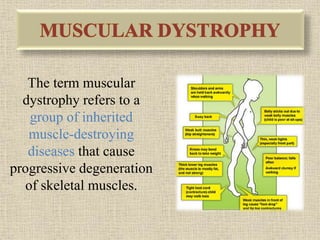
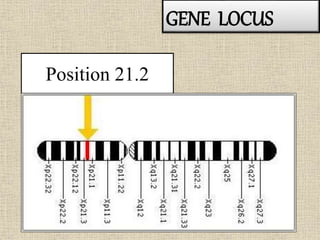
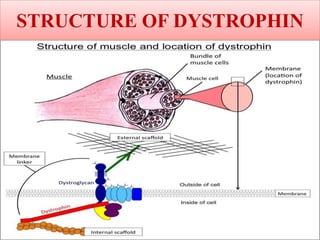
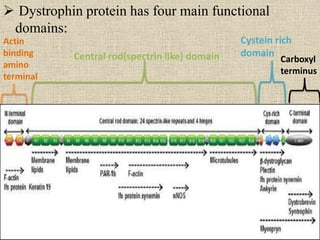
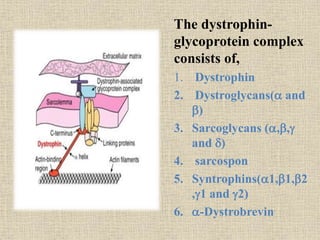
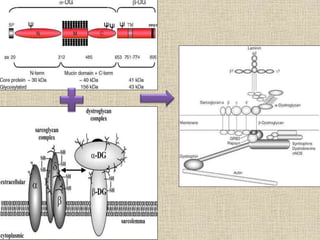
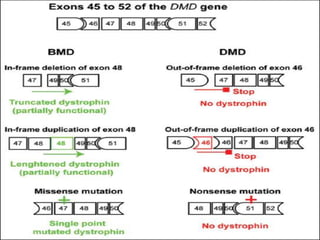
A molecular marker is a DNA sequence fragment indicating specific biological processes, particularly in relation to muscular dystrophy, a group of inherited diseases causing muscle degeneration. The mutations in the dystrophin gene on the X chromosome lead to Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy, with various types of mutations including deletions and point mutations identified through different genetic analysis methods. Dystrophin's protein complex connects muscle fibers to the extracellular matrix, and disruptions in this complex result in muscular dystrophy.