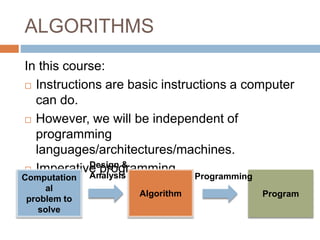
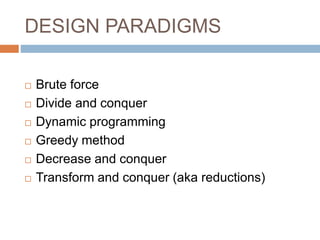
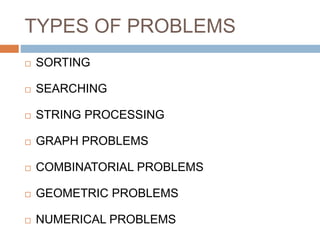
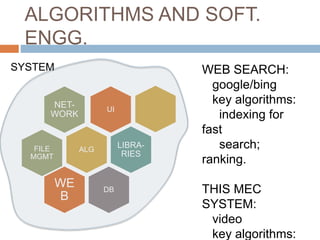
This document provides an introduction to algorithms and algorithm design. It defines an algorithm as a finite list of well-defined instructions to solve a computational problem. Some key algorithm design paradigms discussed include brute force, divide and conquer, dynamic programming, and greedy methods. The document also lists common types of algorithmic problems such as sorting, searching, string processing, and graphs. It notes that algorithms are central to computational thinking and software engineering.