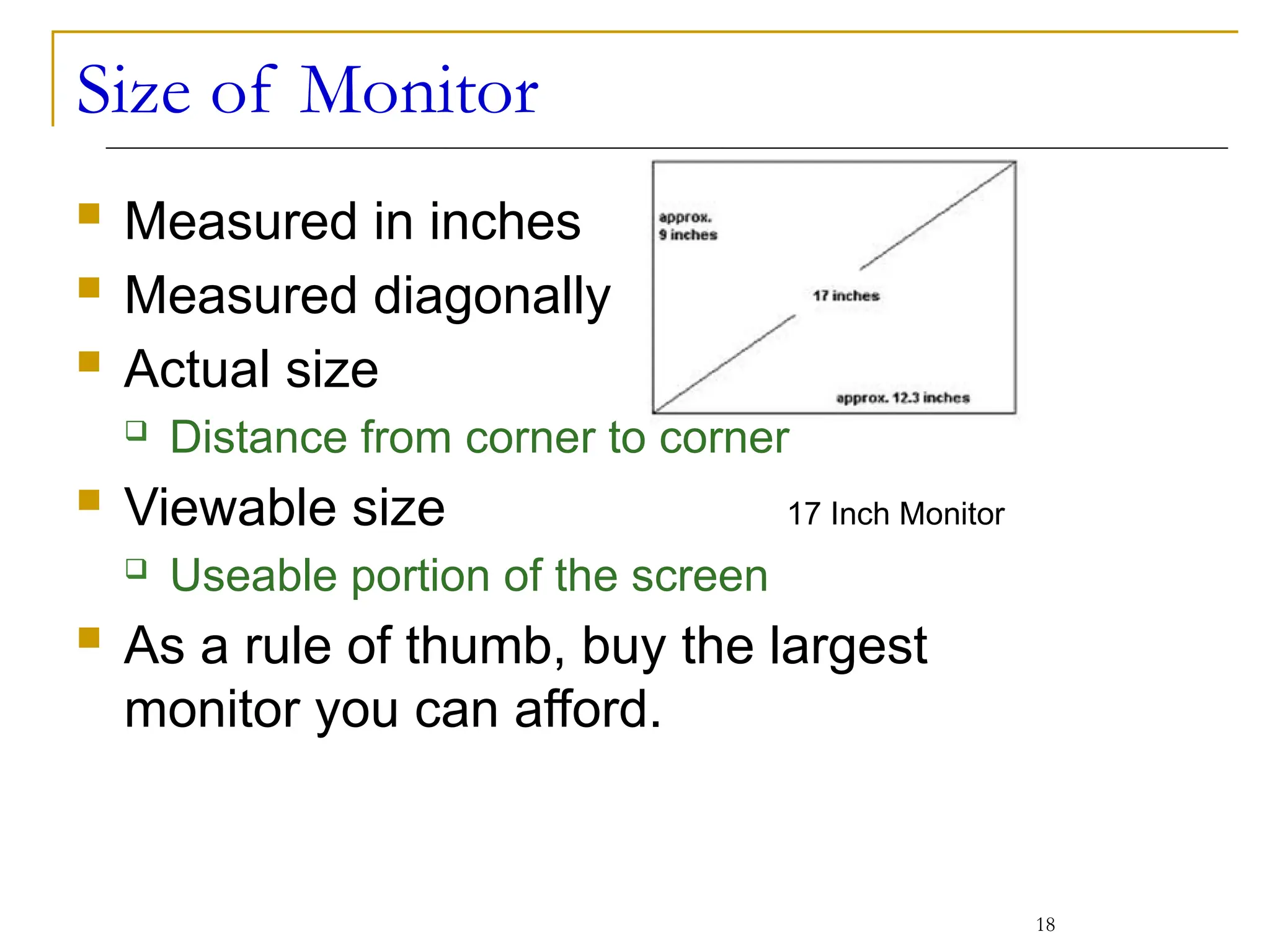
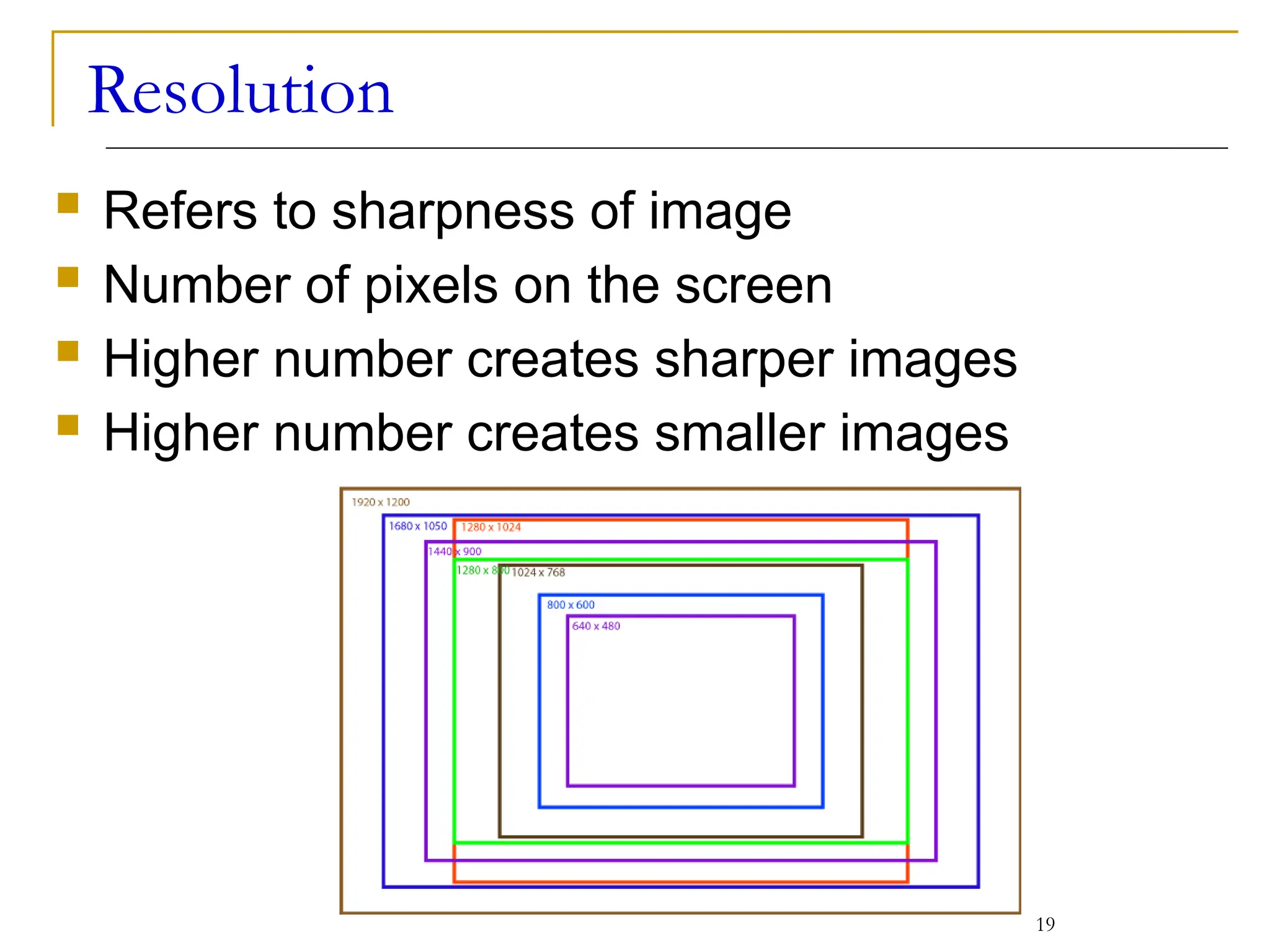
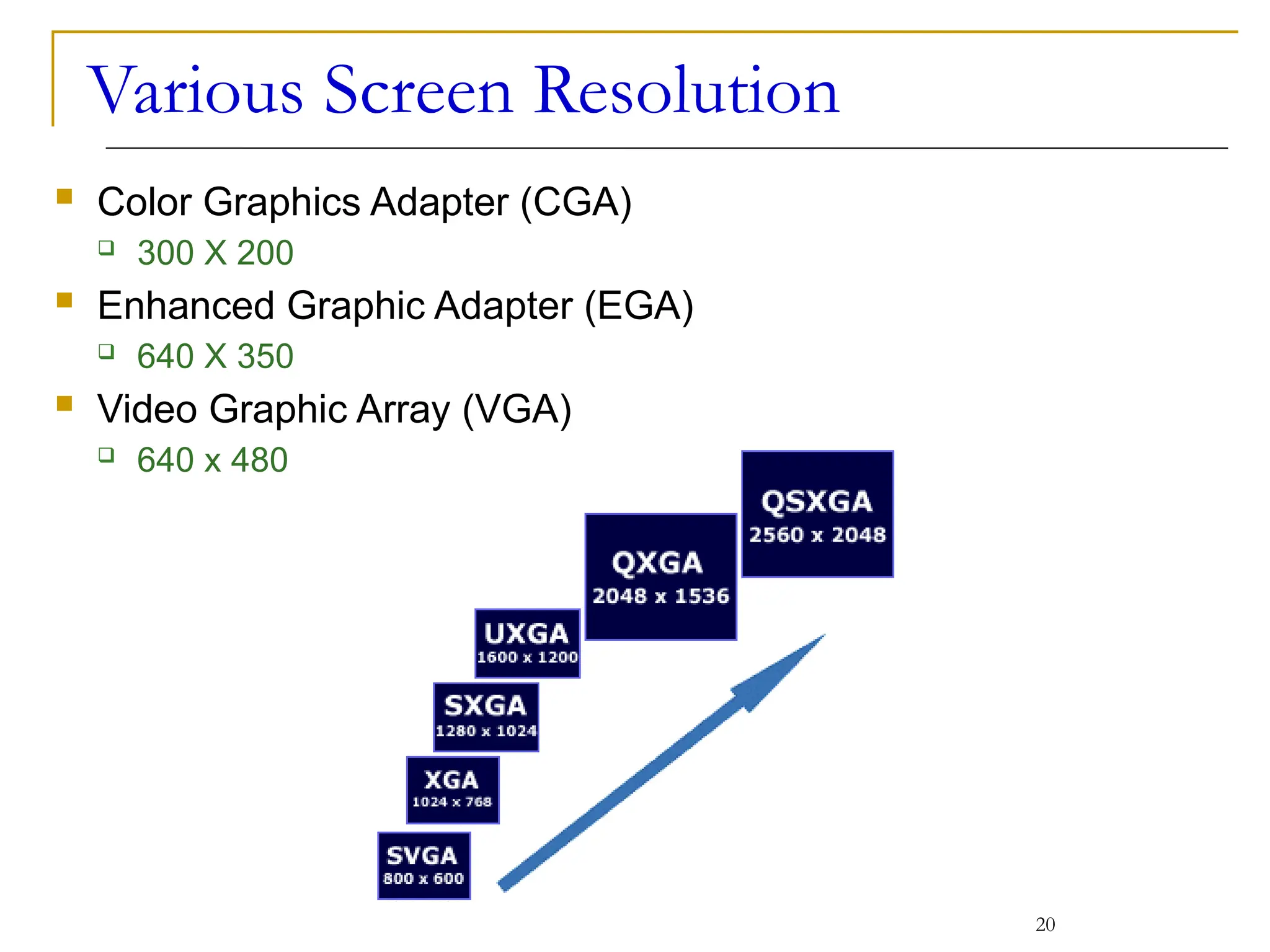
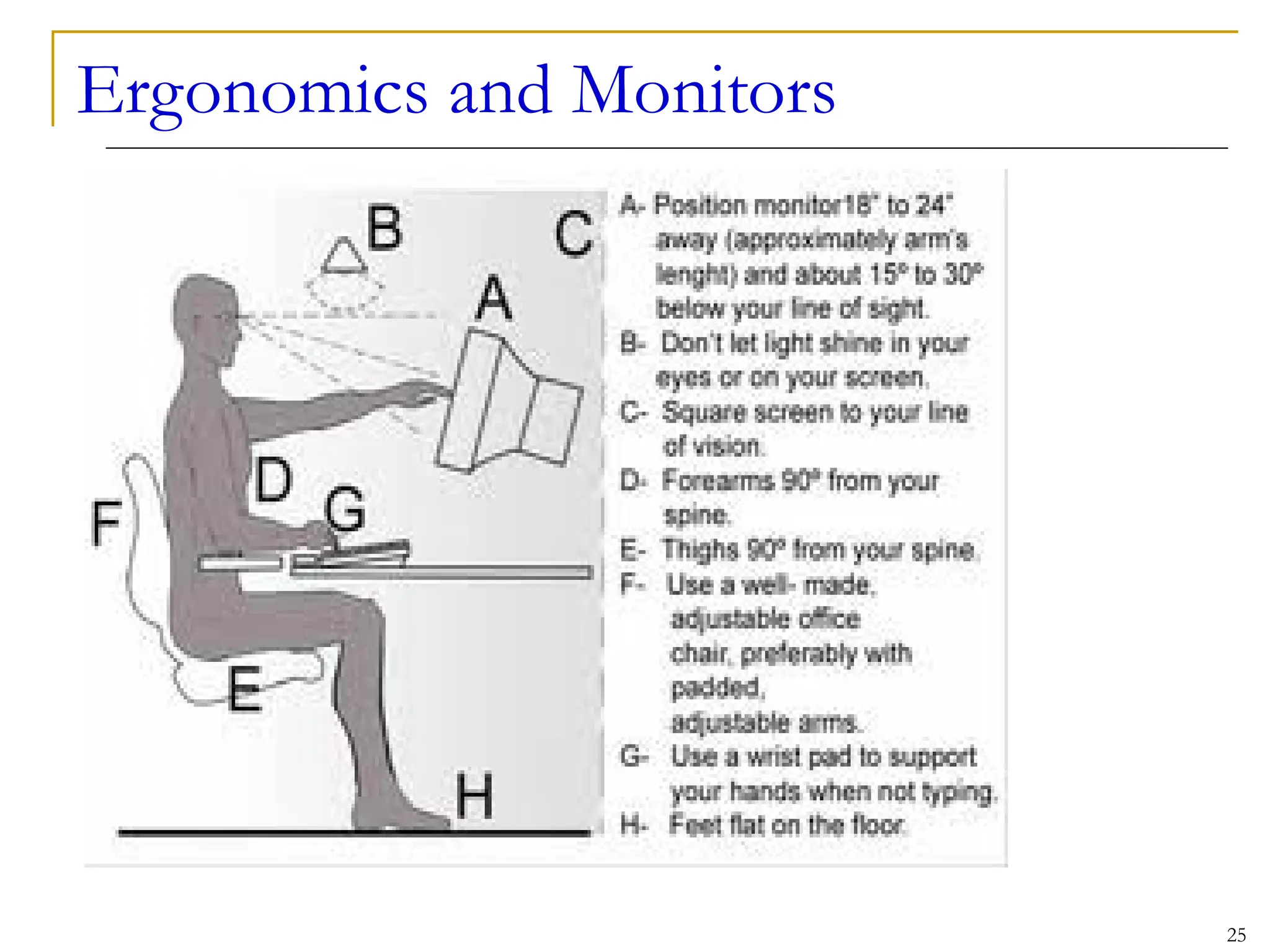
