The document summarizes research on managing bean root rots (BRR) in a bean-based cropping system in Southwestern Uganda. It finds that:
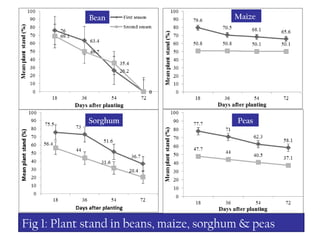
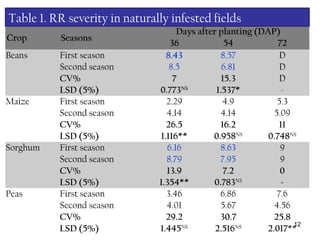
1) BRR are a major problem for beans production and sorghum and peas in the system also suffer from root rots, likely playing a role in sustaining BRR pathogens.
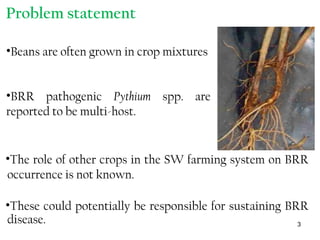
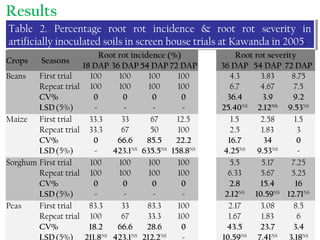
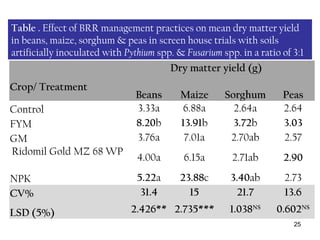
2) Experiments show BRR pathogens infect and cause disease on beans, sorghum, and peas, suggesting these crops serve as alternate hosts.
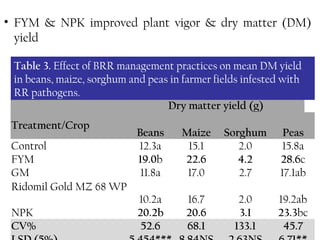
3) Management practices like farmyard manure and inorganic fertilizers improved plant growth and yields but had minimal effect on disease levels, likely due to high pathogen populations in fields. Integrated approaches are needed to effectively