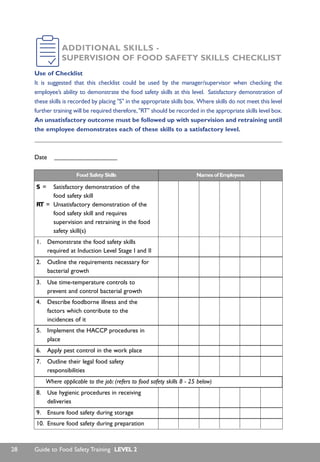
This document provides guidance on food safety training for Level 2 skills, which are additional skills that food handlers and non-food handlers should demonstrate 3-12 months after starting work. It includes an introduction explaining the purpose and use of the training standard. The document then provides general advice on organizing and facilitating food safety training, including assessing training needs, developing a training plan, and the roles of managers, supervisors and trainers. The core of the document is a table outlining the Level 2 food safety skills, how to demonstrate each skill, and how employers can support the training. It concludes with checklists for delivering training and supervising food safety skills.