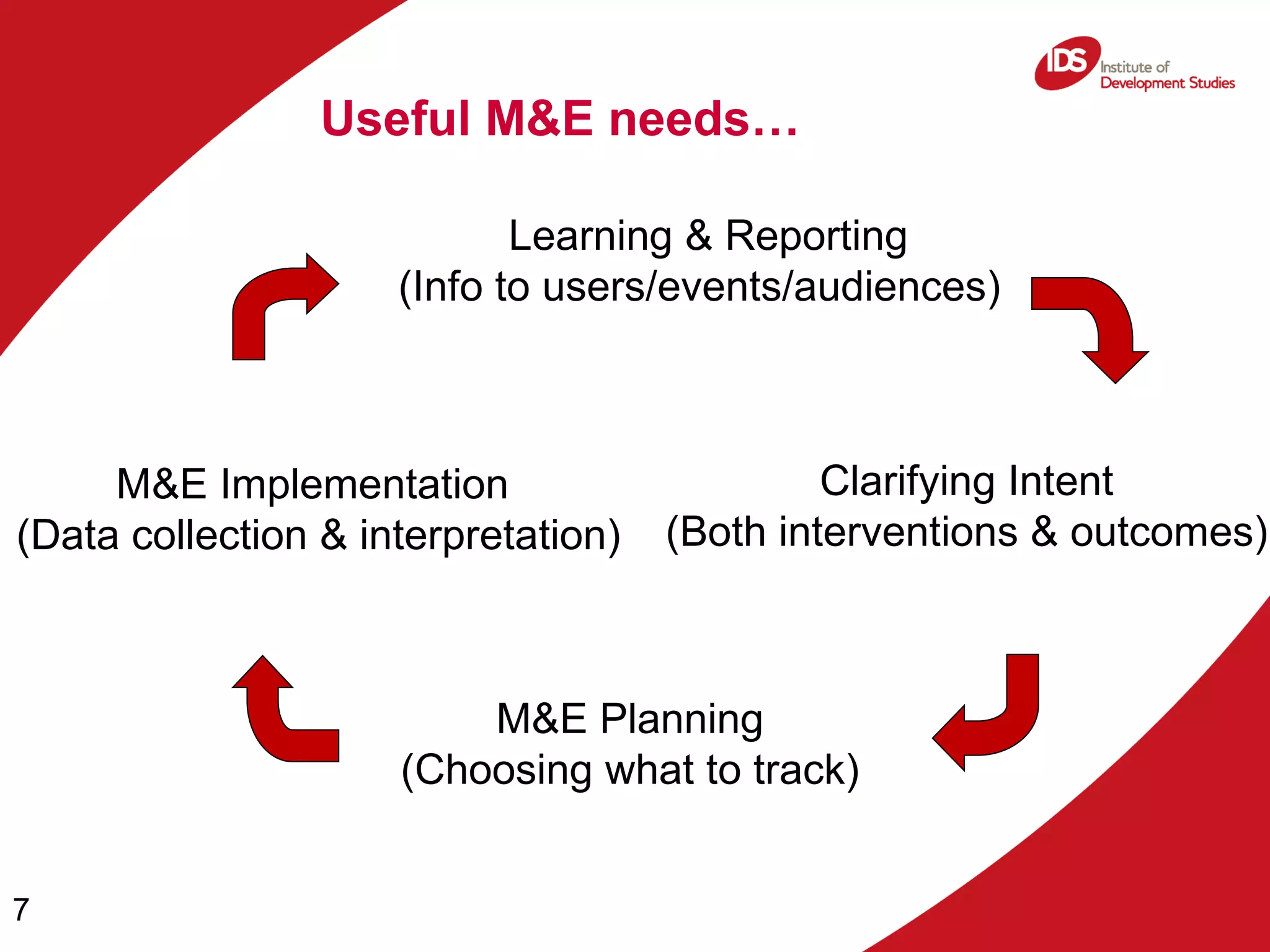
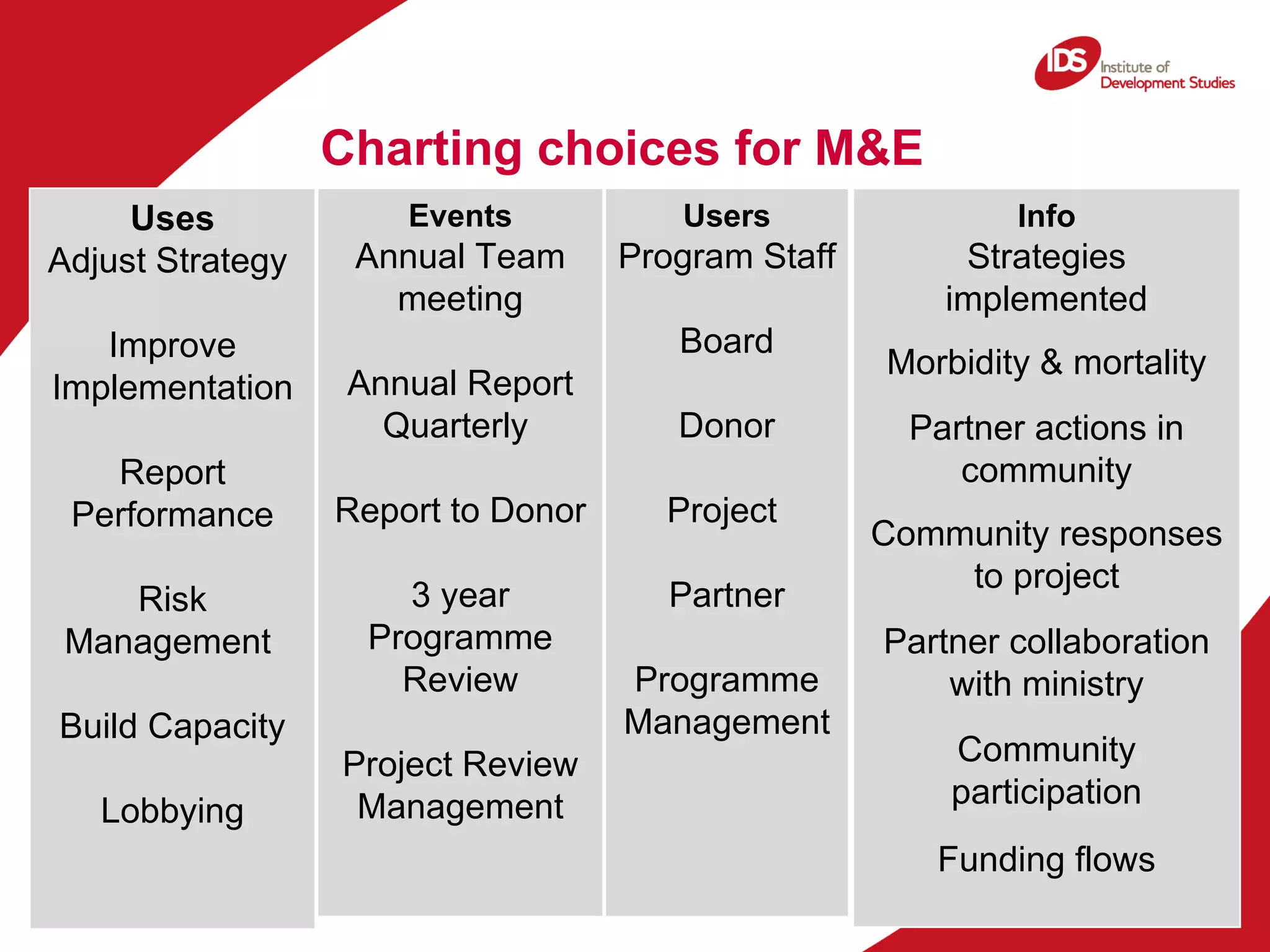
The document discusses the importance of monitoring and evaluation (M&E) in research communications, focusing on how to develop measurable indicators and data collection methods. It highlights the definitions of monitoring and evaluation, the significance of learning from these processes, and the involvement of boundary partners in achieving outcomes. It also emphasizes the complexity of change and encourages adaptive strategies for improvement based on collected data.