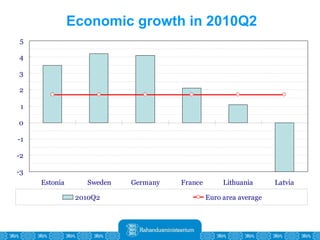
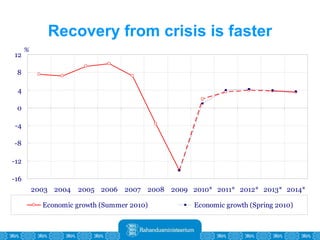
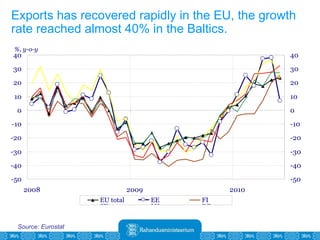
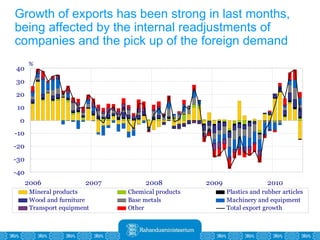
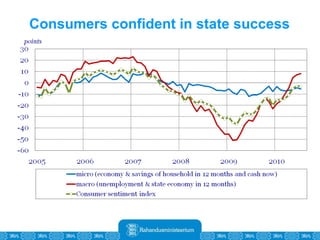
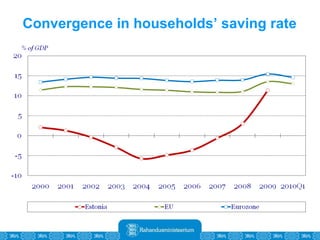
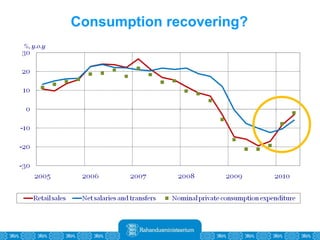
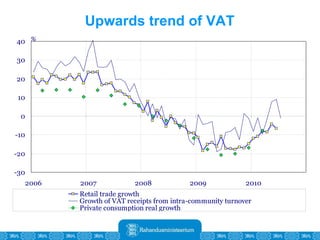
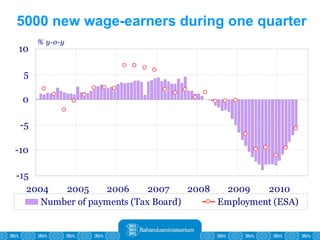
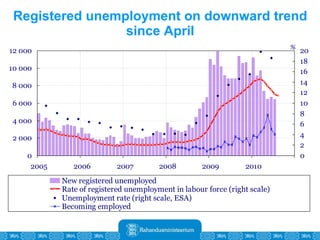
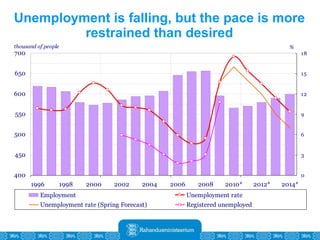
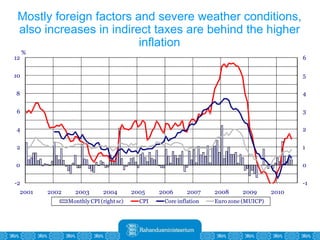
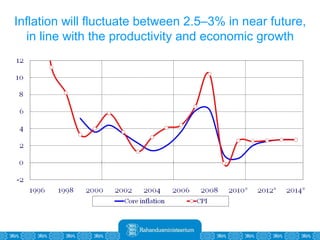
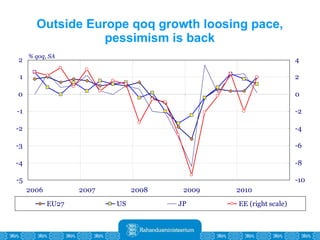
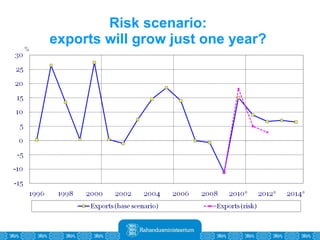
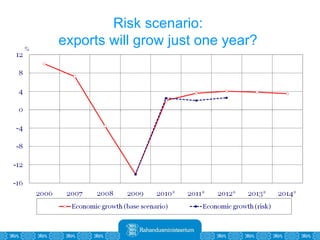
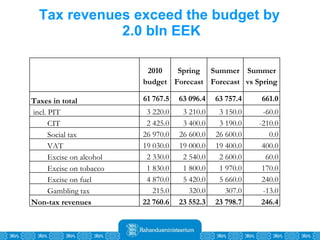
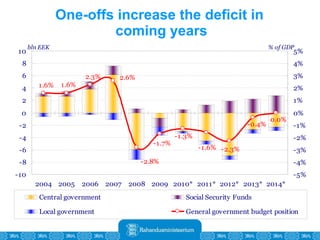
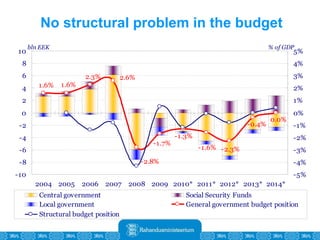
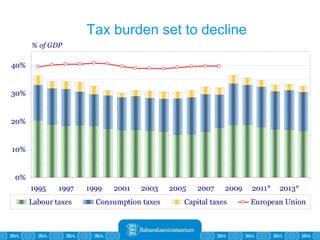
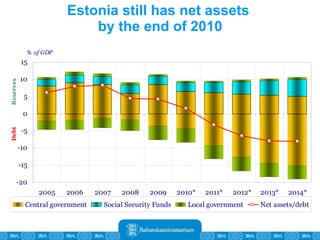
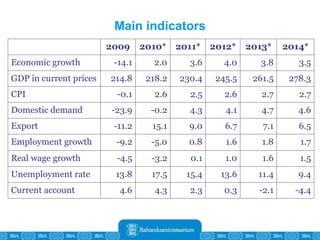
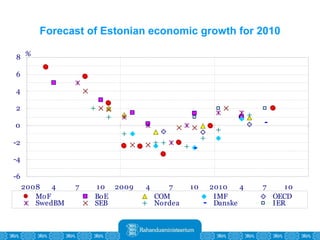
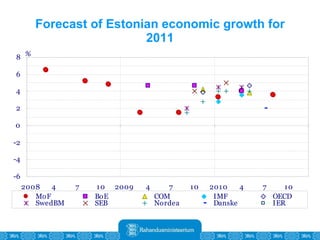
