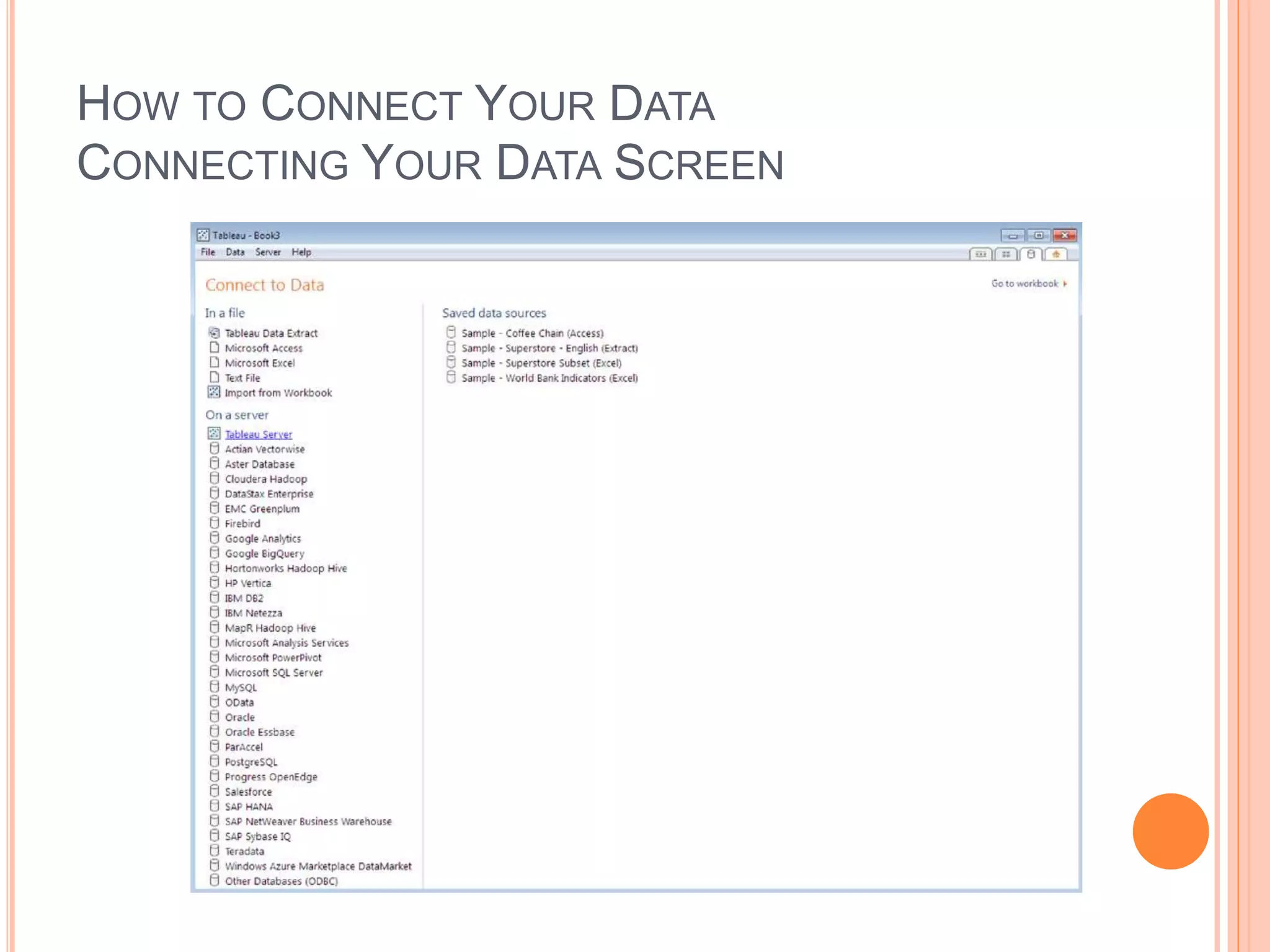
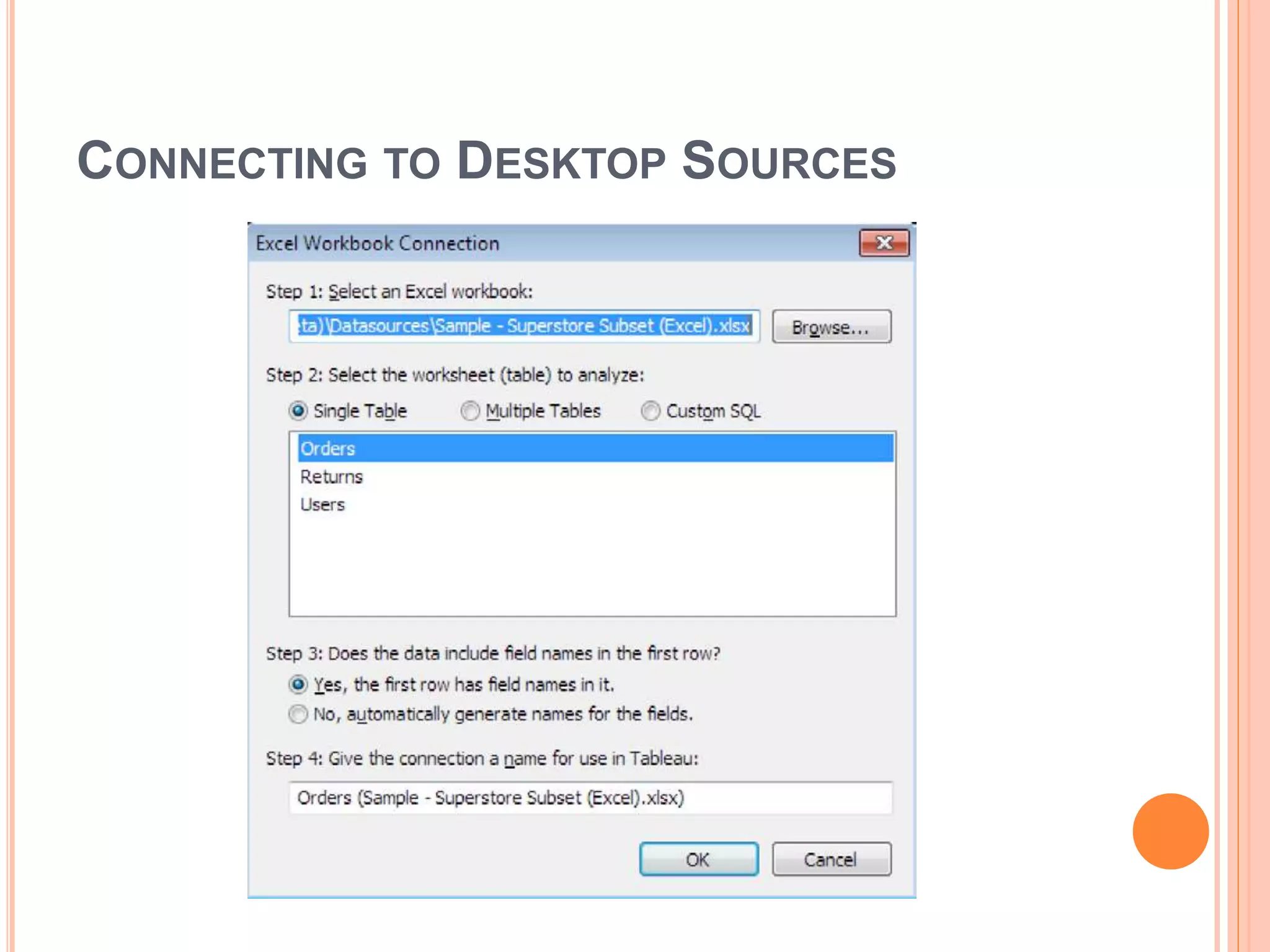
