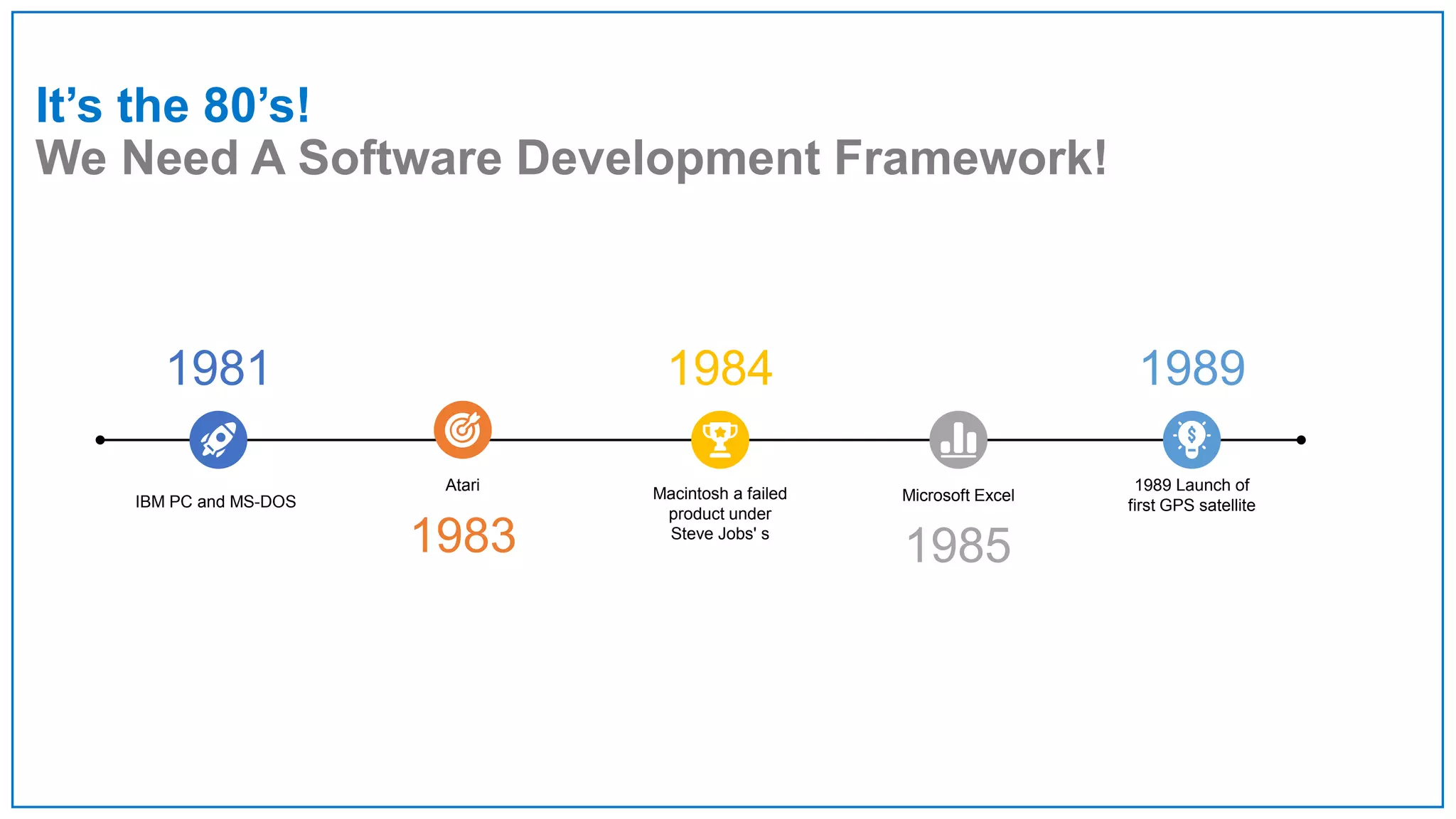
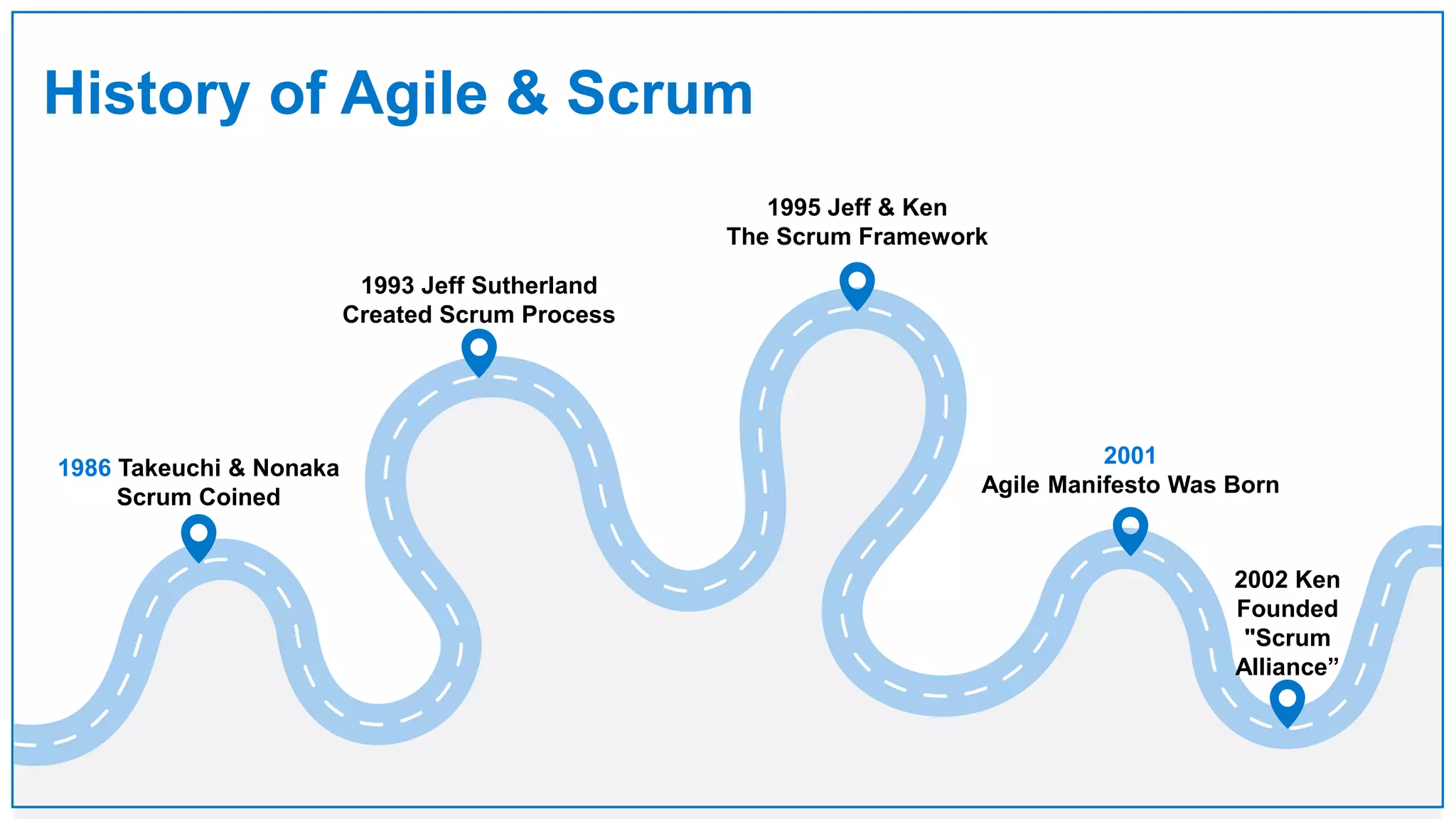
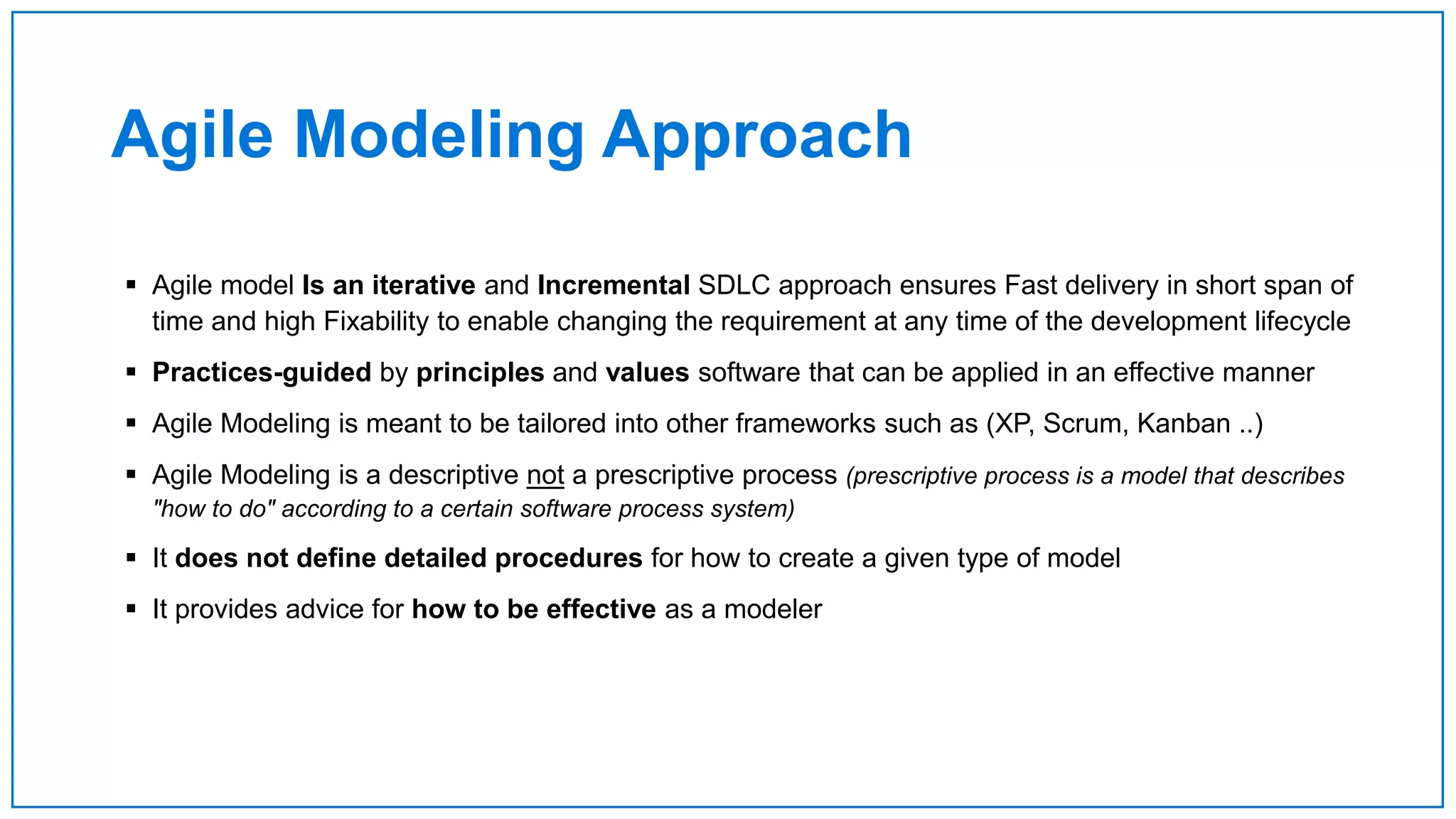
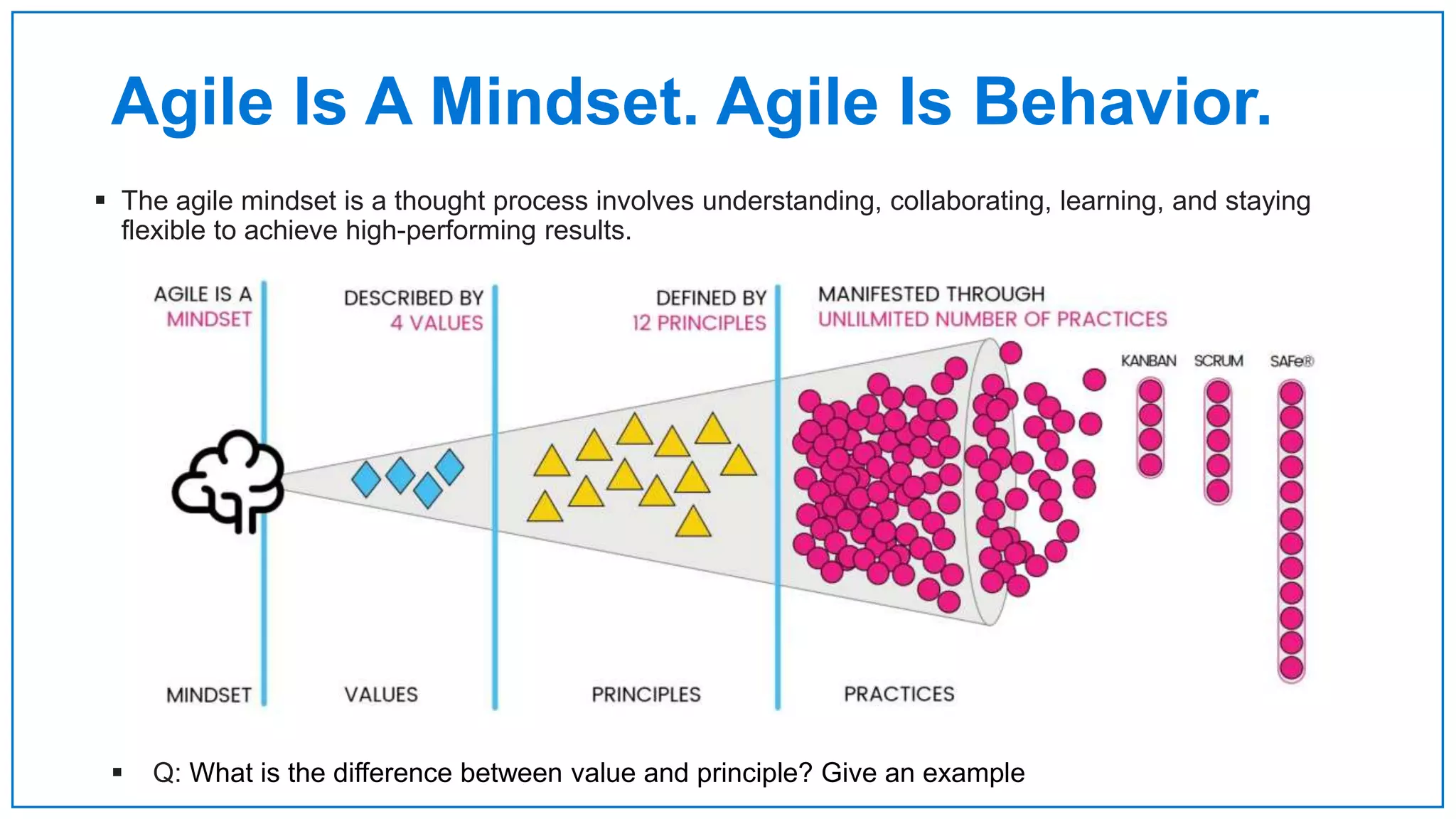
