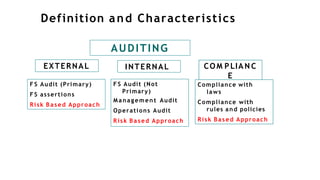
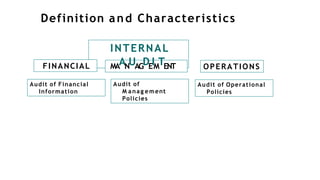
This document provides an overview of operational auditing. It defines operational auditing as the evaluation of organizational activities through a future-oriented and systematic review. The objectives and phases of an operational audit are described. Objectives may include addressing new rules, poor performance, compliance issues, or anomalous revenues/expenses. Phases include planning, fieldwork, reporting, and follow-up. Planning involves scoping and risk assessment. Fieldwork determines if controls are designed and performing effectively. Reporting communicates findings and recommendations. Follow-up ensures corrective actions were implemented. Operational audits require diverse skills and provide a flexible way to assess an organization's pursuit of its mission and vision.