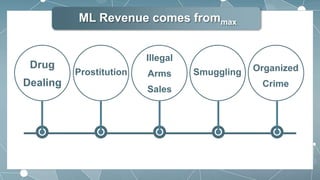
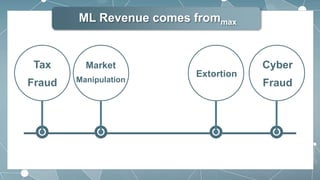
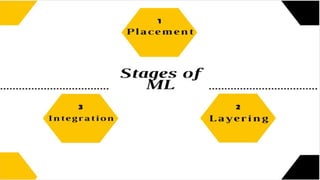
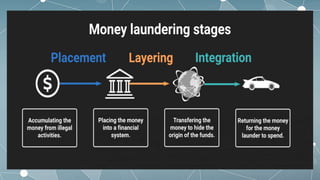
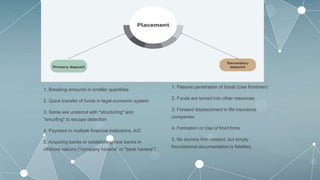
This document outlines the key aspects of money laundering in 9 parts. It defines money laundering as the process of making illegally gained money appear legal. It discusses how money laundering revenue comes from various criminal activities and the reasons people launder money, such as to easily control large amounts of cash. The document also covers the negative impacts of money laundering on businesses and the economy, the features and steps of money laundering including digital money laundering, and international anti-money laundering activities.