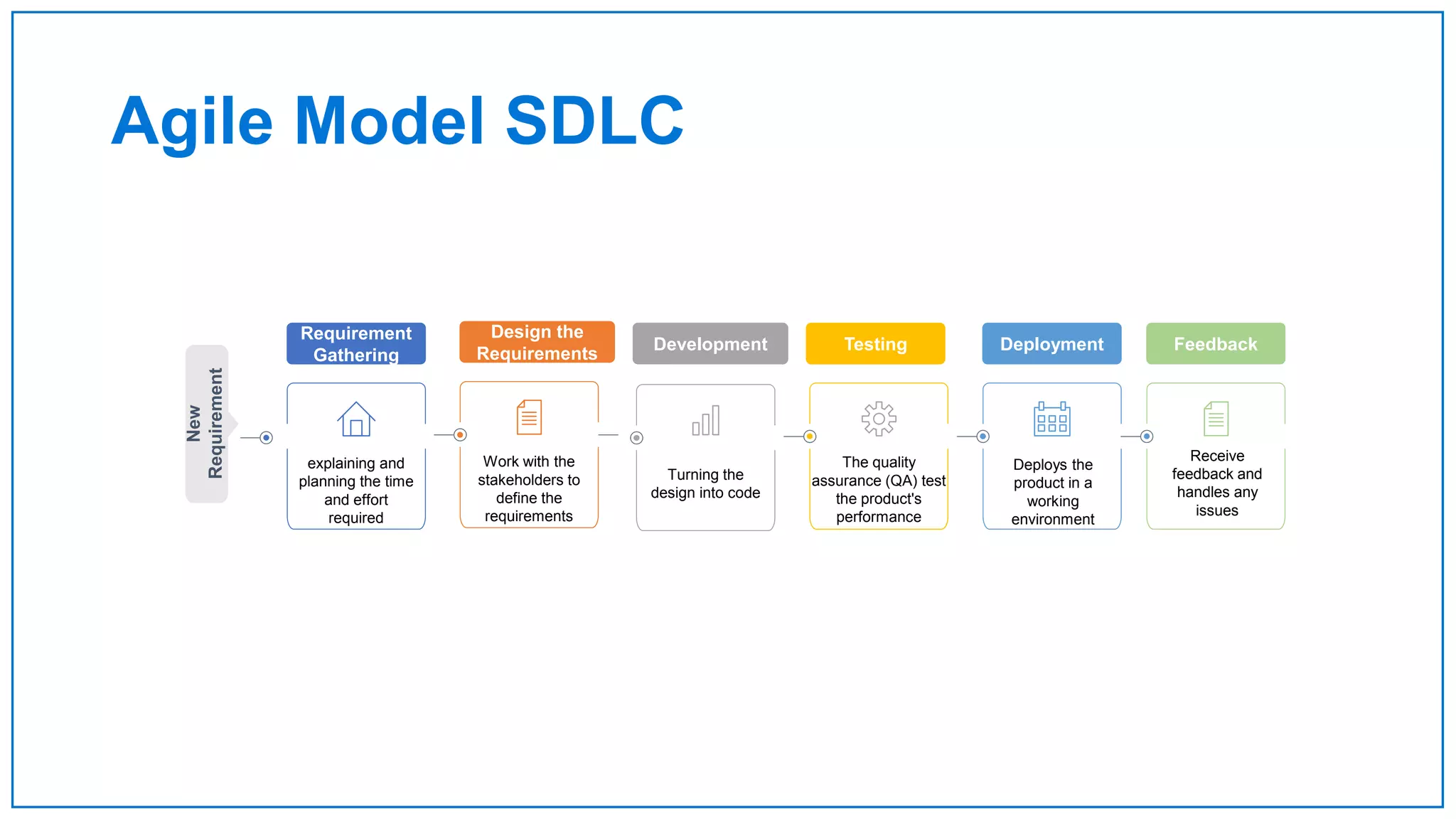
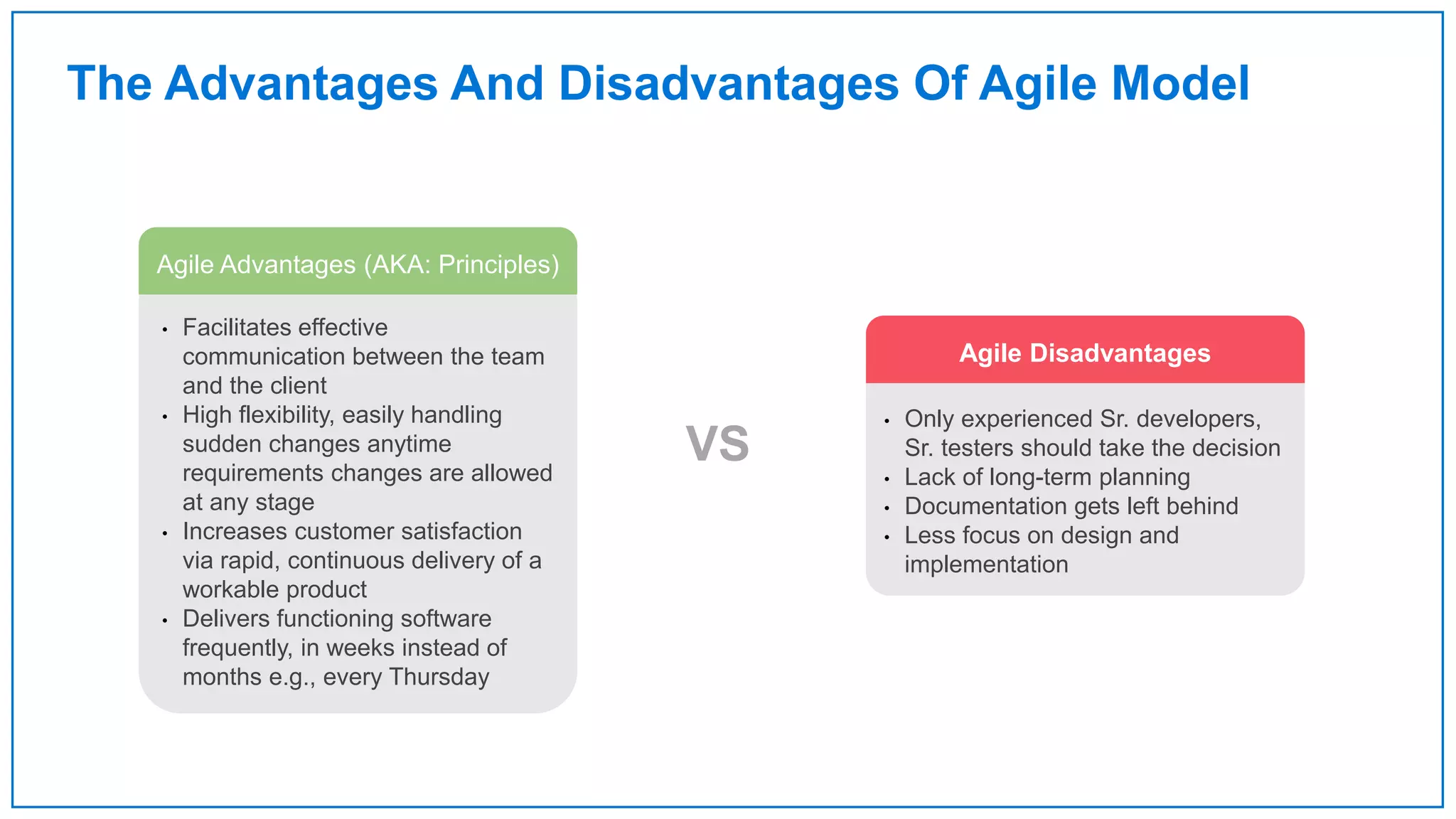
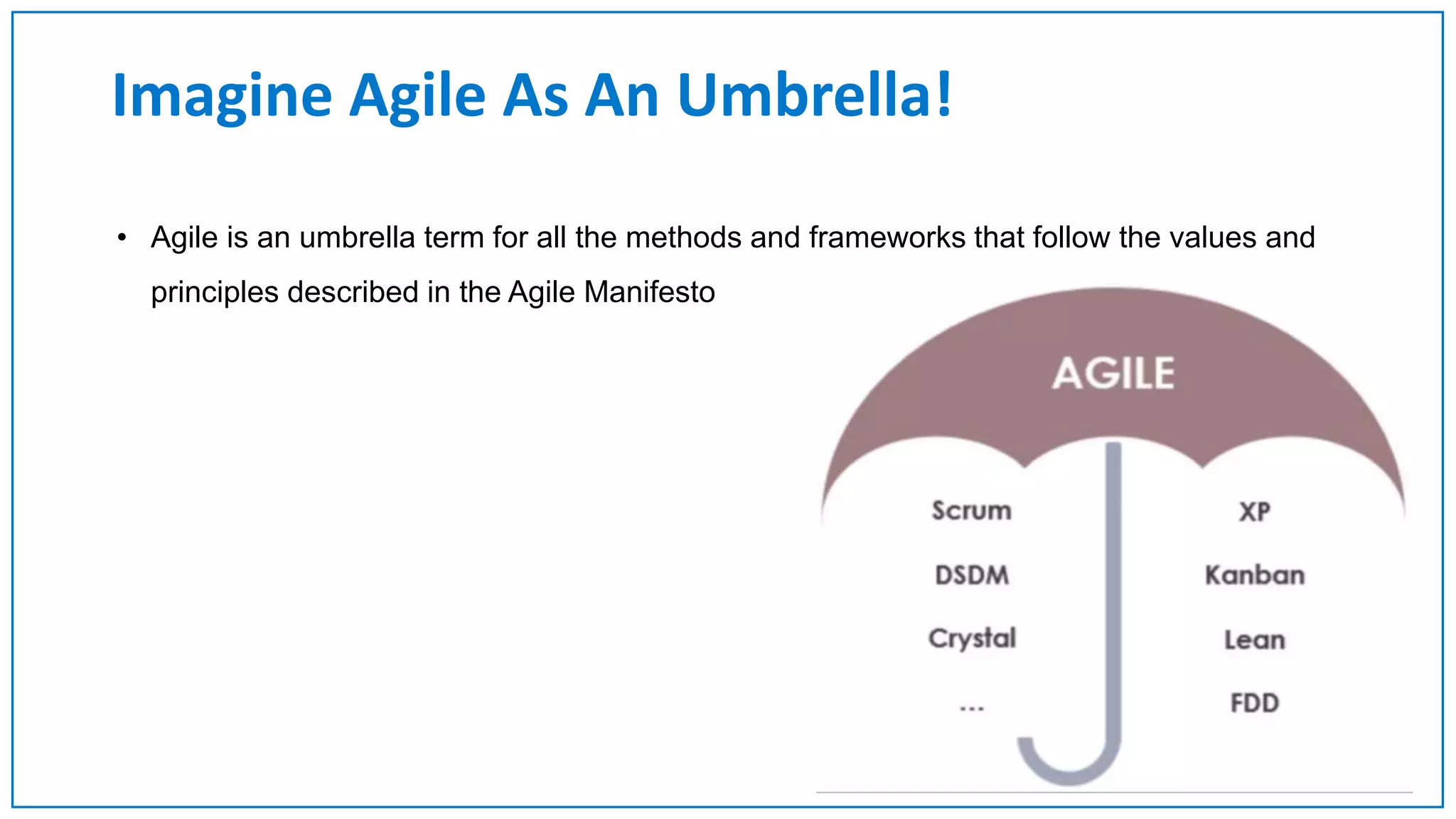
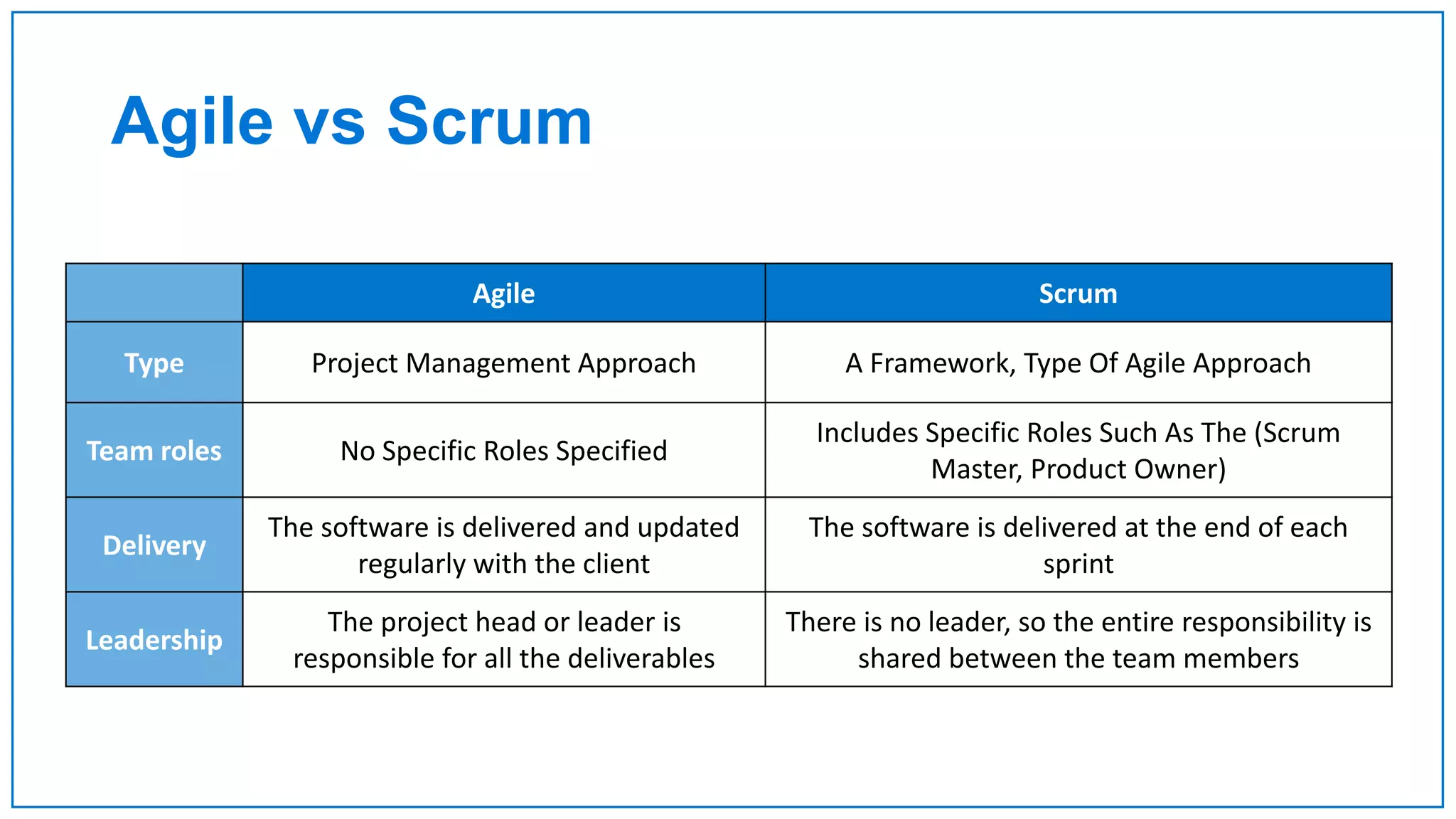