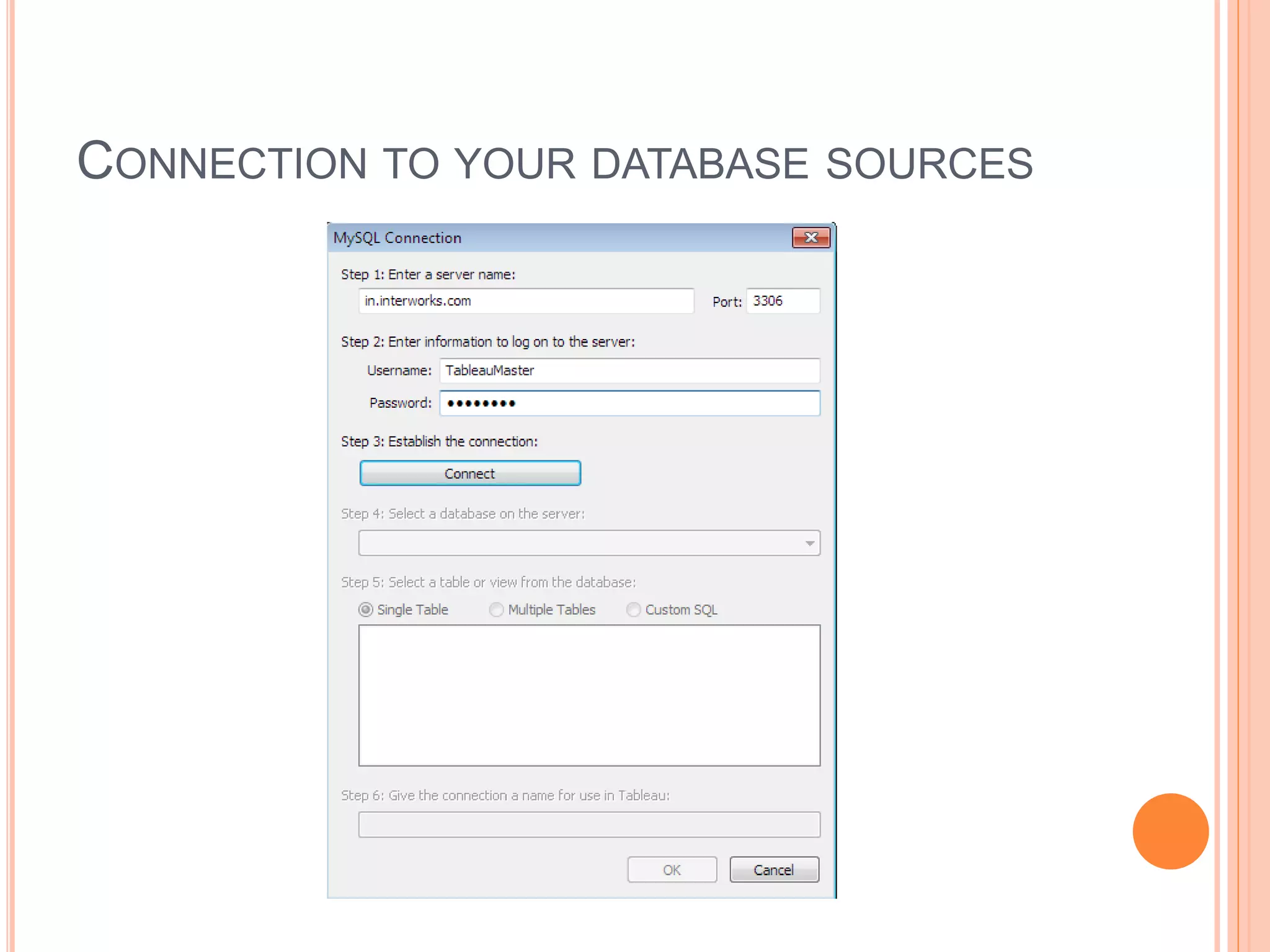
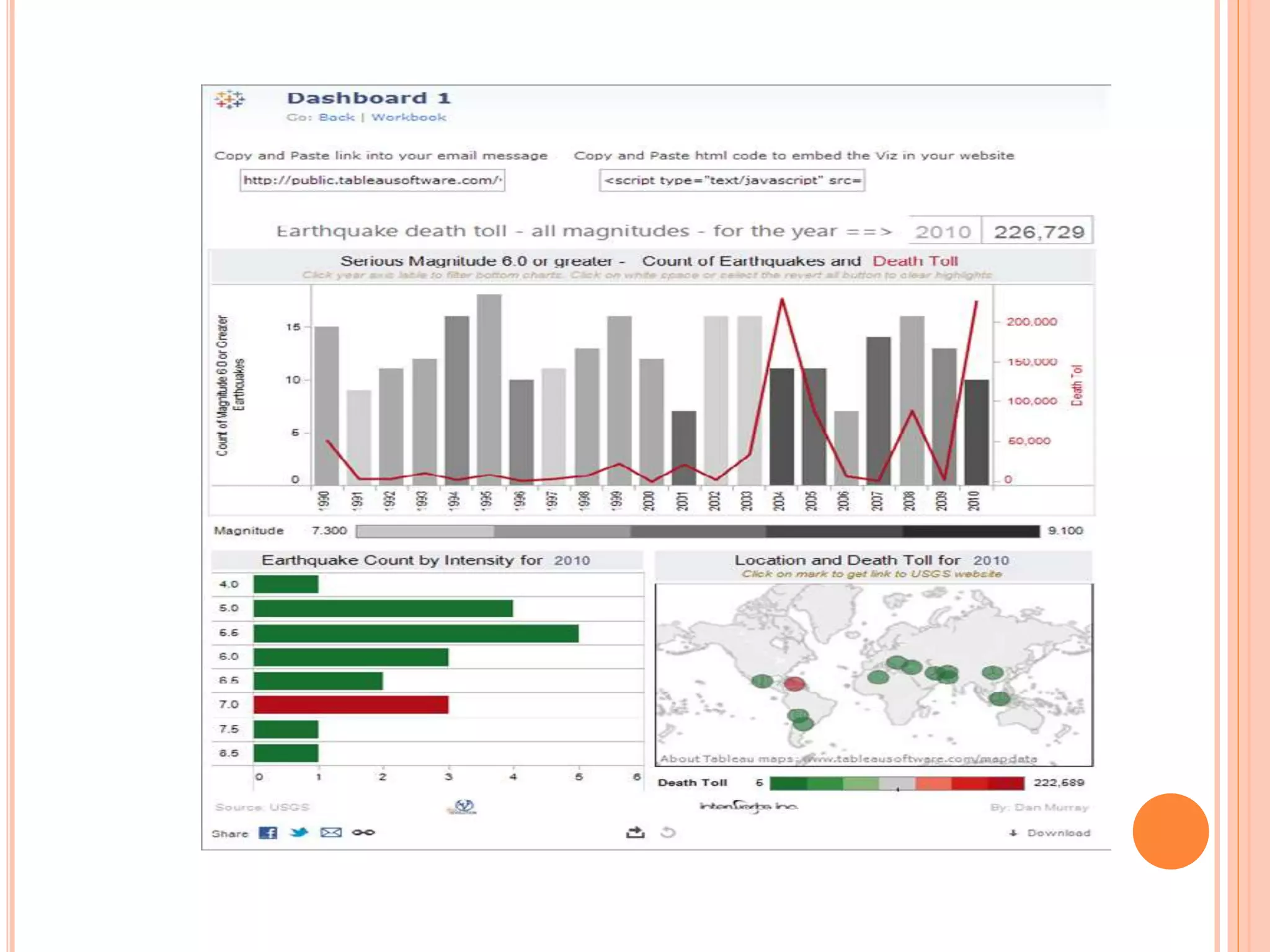
