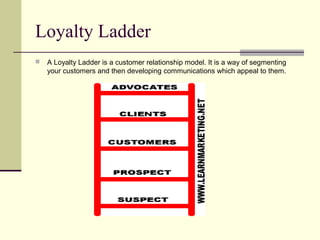
This document discusses customer loyalty and retention. It defines brand loyalty as committed repeat purchases over time due to preferences. Companies use marketing strategies like rewards programs to cultivate loyal customers. Customer loyalty is a key determinant of firm profitability. The loyalty ladder segments customers from suspects to advocates. Reasons for loyalty include psychological, economic, technical/functional, and contractual factors. Retaining customers is important because they spend more, cost less, and bring in new customers. The document provides tips for outstanding customer retention like addressing complaints, loyalty programs, and memorable service.