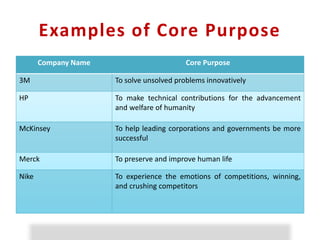
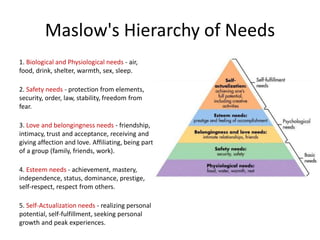
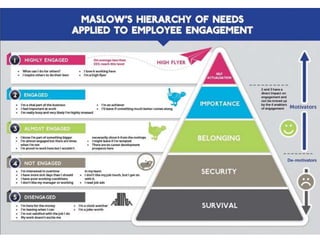
This document discusses motivation and how to motivate employees. It defines motivation and discusses intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Maslow's hierarchy of needs is presented as influencing motivation. Recognition and rewarding are discussed as ways to motivate employees. Expectations at work from both managers and employees are outlined. Ten stimuli that can motivate are listed. Key aspects that motivate employees are described as having a compelling purpose, clear roles and responsibilities, and challenging goals and plans.