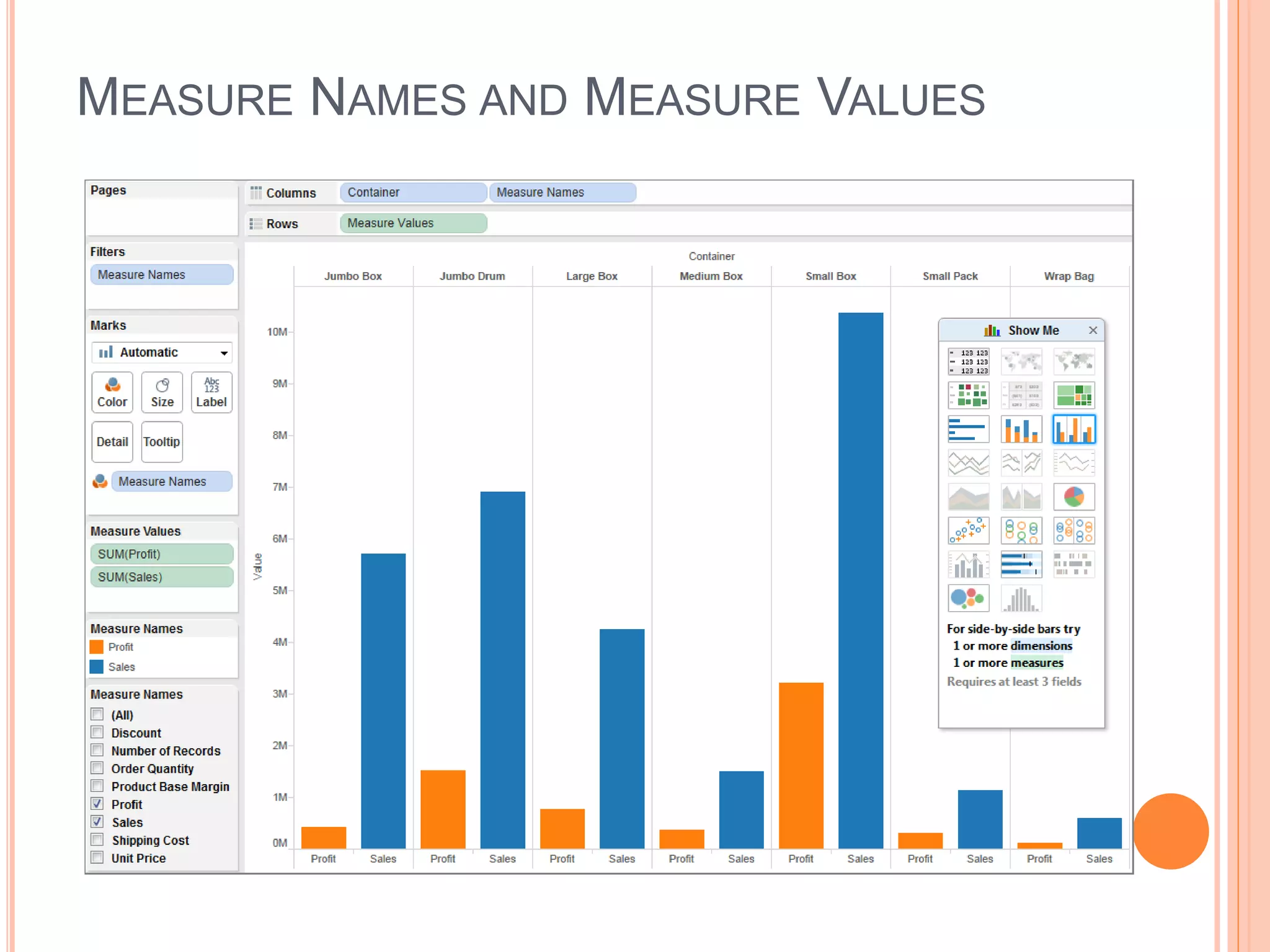
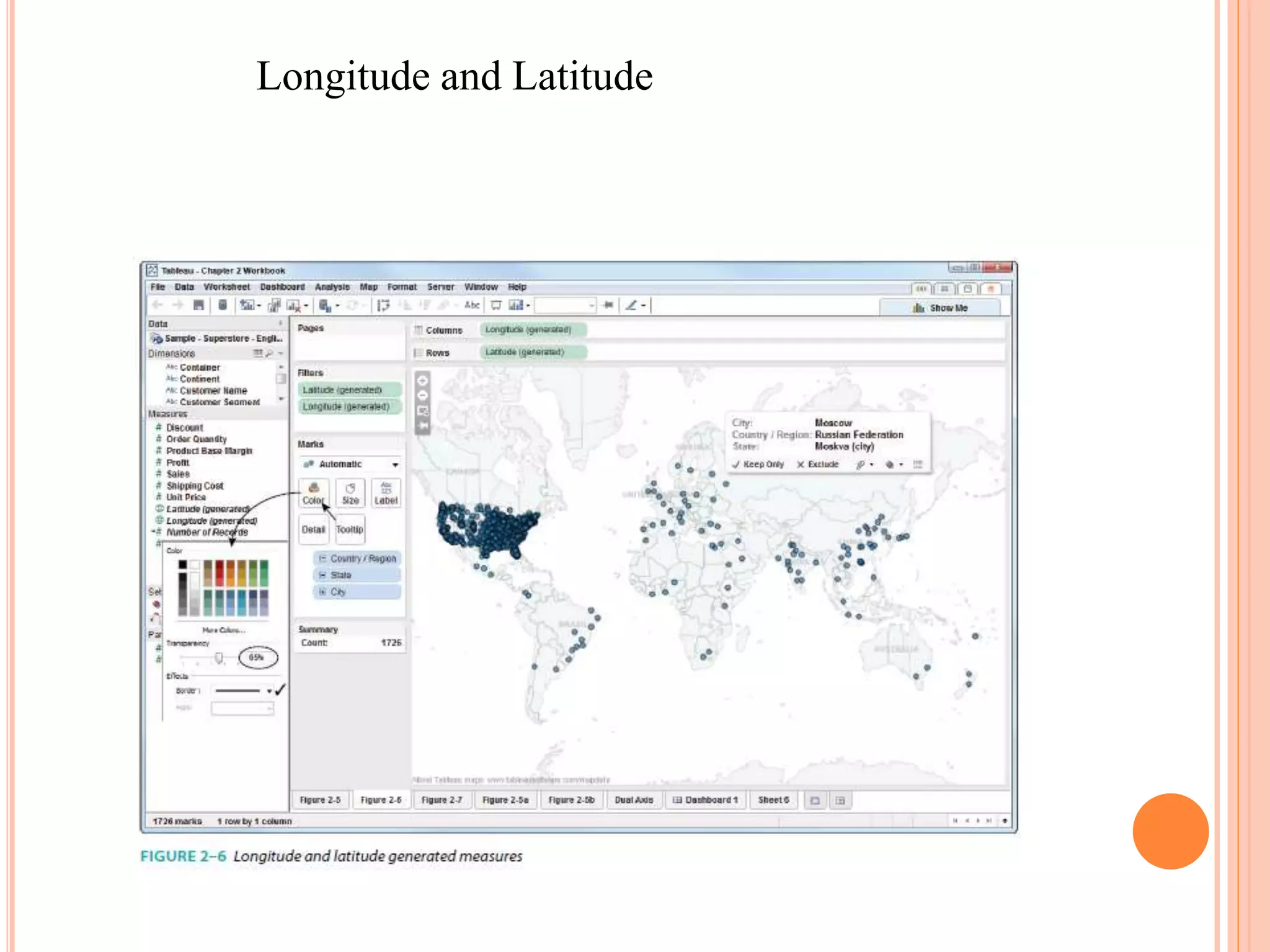
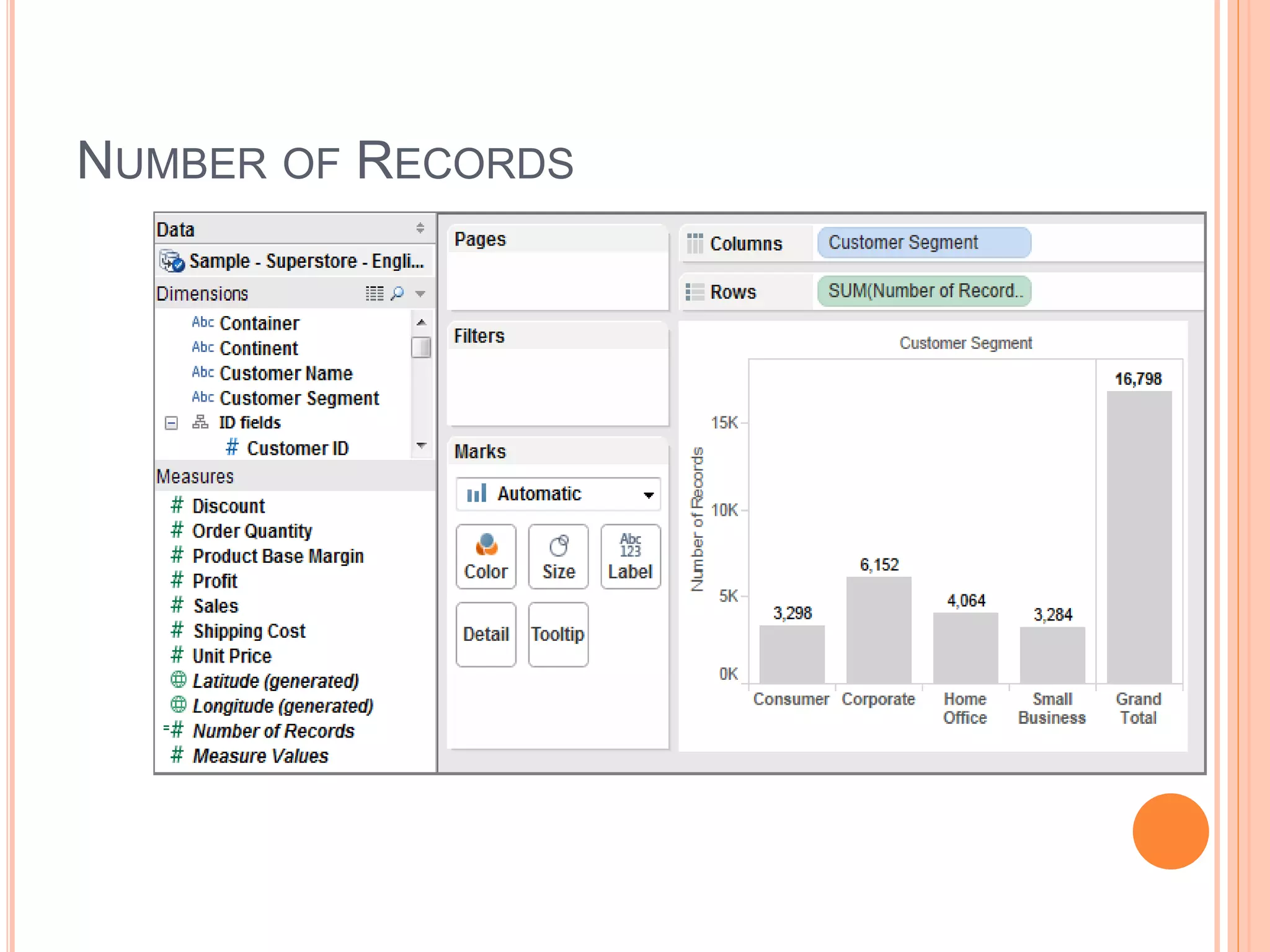