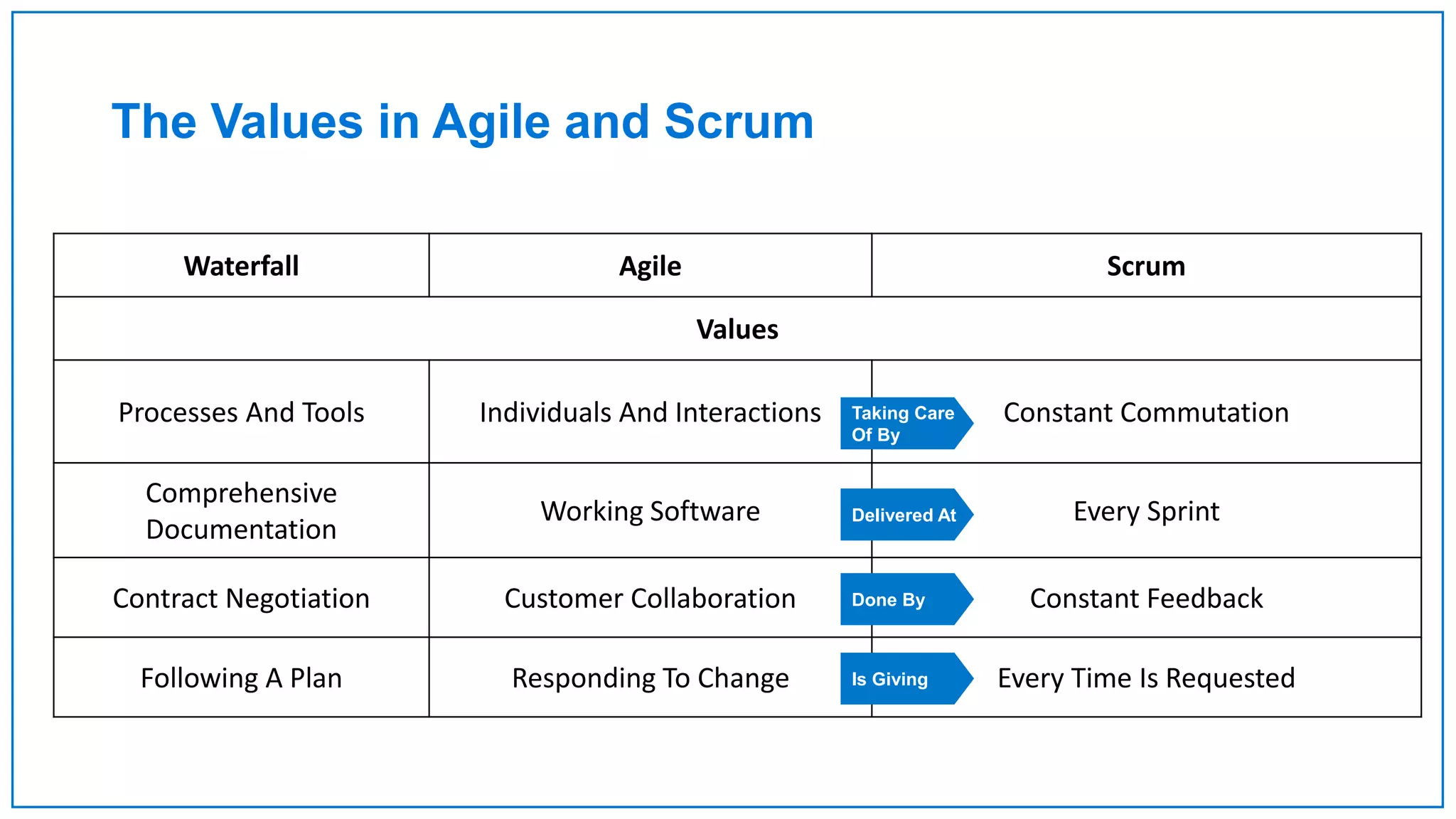
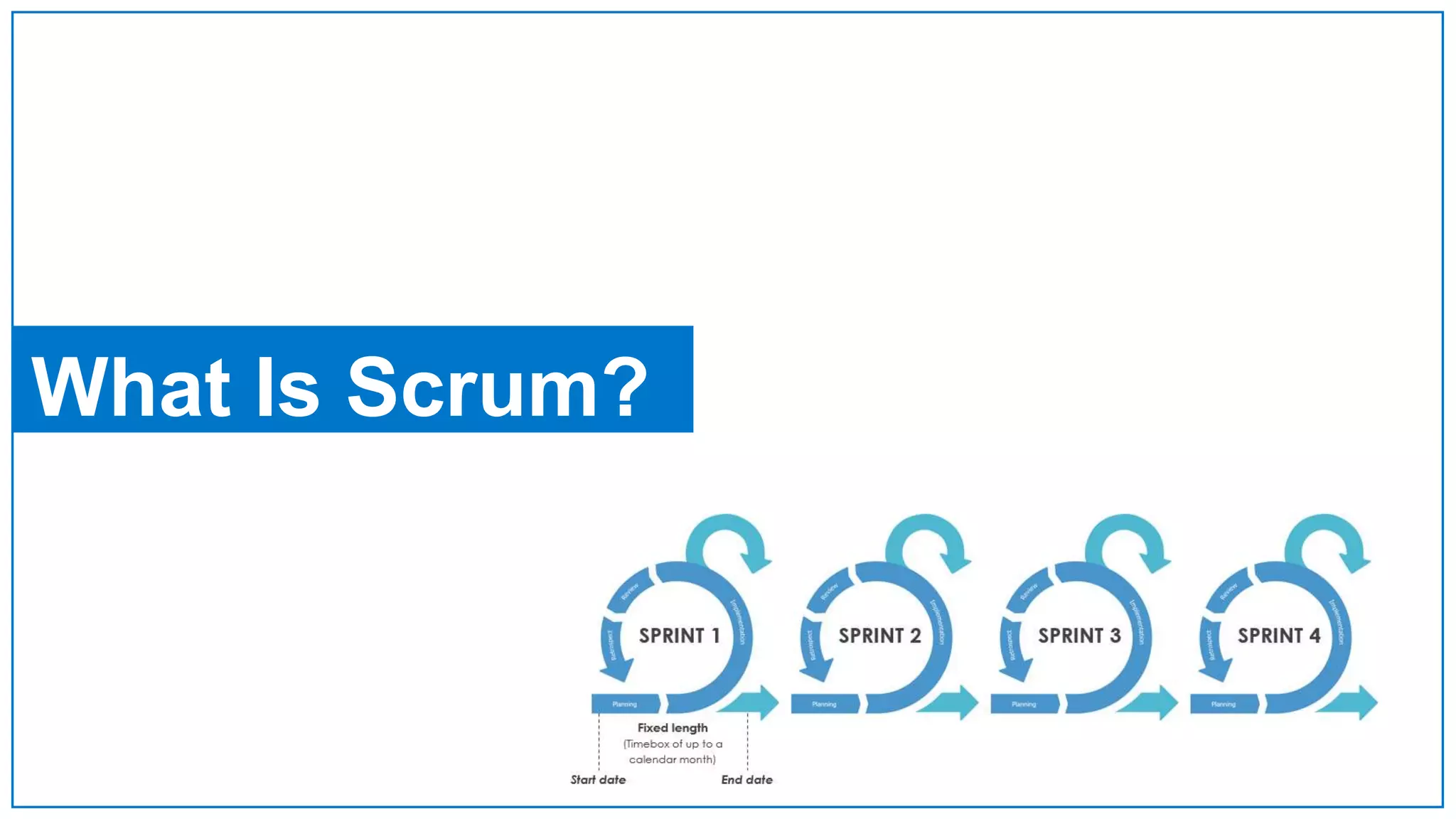
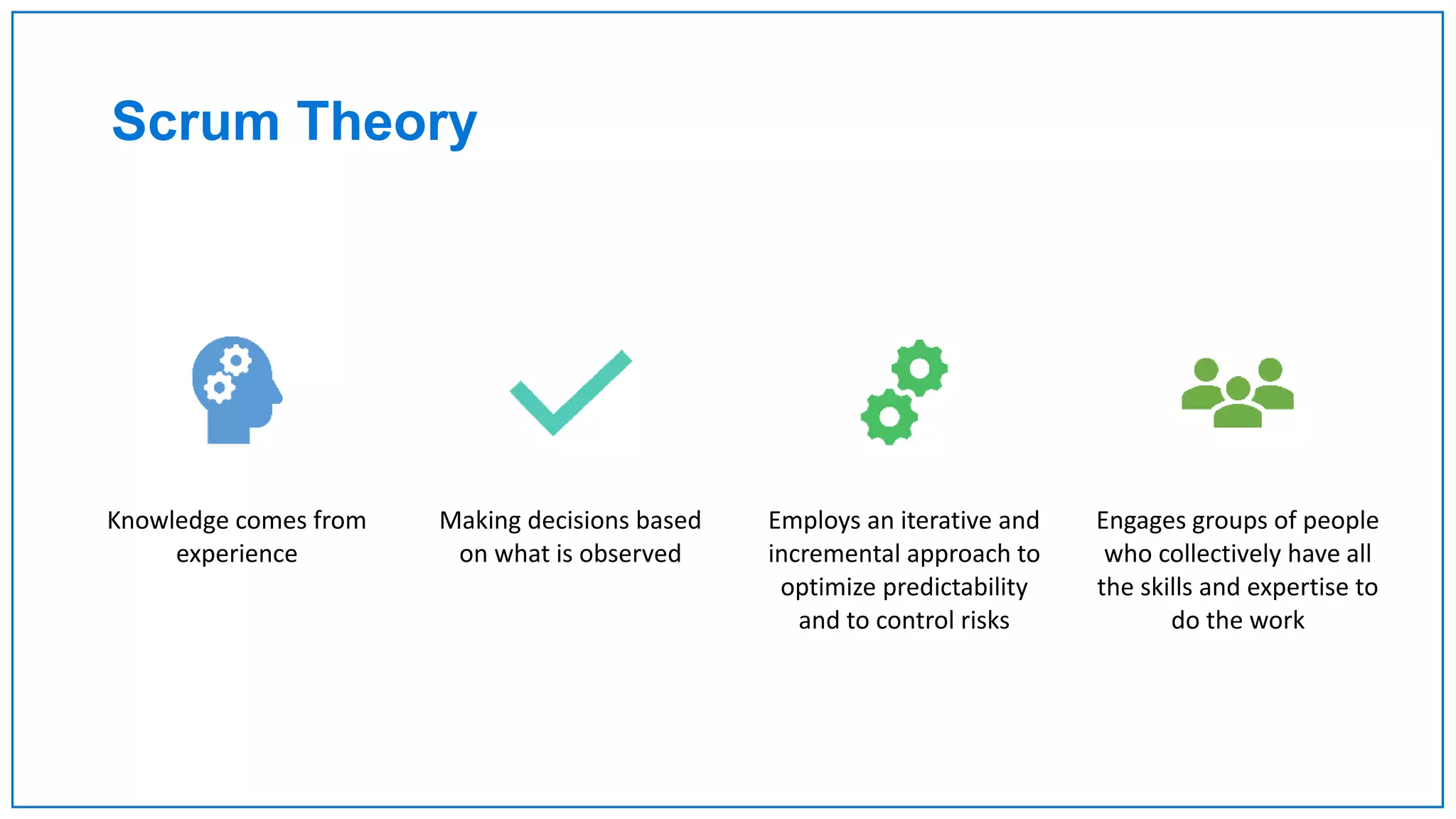
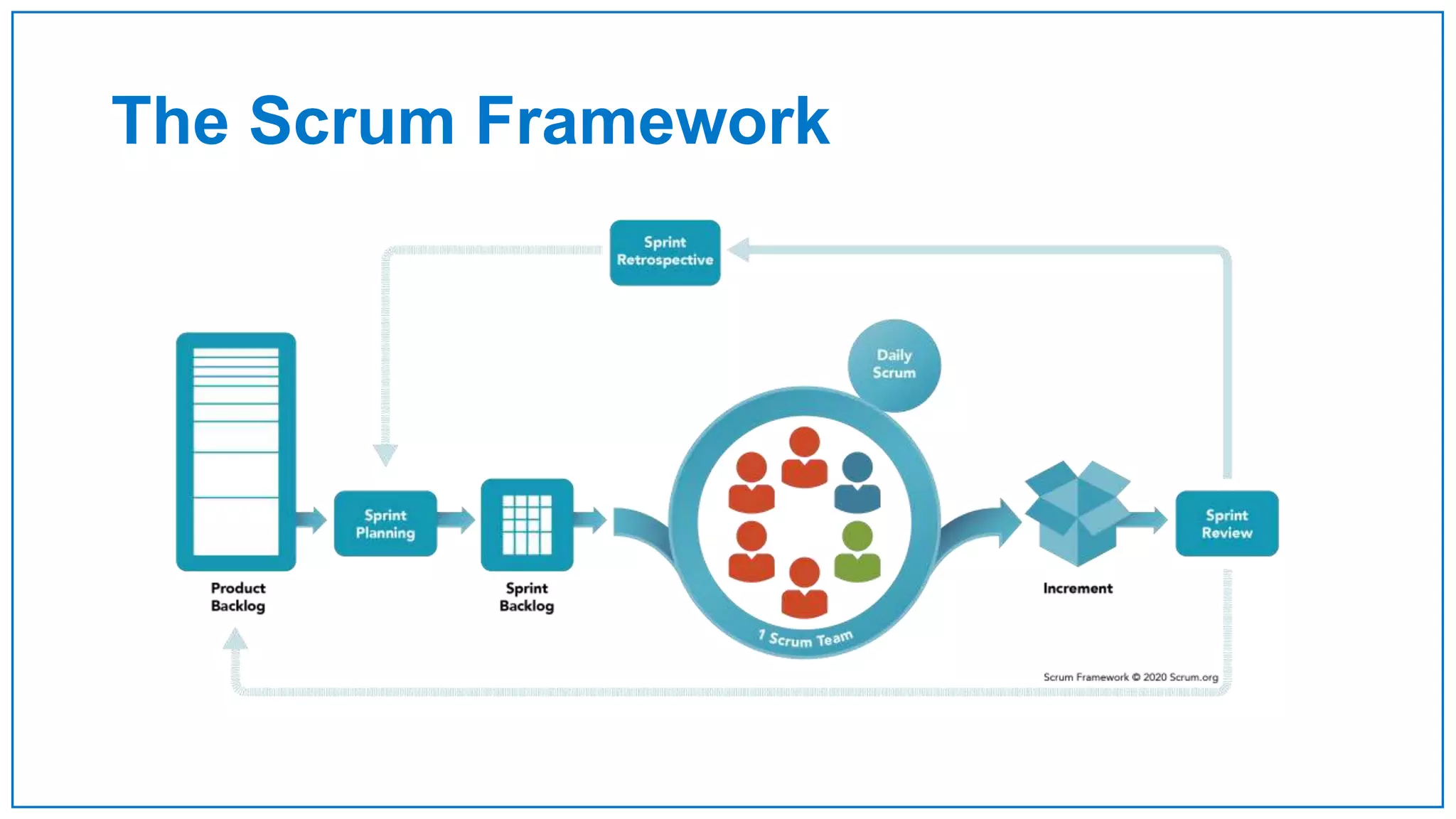
