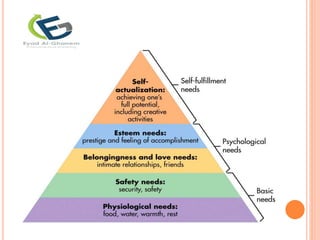
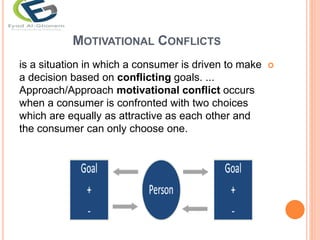
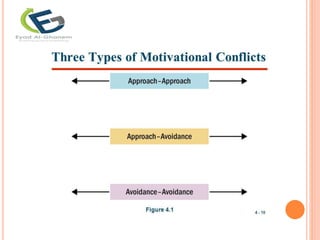
The document discusses the concept of motivation, distinguishing between needs and wants, and categorizing needs into biogenic, psychogenic, utilitarian, and hedonic. It explores Maslow's hierarchy of needs and their relevance to consumer behavior by highlighting the need for affiliation, power, and uniqueness. Additionally, it addresses motivational conflicts, levels of involvement in consumption, and cultural values that shape consumer behavior.