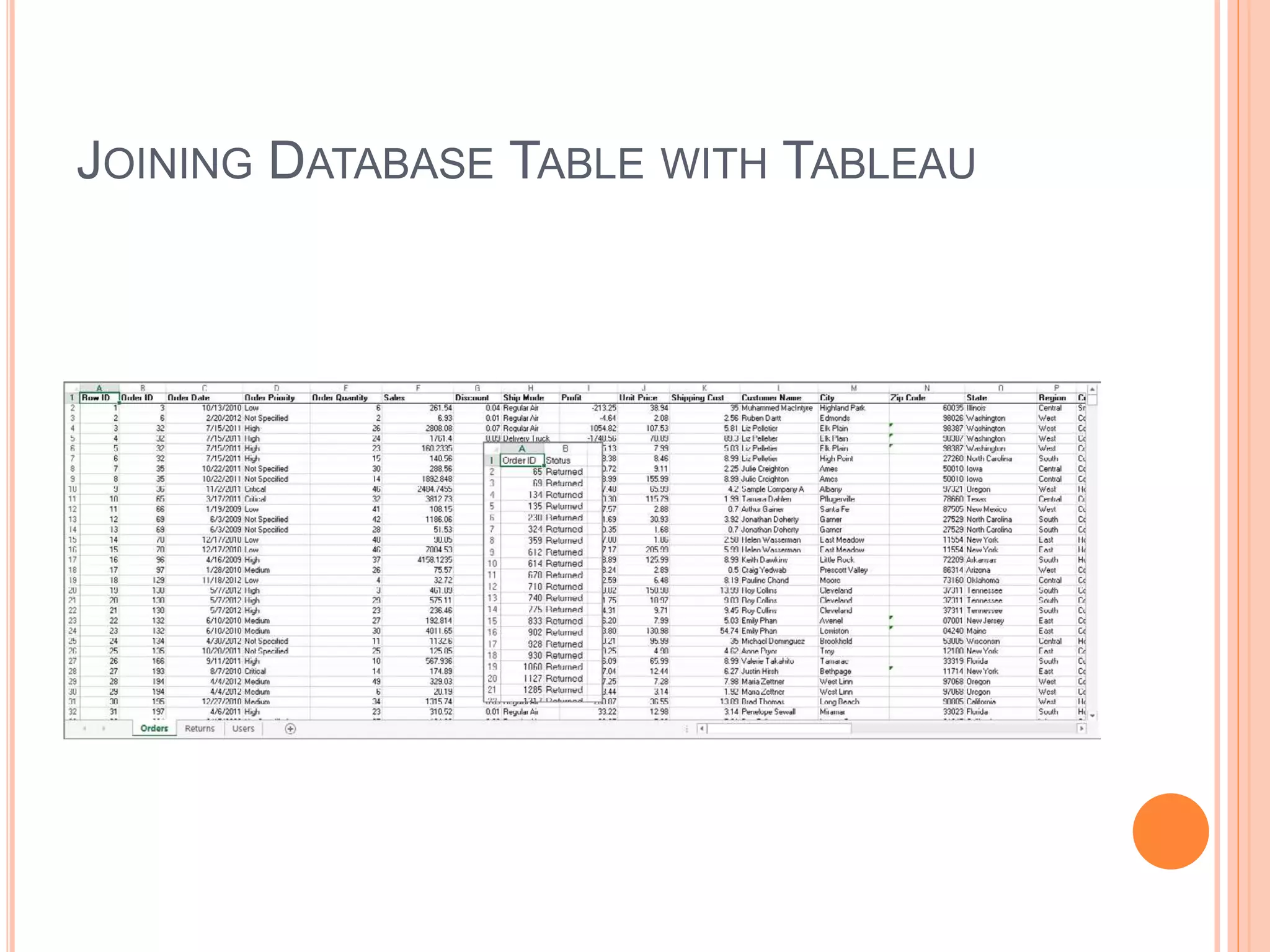
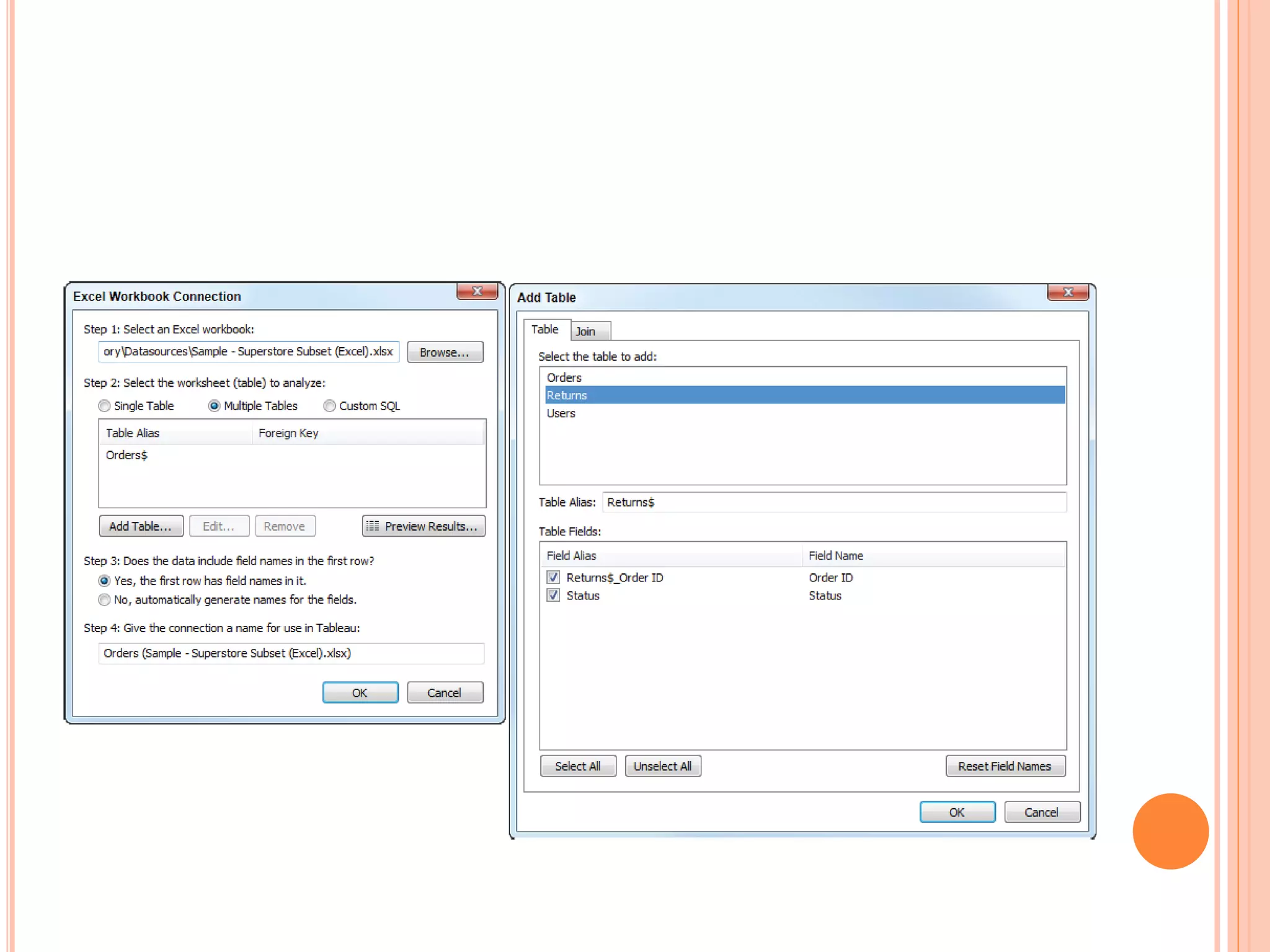
