The document presents a model of contributions in Scrum software engineering teams, aiming to clarify and categorize the diverse roles and activities that team members engage in to achieve project goals. It identifies 17 individual contributions, organized into technical, contentual, and managerial dimensions, and emphasizes the importance of visibility and acknowledgment in scrum practices. The model facilitates self-reflection and discussion during retrospective meetings to enhance teamwork processes.

![Motivation & Background
2
Agile Software Development and Scrum
[1] CollabNet Inc. 2019. “13th Annual State of Agile Report”. Technical Report.
https://www.stateofagile.com/#ufh-i-521251909-13th-annual-state-of-agile-report
[2] Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland. 2017. “The Scrum Guide - The Definitive Guide to Scrum: The Rules of the Game”.
Technical Report. scrumguides.org. 19 pages. http://scrumguides.org/docs/scrumguide/v2017/2017-Scrum-Guide-US.pdf
■ Agile methods, e.g. Scrum, are de facto standards in SE [1]
■ Teams with all the competencies required for project work [2]
Software engineers’ contributions to progress &
success of modern software projects are varied](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chasepaper9morethancode-presentationslides-200702132157/85/More-than-Code-Contributions-in-Scrum-Software-Engineering-Teams-2-320.jpg)
![Research Goal
3
A Model of Scrum Teamwork Contributions
■ Scrum and Agile approaches rely on visibility of project progress [3]
■ Capturing & categorizing contributions to project success
ensures team awareness of accomplished work
Goal: Model of Scrum contributions. Enable appropriate
appraisal & appreciation of Scrum team efforts
[3] Henrik Kniberg. 2015. “Scrum and XP From the Trenches” (2nd ed.). C4Media](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chasepaper9morethancode-presentationslides-200702132157/85/More-than-Code-Contributions-in-Scrum-Software-Engineering-Teams-3-320.jpg)
![Definition
4
What is a Contribution of a Software Engineering Team Member?
Contribution: Any activity, demanding human resources, that
adds to the fulfillment of project goals, by adding value to the
developed product or the (future) effectiveness of the team.
■ Technical aspects, e.g., source code changes
■ Also process improvement activities,
meeting facilitation & effective communication [4]
[4] D. Ford, T. Zimmermann, C. Bird, and N. Nagappan. 2017. “Characterizing Software Engineering Work with Personas Based on Knowledge Worker
Actions”. ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement. 394–403.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chasepaper9morethancode-presentationslides-200702132157/85/More-than-Code-Contributions-in-Scrum-Software-Engineering-Teams-4-320.jpg)
![Related Work
5
What do Software Engineers Spend their Time on?
■ Devs spend only ¼ of their time on coding-related activities [5]
[5] André N Meyer, Gail C Murphy, Thomas Fritz, and Thomas Zimmermann. 2019.
“Developers’ Diverging Perceptions of Productivity”. Apress, 137–146.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chasepaper9morethancode-presentationslides-200702132157/85/More-than-Code-Contributions-in-Scrum-Software-Engineering-Teams-5-320.jpg)
![Contributions in Scrum
6
Roles of the Scrum Process
■ Scrum acknowledges different
task profiles / “roles” within teams [2]:
■ Product Owner (PO)
■ Scrum Master (SM)
■ Development Team (Dev.)
[2] Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland. 2017. “The Scrum Guide - The Definitive Guide to Scrum: The Rules of the Game”.
Technical Report. scrumguides.org. 19 pages. http://scrumguides.org/docs/scrumguide/v2017/2017-Scrum-Guide-US.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chasepaper9morethancode-presentationslides-200702132157/85/More-than-Code-Contributions-in-Scrum-Software-Engineering-Teams-6-320.jpg)
![Model Construction
7
Contributions Listed in the Scrum Guide
■ Model from first principles, based on the seminal Scrum Guide [2]
■ Successively code text passages
■ Extract mentions of work items, tasks, meetings,
project requirements and responsibilities
■ Deduplicate and cluster
■ Assign short name and designated role
[2] Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland. 2017. “The Scrum Guide - The Definitive Guide to Scrum: The Rules of the Game”.
Technical Report. scrumguides.org. 19 pages. http://scrumguides.org/docs/scrumguide/v2017/2017-Scrum-Guide-US.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chasepaper9morethancode-presentationslides-200702132157/85/More-than-Code-Contributions-in-Scrum-Software-Engineering-Teams-7-320.jpg)
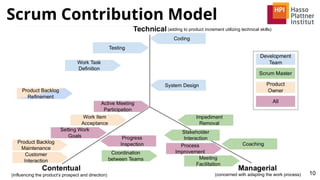
![Results
8
Extracted Scrum Teamwork Contributions
■ 17 individual Scrum teamwork contributions
■ Explicitly included the role All
■ Highlight level of collaboration
■ Contributions arranged along 3 dimensions
■ Technical, Contentual, Managerial
■ Based on related work [4,6]
[4] D. Ford, T. Zimmermann, C. Bird, and N. Nagappan. 2017. “Characterizing Software Engineering Work with Personas Based on Knowledge Worker
Actions”. ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement. 394–403.
[6] Judy L. Wynekoop and Diane B. Walz. 2000. “Investigating traits of top performing software developers”.
Information Technology & People 13, 3 (2000), 186–195](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chasepaper9morethancode-presentationslides-200702132157/85/More-than-Code-Contributions-in-Scrum-Software-Engineering-Teams-8-320.jpg)
![Example
9
Extracted Scrum Teamwork Contributions
■ Scrum Guide extracts [2]
■
■
■ Short name: Process Improvement
■ Role: All
■ Dimension: Managerial
[2] Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland. 2017. “The Scrum Guide - The Definitive Guide to Scrum: The Rules of the Game”.
Technical Report. scrumguides.org. 19 pages. http://scrumguides.org/docs/scrumguide/v2017/2017-Scrum-Guide-US.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chasepaper9morethancode-presentationslides-200702132157/85/More-than-Code-Contributions-in-Scrum-Software-Engineering-Teams-9-320.jpg)
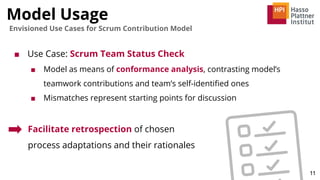
![Summary
12
A Model of Scrum Contributions
■ Structured exploration of the project member’s
contributions described by the Scrum Guide
■ Constricted scope of initial model promotes
clarity and traceability of construction
■ Representative of key contributions in
unmodified, theoretical, “vanilla Scrum” [7]
[7] Lucas Gren, Richard Torkar, and Robert Feldt. 2017. “Group development and group maturity when building agile teams: A qualitative and
quantitative investigation at eight large companies”. Journal of Systems and Software 124 (2017),104–119.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chasepaper9morethancode-presentationslides-200702132157/85/More-than-Code-Contributions-in-Scrum-Software-Engineering-Teams-12-320.jpg)