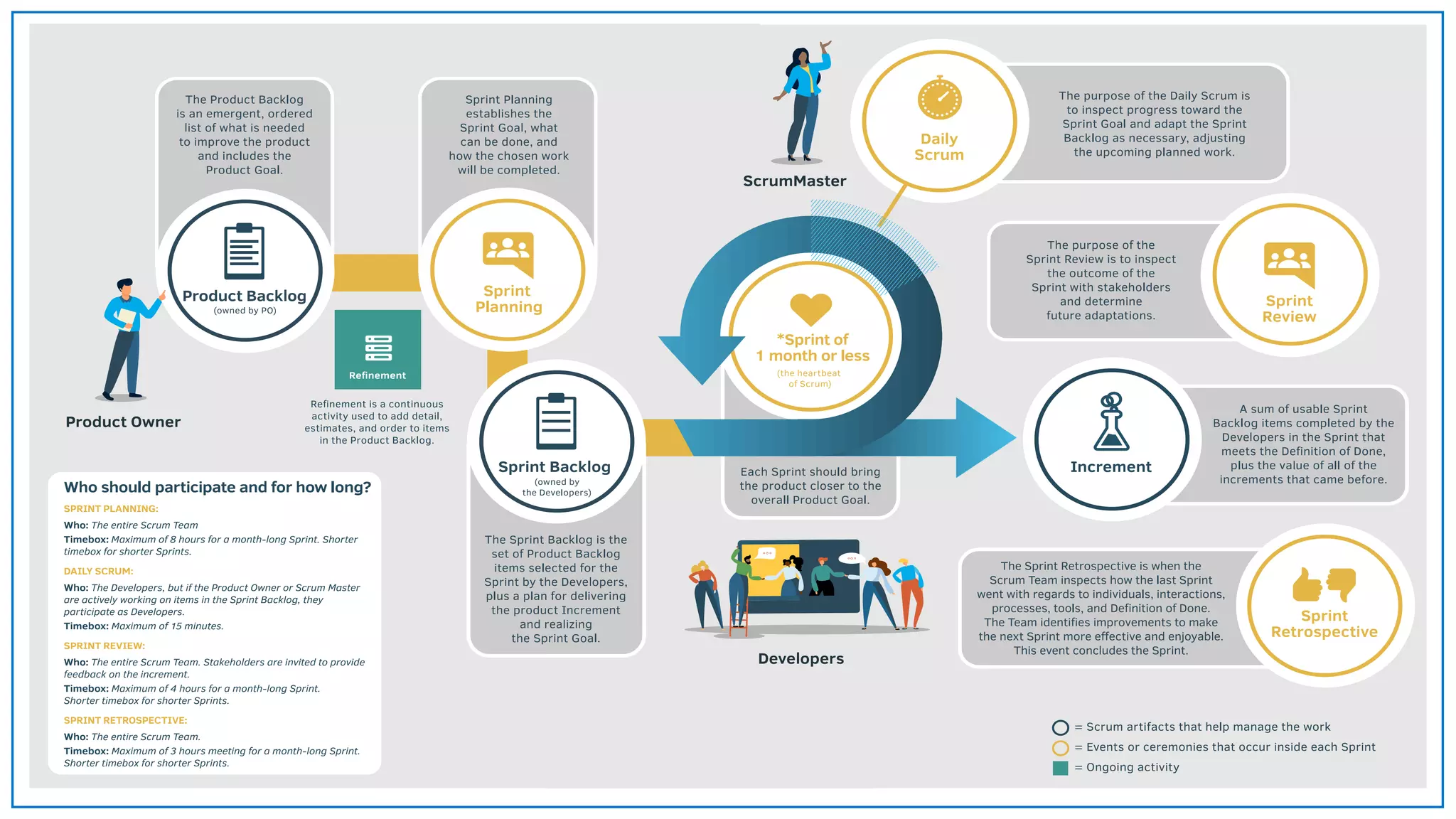
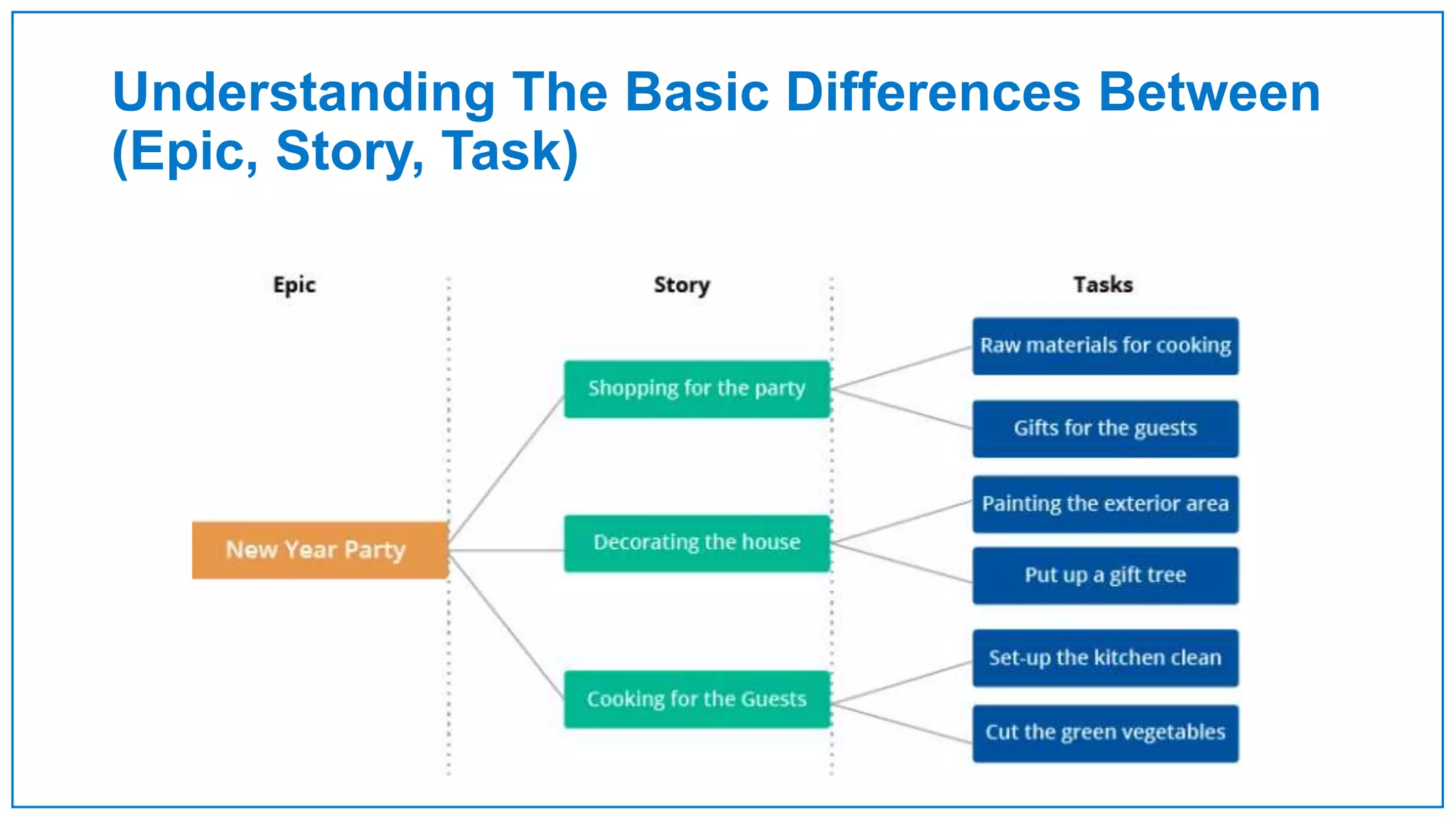
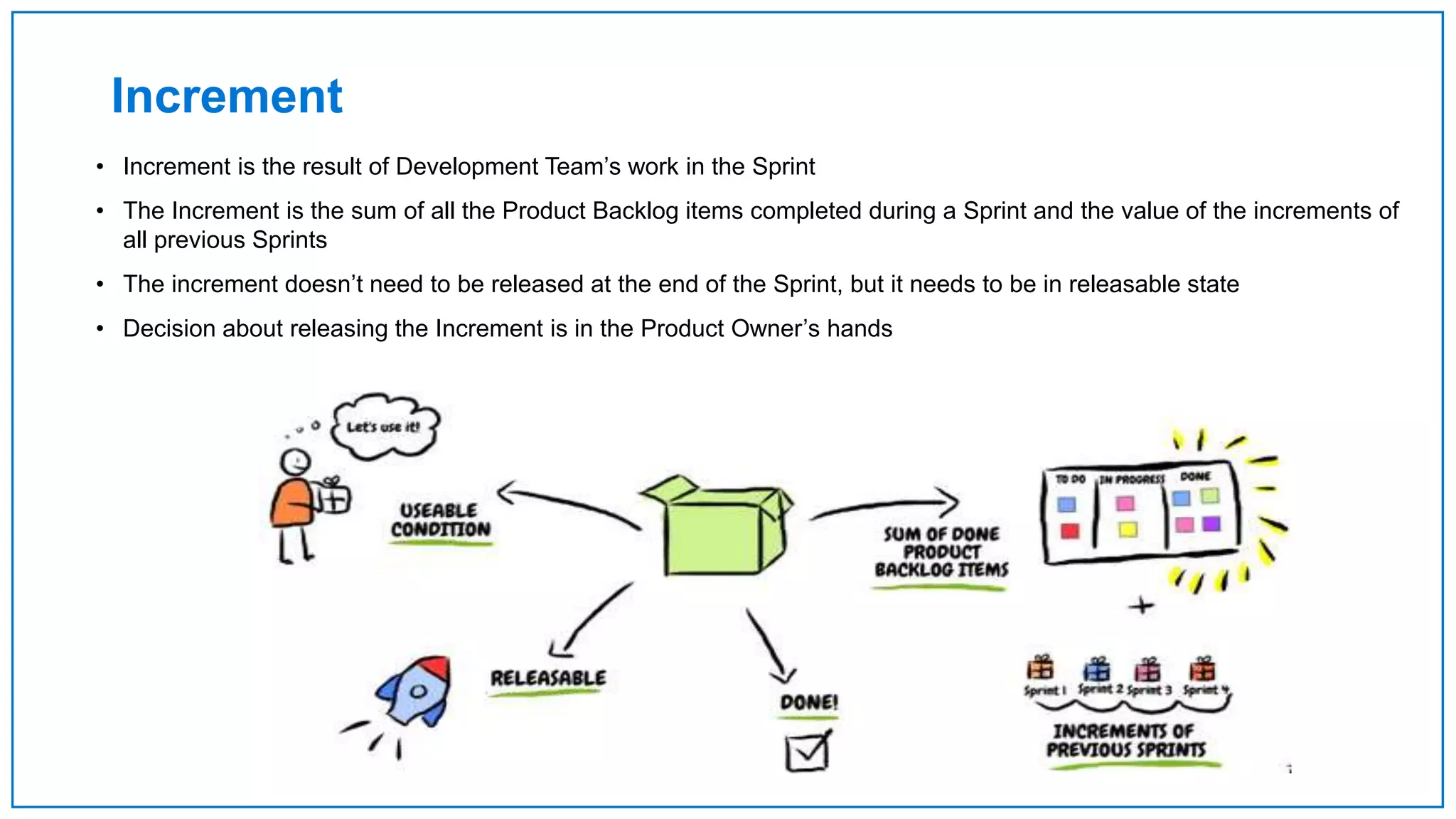
Agile Approach & Scrum Framework provides a history of agile methodology and the scrum framework. It describes how agile and scrum were developed in response to the need for more flexible software development processes. The document outlines the key principles of agile, including valuing individuals, collaboration, and responding to change. It then explains the scrum framework, including defining the scrum team roles of product owner, scrum master, and developers. The core scrum events of sprint planning, daily standups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives are summarized to close out the incremental sprint-based process.