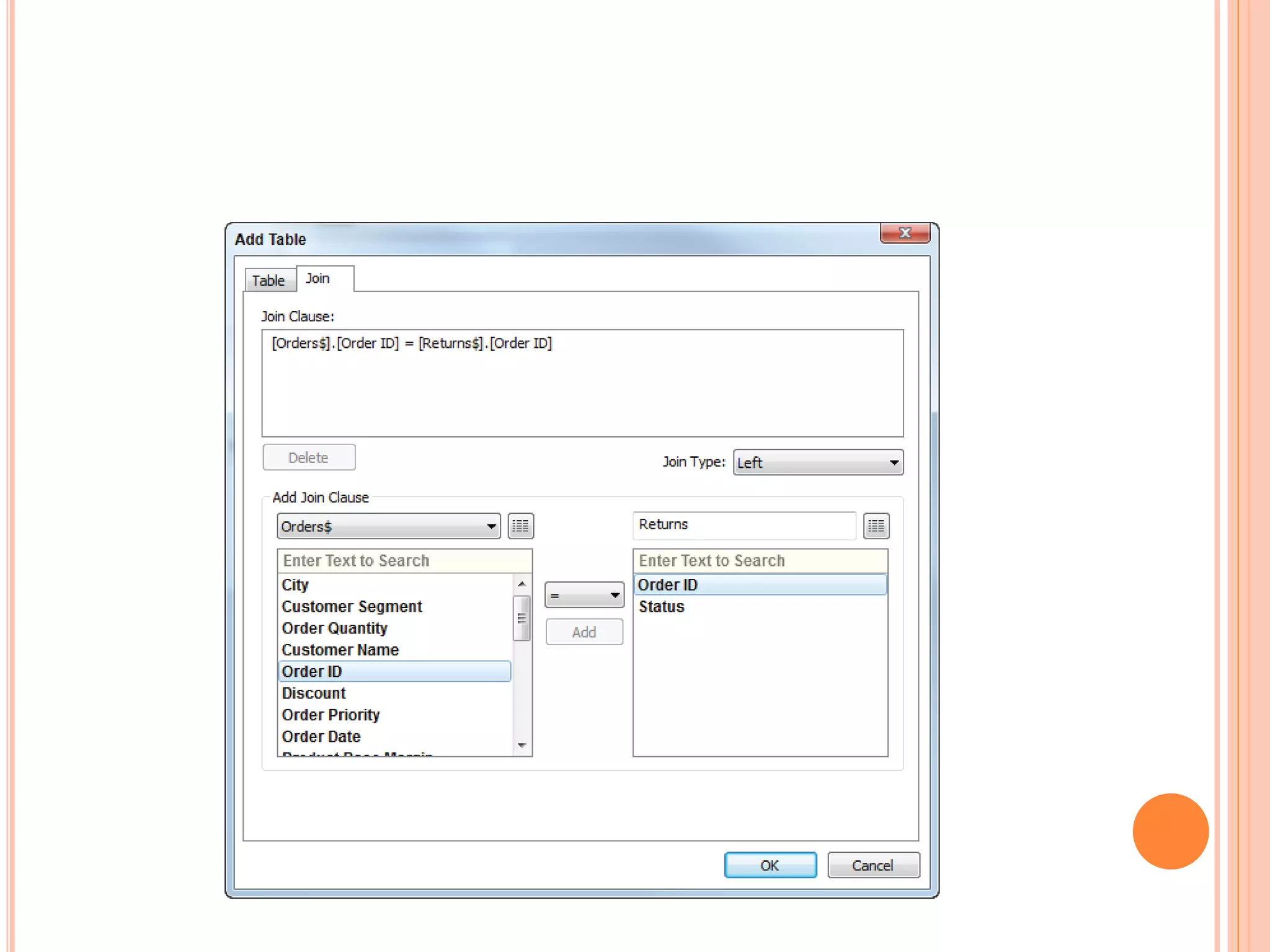
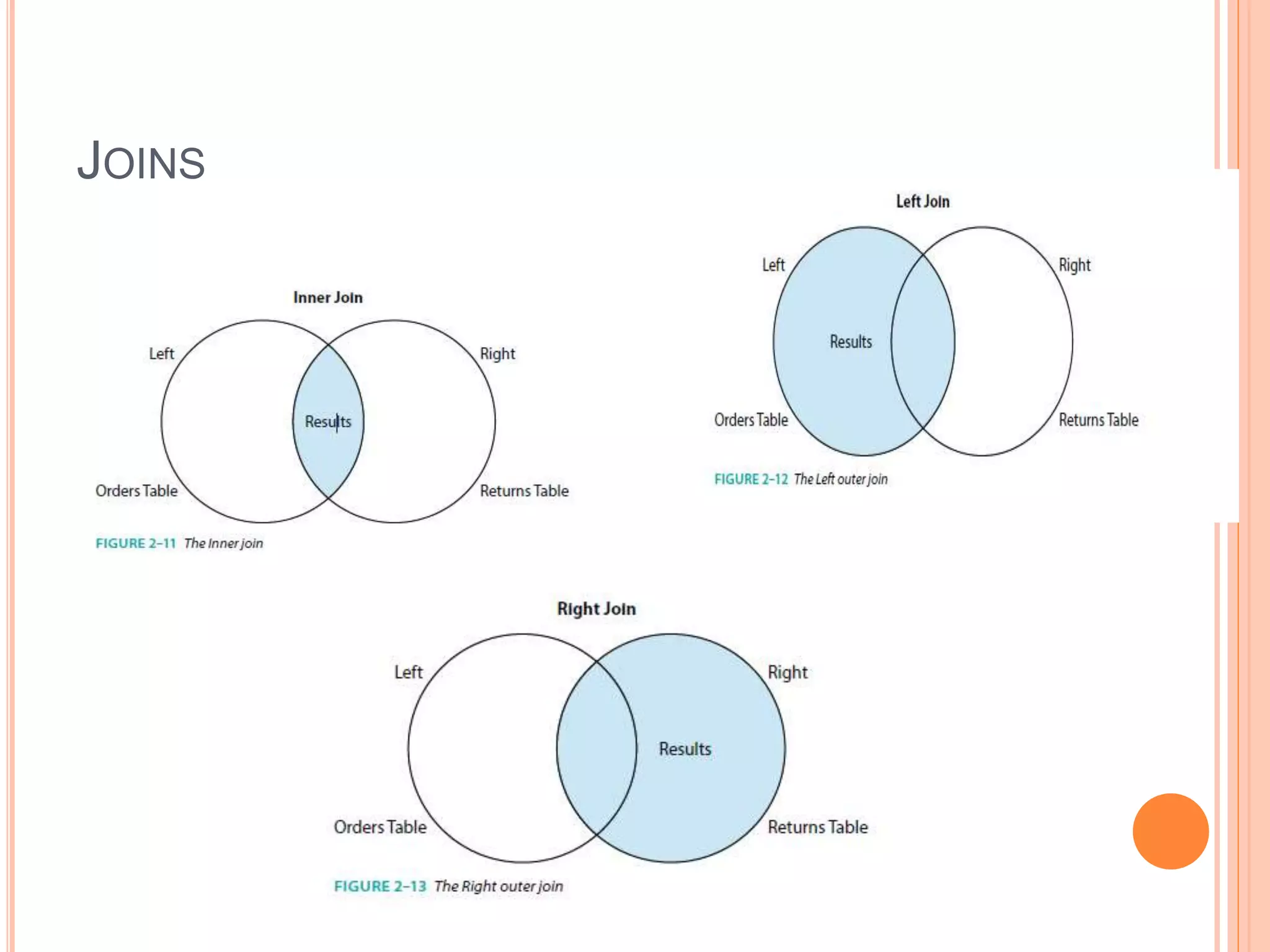
