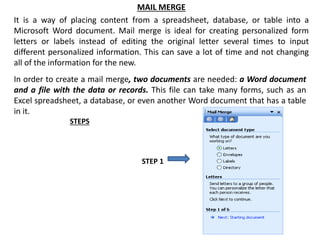
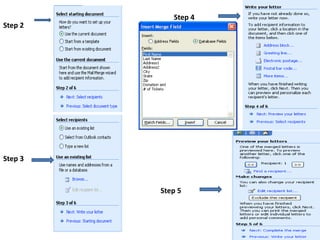
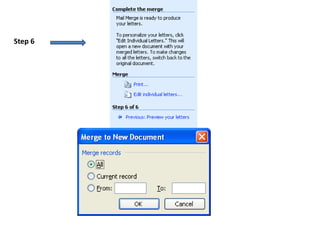
Ms Word allows users to create and edit documents with features like formatting text, inserting tables and pictures, checking spelling, and generating word counts. It supports both word processing and desktop publishing. Documents can be opened in different versions of Word but formatting may not display correctly as the file formats change between versions. Word also has features for creating mail merges, encrypting documents with passwords, and setting permissions to restrict document access.