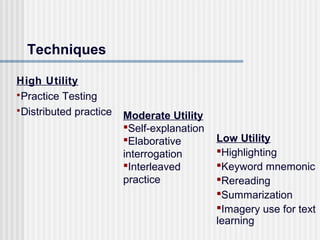
The document summarizes a study on the most effective study techniques for increasing student learning. The study reviewed research on 10 common techniques and found that practice testing and distributed practice were the most effective techniques. Practice testing improves learning through retrieval and feedback, while distributed practice improves long-term retention by spacing out study sessions over time. The study recommends training students on these high-impact techniques starting in upper elementary grades and integrating them into lesson plans and homework assignments.