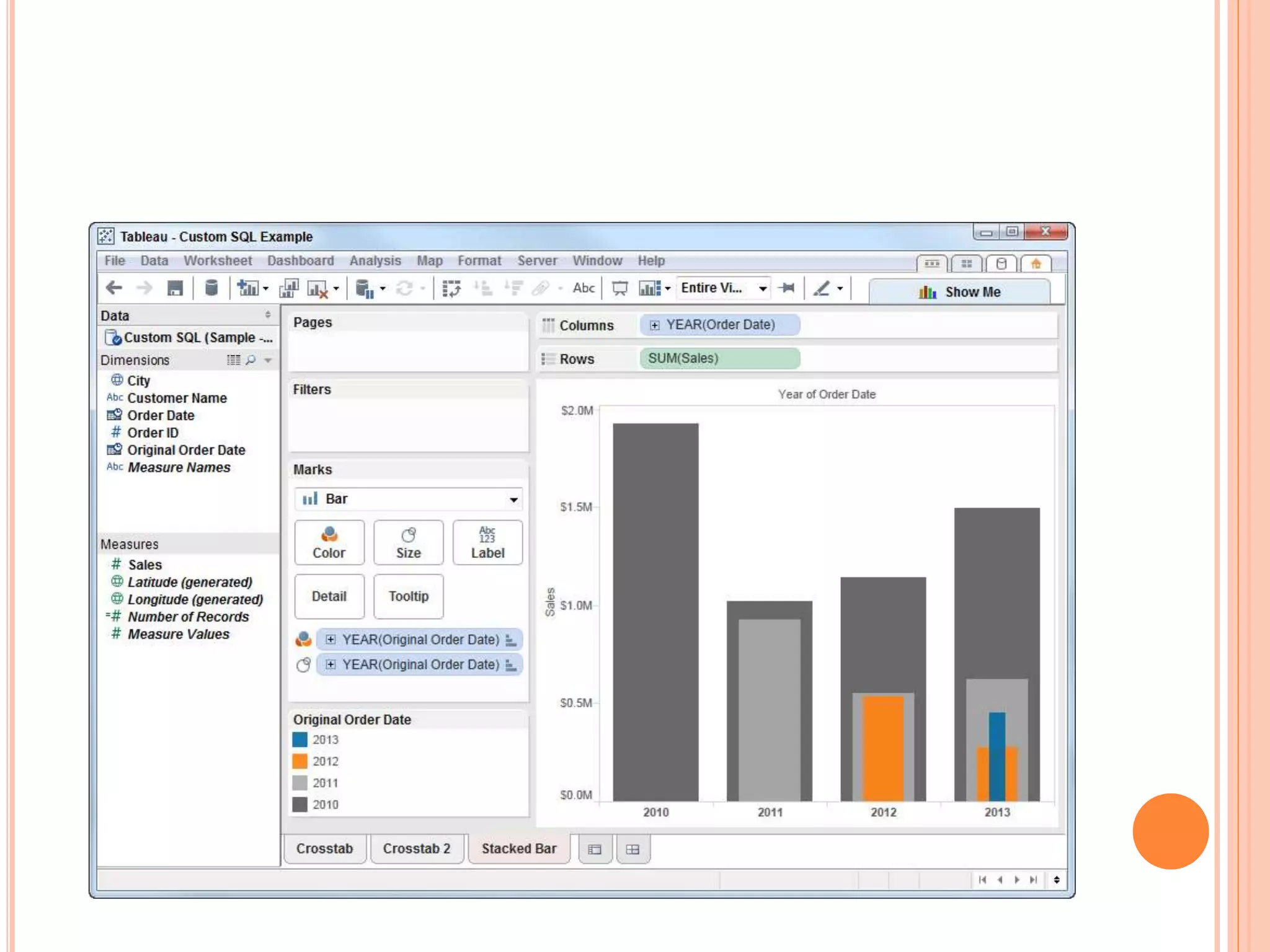
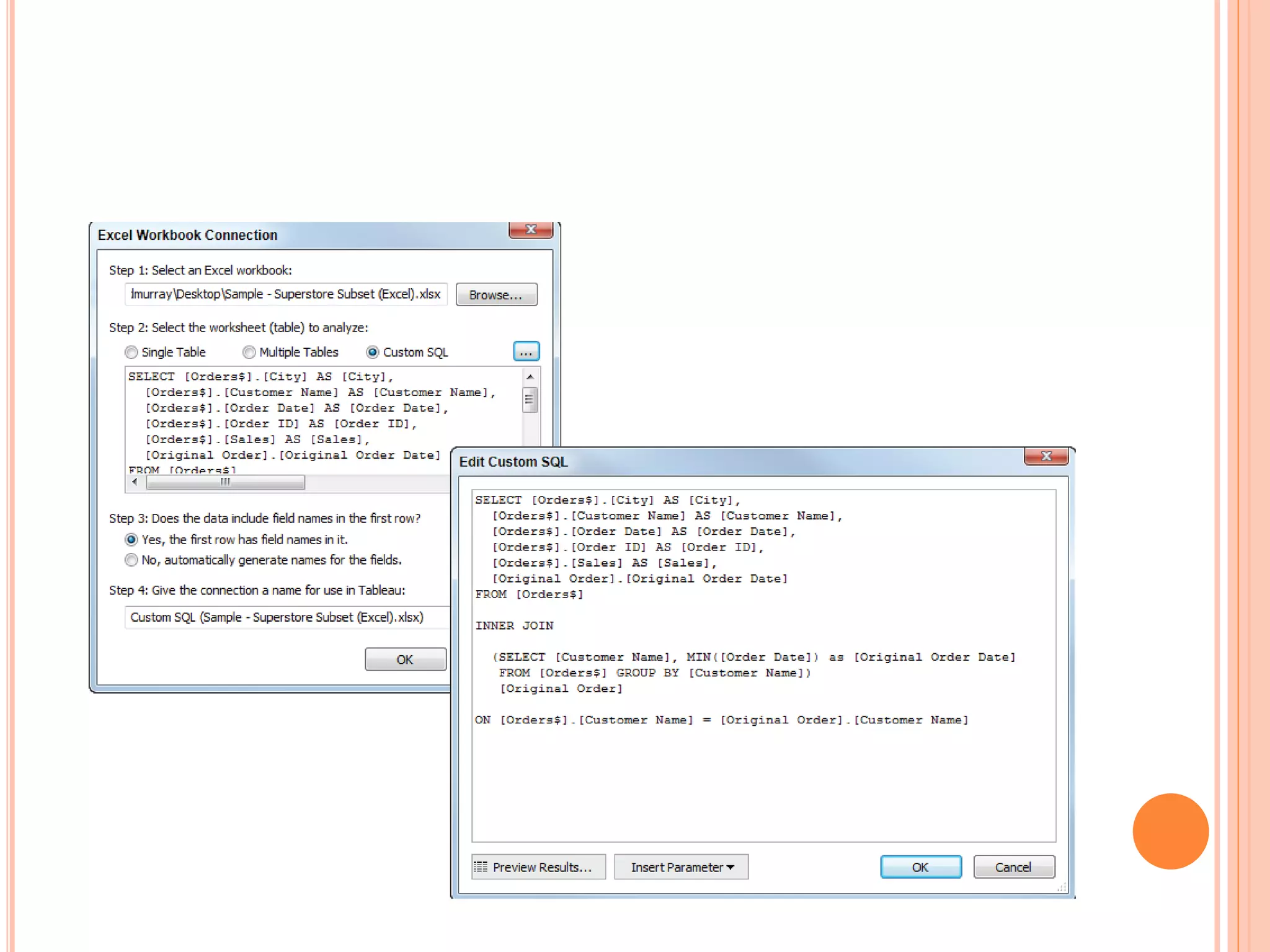
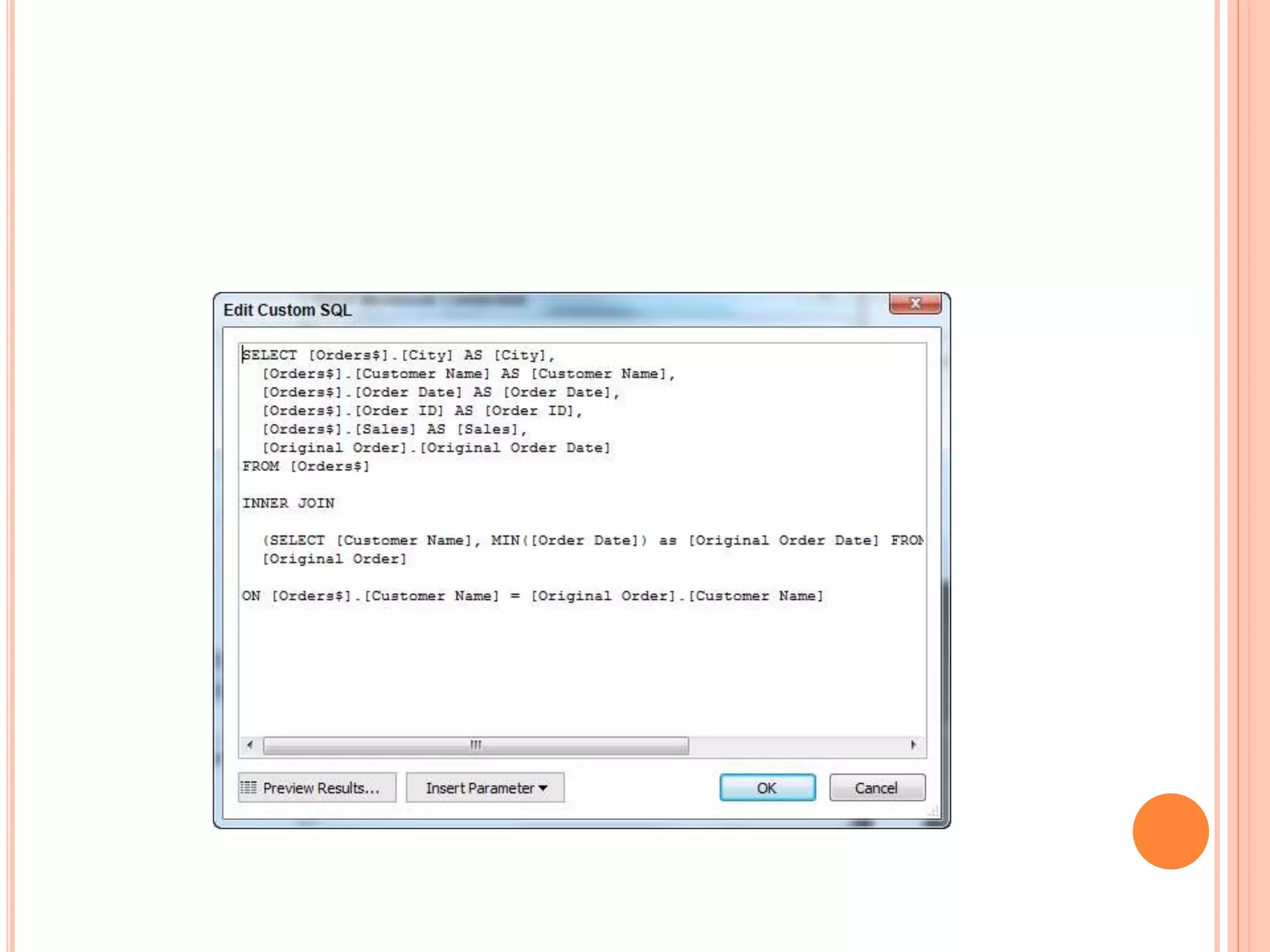
