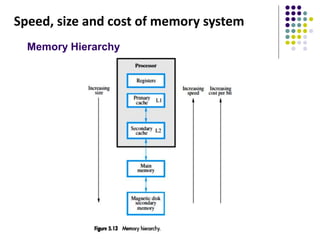
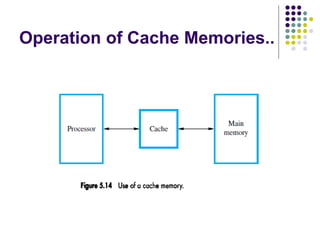
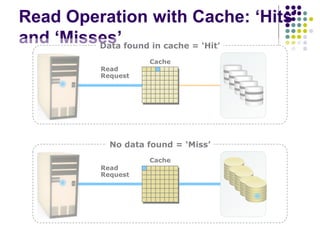
The document discusses cache memories and how they improve processor performance. Cache memories store frequently accessed instructions and data from main memory in a faster cache located closer to the processor. This takes advantage of locality of reference, where programs tend to access the same memory locations repeatedly. On a cache hit, the processor can access the needed data from the fast cache instead of waiting for the slower main memory, improving performance. On a cache miss, the needed block of memory is copied from main memory to cache.