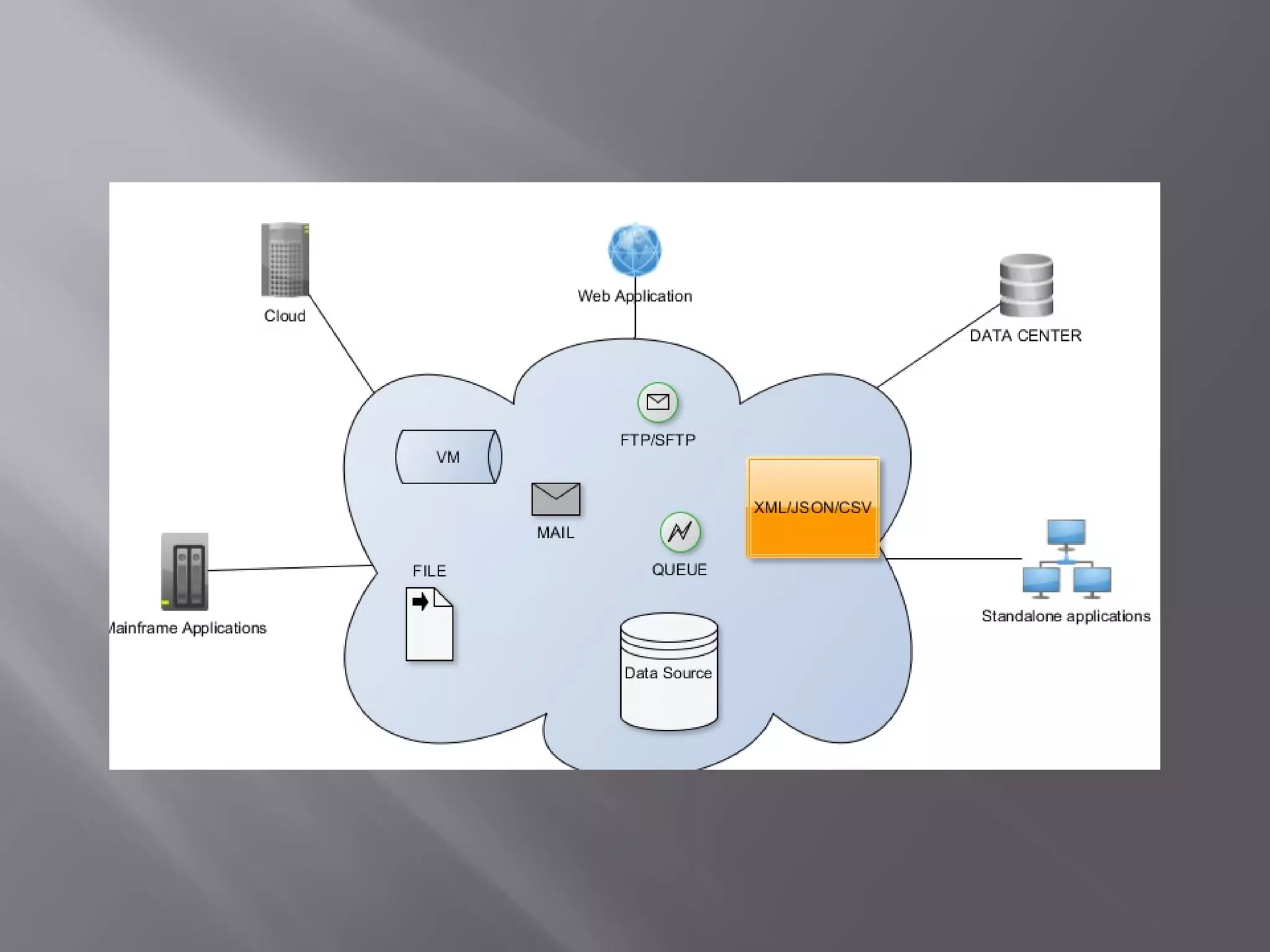
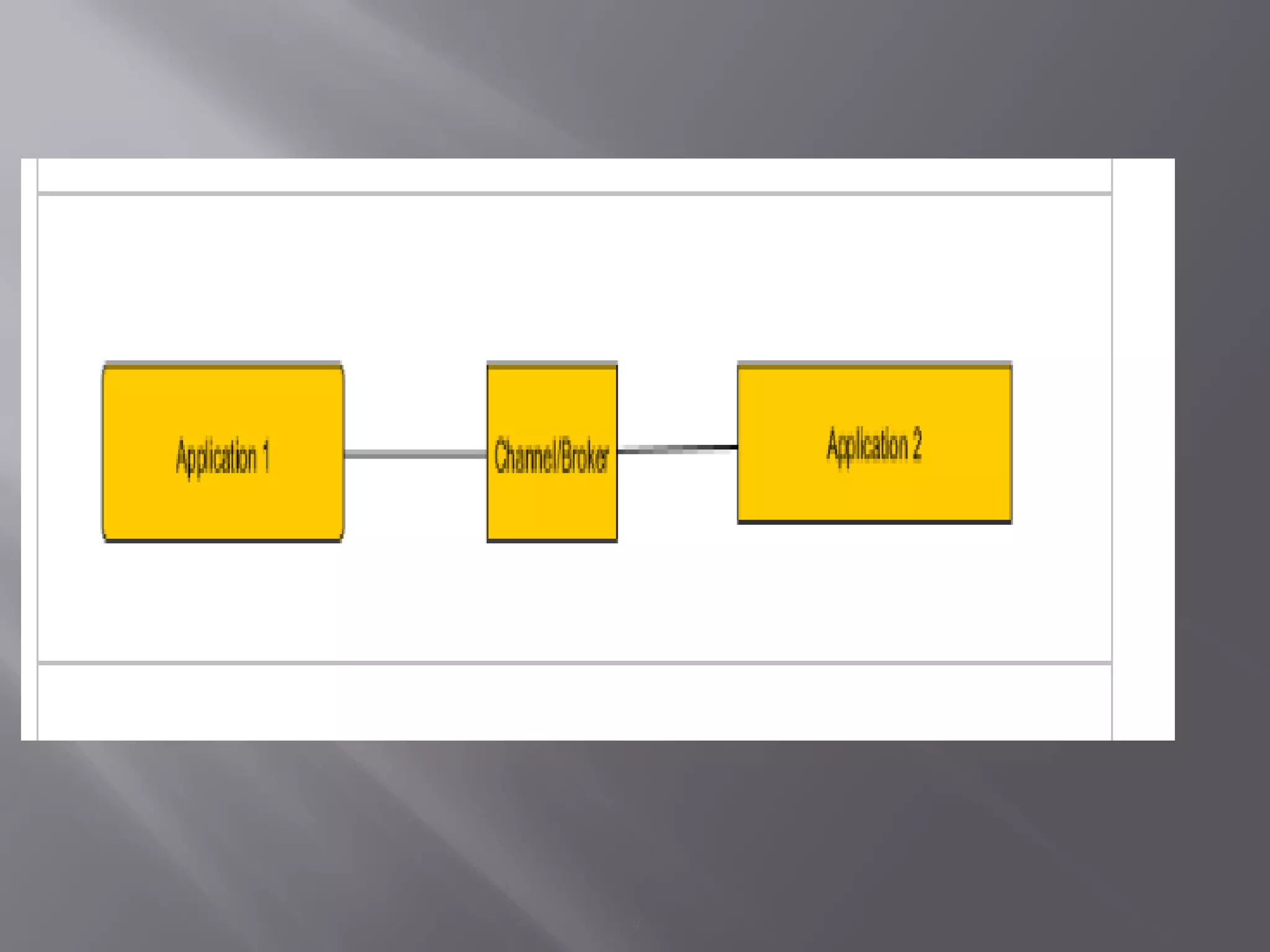
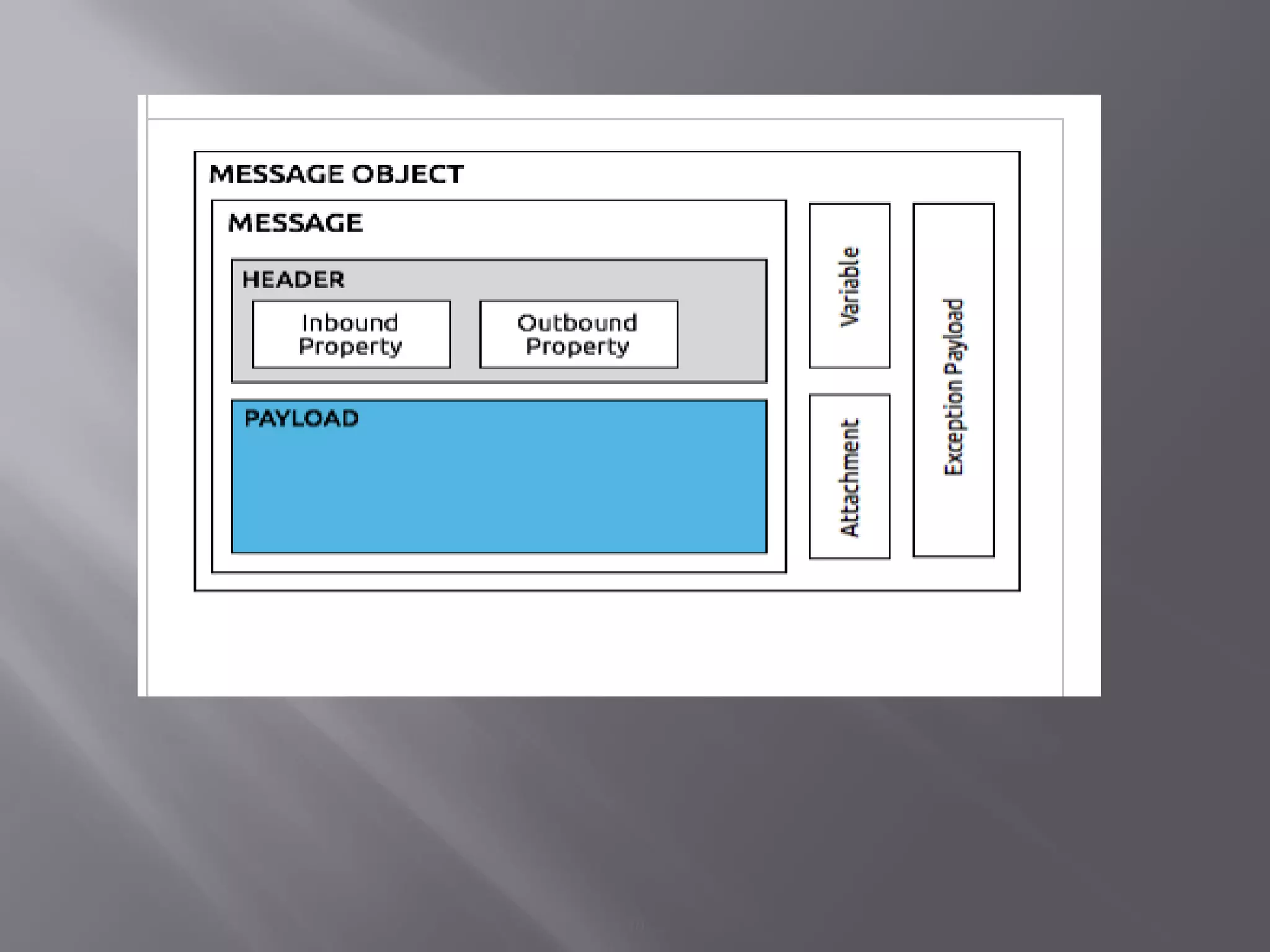
Mule is a lightweight integration platform that connects systems, services, APIs and devices. It intelligently manages message routing, data mapping, orchestration, reliability, security and scalability between nodes. Mule allows different applications to communicate by acting as a transit system that reads, transforms and sends data as messages between applications. The key elements in Mule include flows, message sources, message processors and endpoints that allow applications to send and receive data.