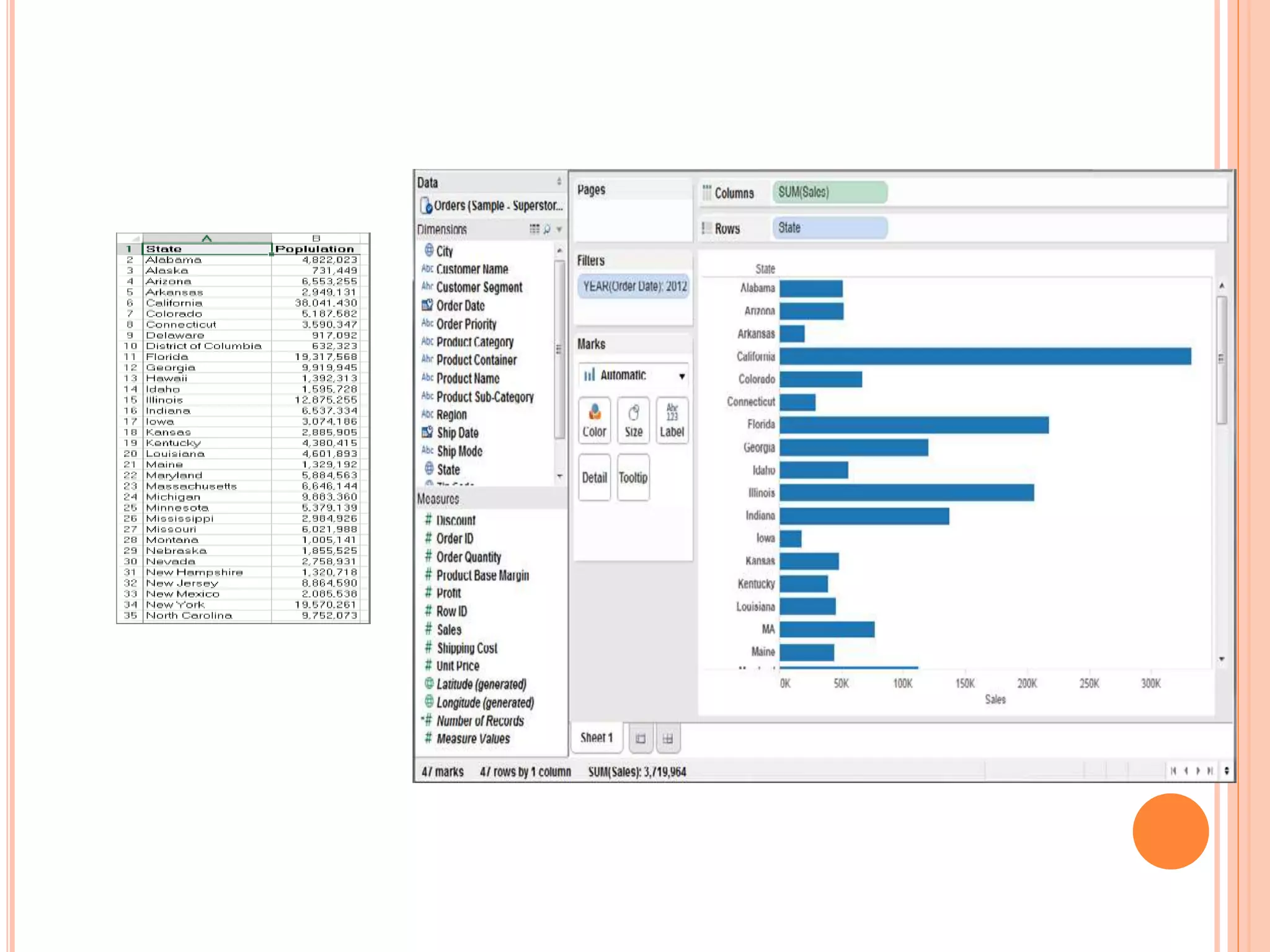
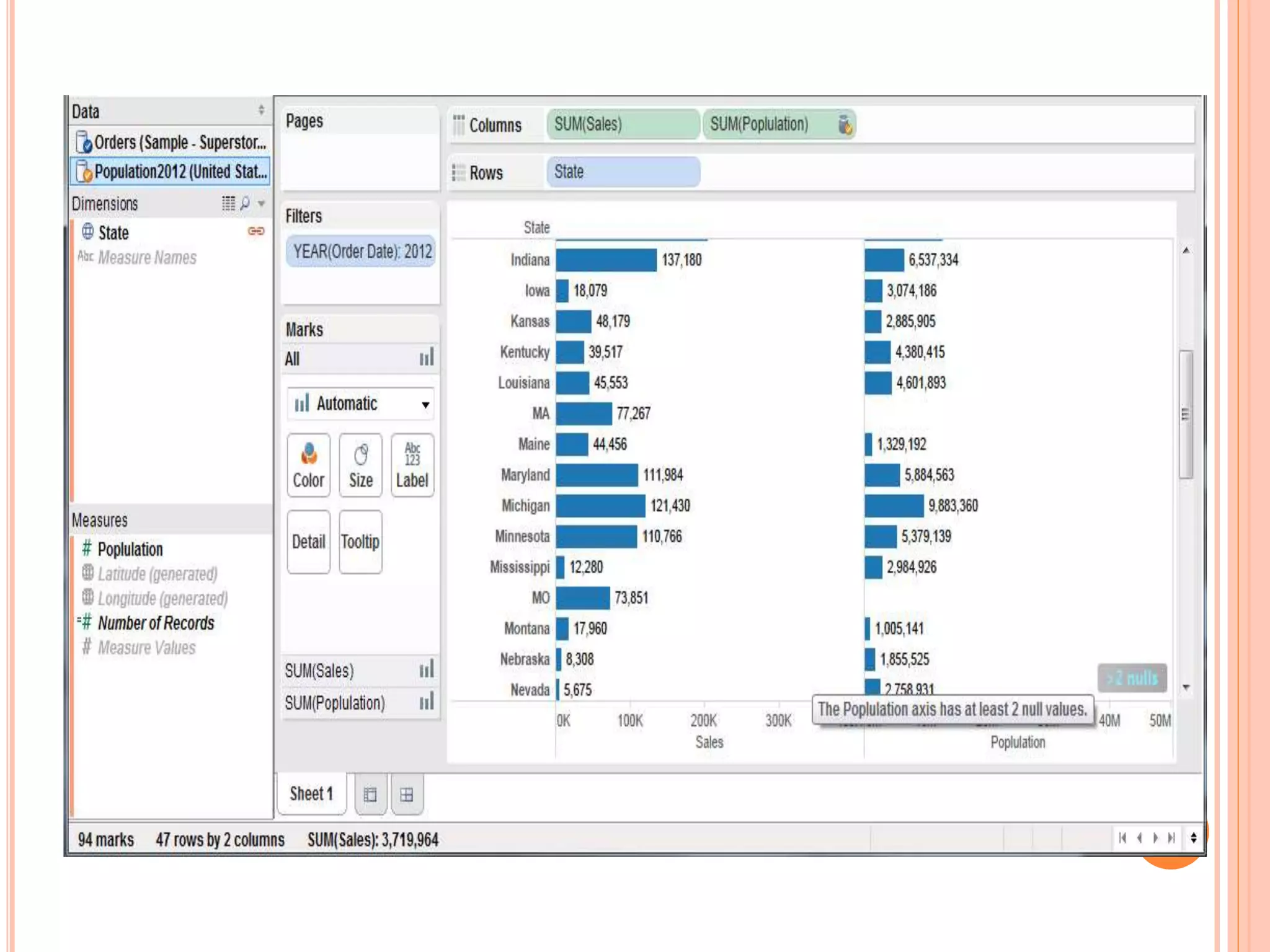