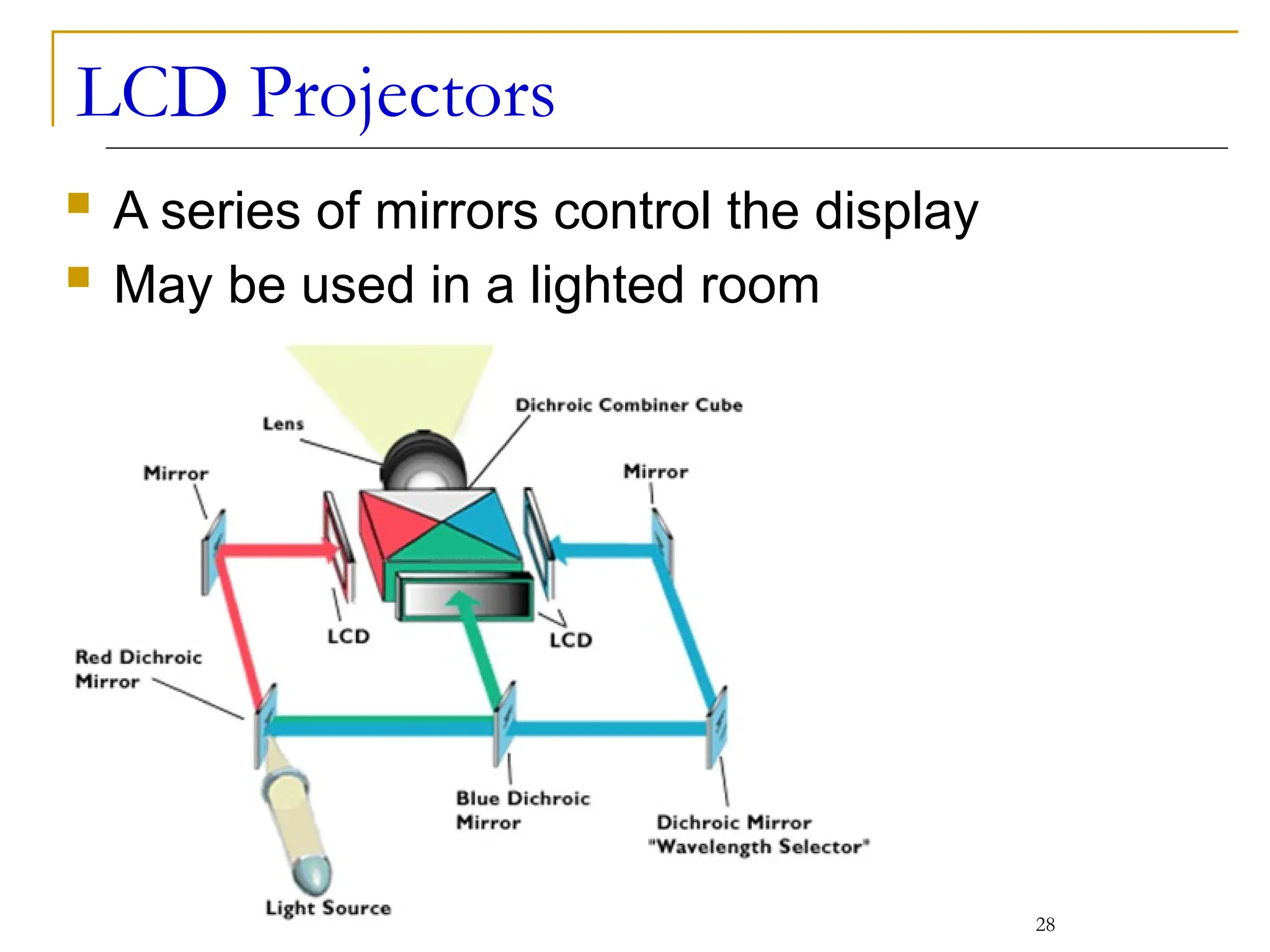
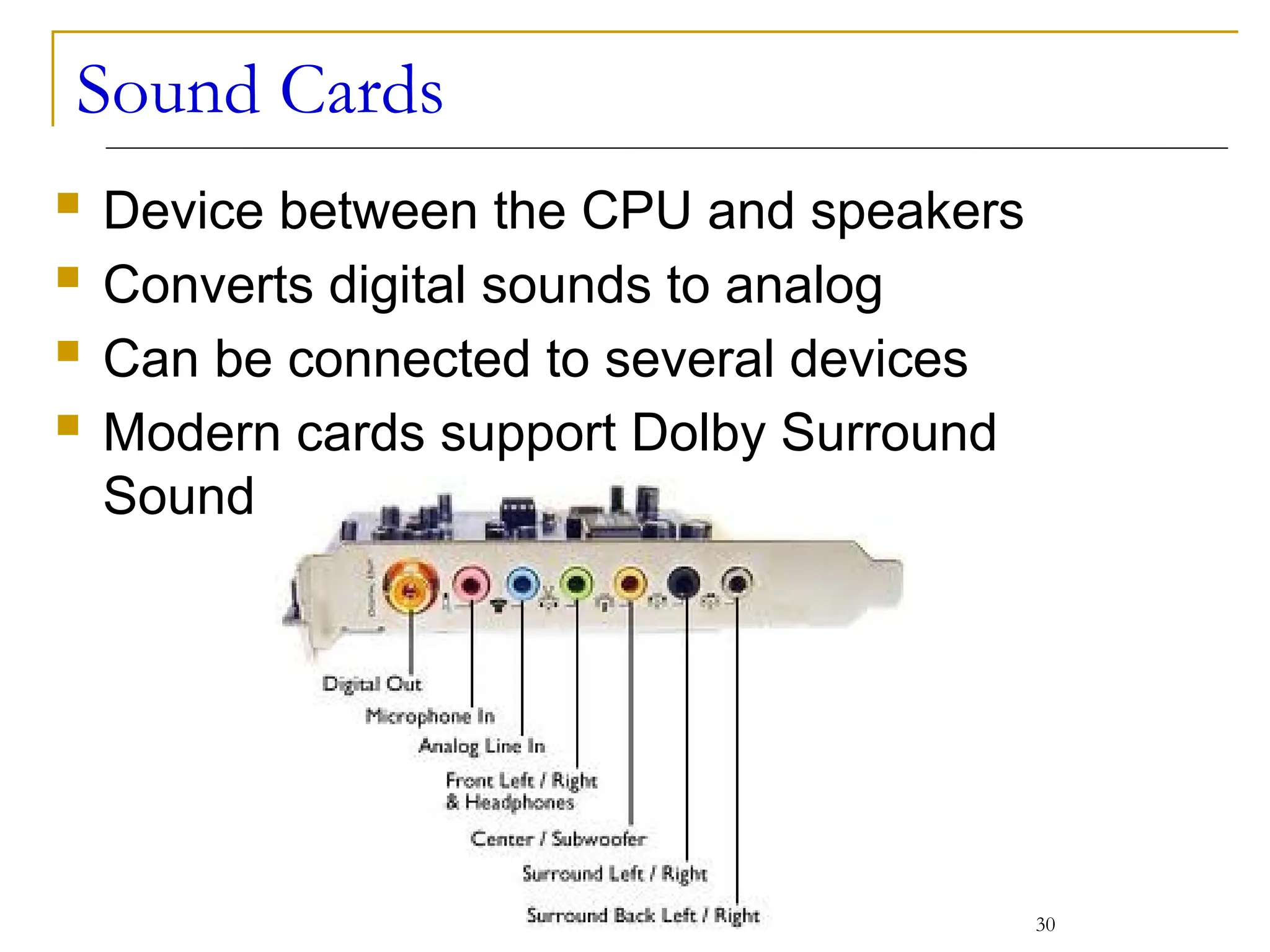
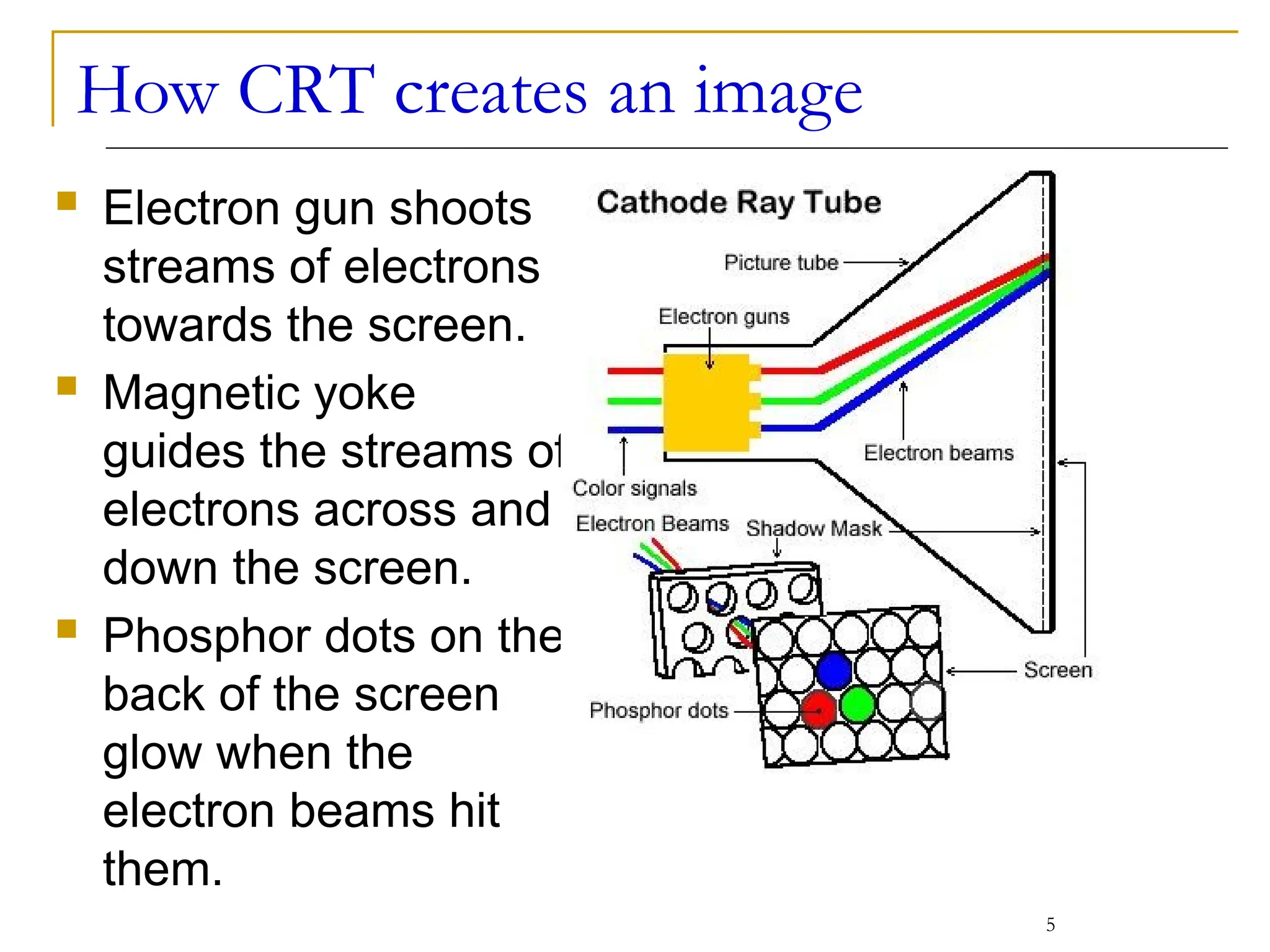
This document covers various output devices used in computing, focusing on display technology such as CRT, LCD, plasma displays, and LED monitors. It details their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and technical specifications, including resolution, refresh rates, and ergonomics. Additionally, it discusses sound systems, sound cards, and the role of data projectors in the computing experience.










![Light Emitting Diodes (LED)
uses light-emitting diodes as a video
display
produce images with greater dynamic
contrast;
can be extremely slim, some screens less
than half an inch (0.92 cm) thick;[6]
produce less environmental pollution on
disposal;
are more expensive;
have typically 20 to 30% lower power
consumption
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture6-241007120118-9d33650e/75/COMPUTER-SCIENCEBASIC-LECTURE-Lecture_5-pptxlecture_6-pptx-15-2048.jpg)