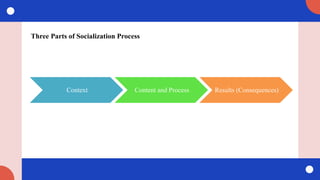
The document discusses the significance of socialization, outlining its context, content, processes, and consequences as well as various theories and types involved. It emphasizes the lifelong experience of learning cultural norms and values, highlighting the roles of different agents of socialization such as family, peers, and media. Additionally, it includes key theories from notable sociologists to explain how individuals develop their identities and behaviors through socialization.























![Sources:
Alejandria-Gonzales, M.C. (2016). Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics. Makati City: Diwa Learning Systems, Inc.
Basas, R. M. A. (2016). Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics. Pasay City: JFS Publishing Services.
Cole, N. L. (2020). Understanding Socialization in Sociology. Thought.co. https://www.thoughtco.com/socialization-in-sociology-4104466
K12 Study Club (2020). UCSP 5.0 Becoming a Member of Society: Concepts, Context and Consequence of Socialization [Youtube Video].
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LAaBbwwtY_Y
Lanuza, G. M., and Raymundo, S. S (2016). Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics. Manila City: Rex Book Store, Inc.
Lumen Learning (nd). The Role of Socialization. Boundless Sociology. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-sociology/chapter/the-role-
of-socialization/#:~:text=Socialization%20has%20three%20primary%20goals,sources%20of%20meaning%20and%20value
Persell, C. H. (1990). Becoming a Member of Society Through Socialization. Understanding Society: An Introduction to Sociology. New York:
Harper & Row, Publishers, Inc., p. 98-107 https://www.asanet.org/sites/default/files/savvy/introtosociology/Documents/
PersellSocializationReading37.htm
Samiksha S. (nd). Socialisation: The Meaning, Features, Types, Stages and Importance.
https://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/sociology/socialisation-the-meaning-features-types-stages-and-importance/8529
Sicat, C. (2020). UCSP Module 5 Socialization Understanding Culture Society and Politics [Youtube Video]. https://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=kOlBN0Ef0tA
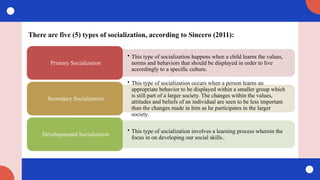
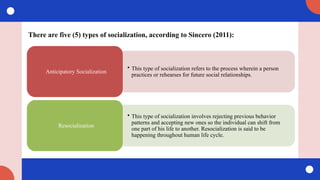
Sincero, S. M. (2011). Socialization. Explorable. https://explorable.com/socialization#:~:text=Types%20of%20Socialization,%2C
%20developmental%2C%20anticipatory%20and%20resocialization.&text=This%20type%20of%20socialization%20happens,accordingly
%20to%20a%20specific%20culture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module5-contextcontentprocessesandconsequencesofsocialization-240901085015-403360b4/85/Module-5-Context_-Content-Processes-and-Consequences-of-Socialization-pptx-32-320.jpg)