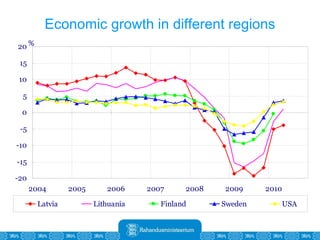
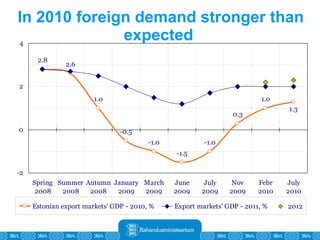
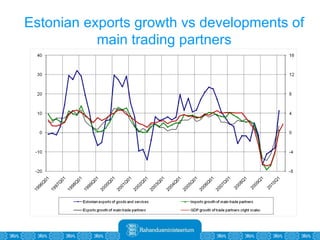
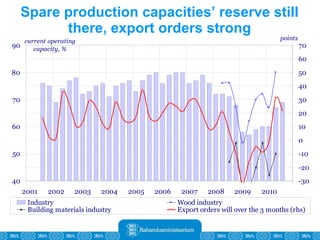
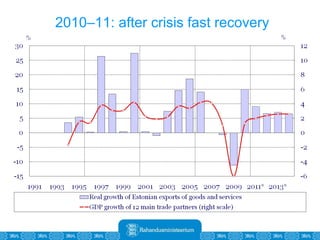
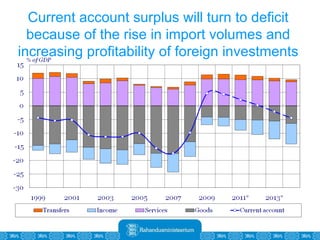
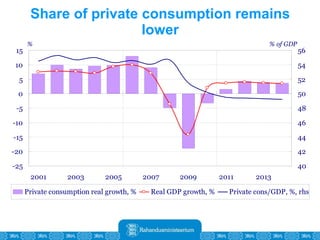
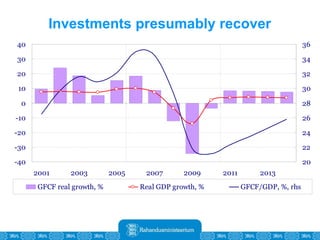
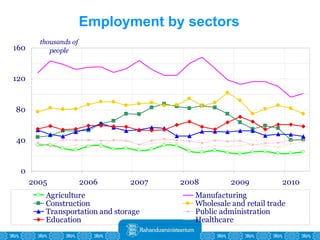
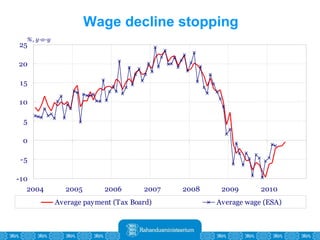
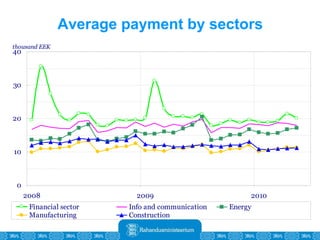
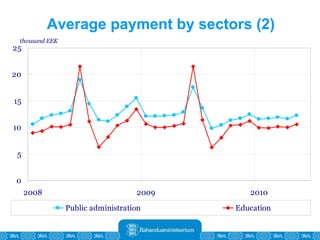
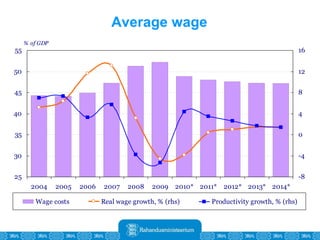
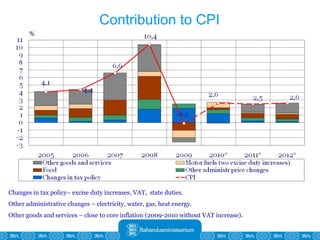
The Estonian Ministry of Finance summer forecast predicts economic growth of 2% in 2010 and 3.6% in 2011, with inflation around 2.5-2.6% both years. Exports have recovered rapidly due to increased competitiveness and external demand. While employment is increasing, the pace is more restrained than desired. Risks to the outlook include uncertainty about export growth continuing in 2011 and higher than expected inflation in the short term.