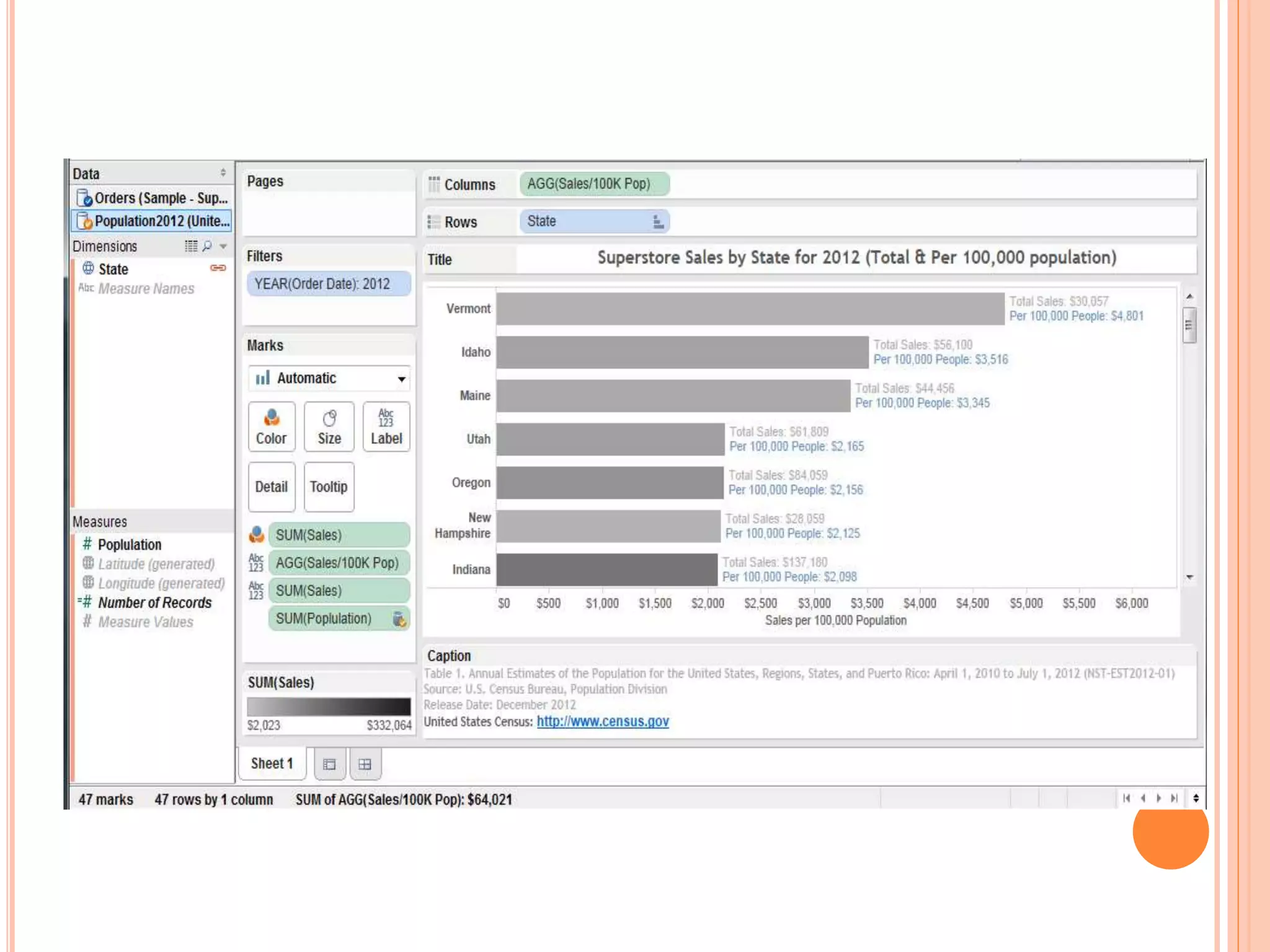
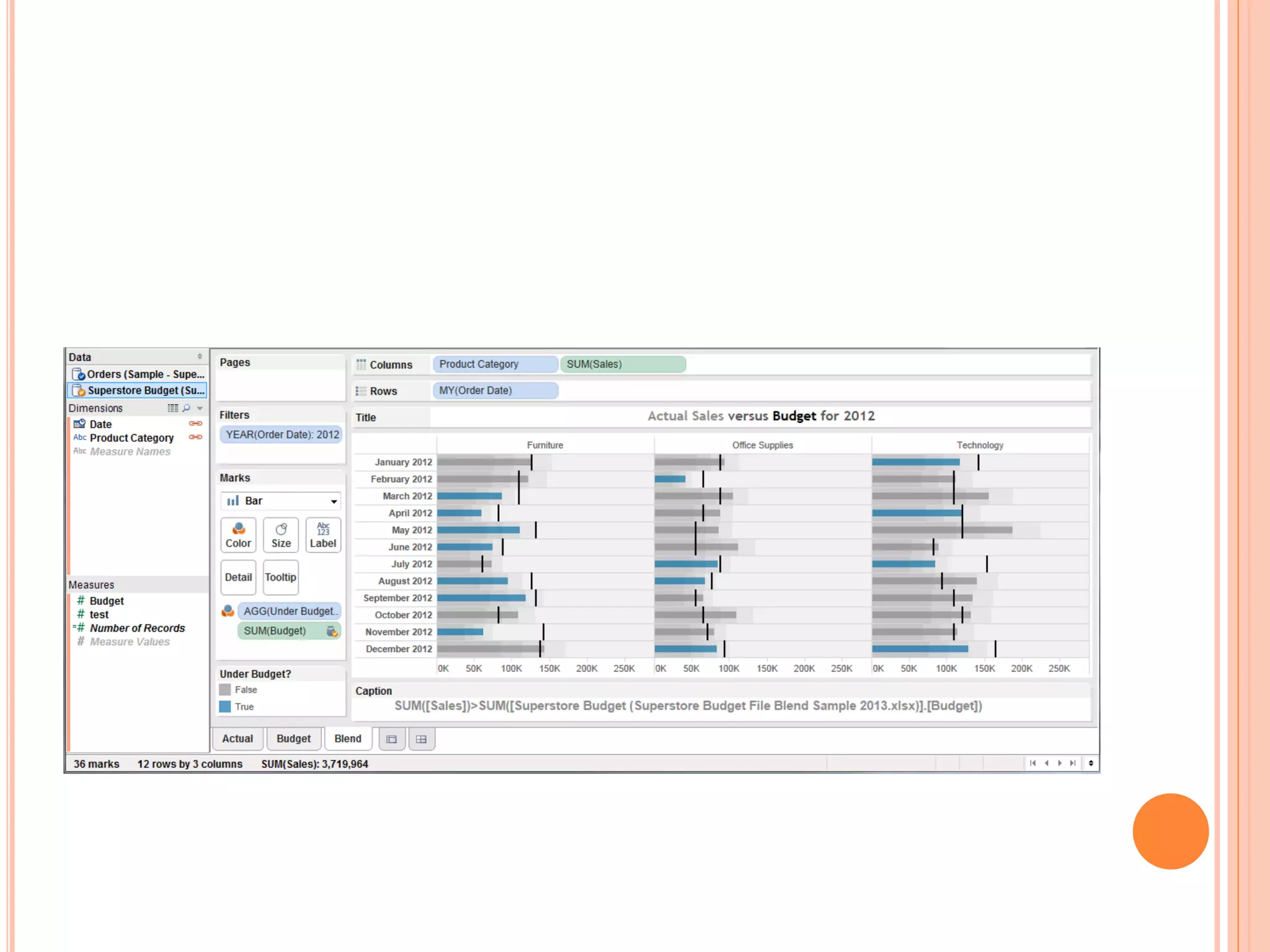
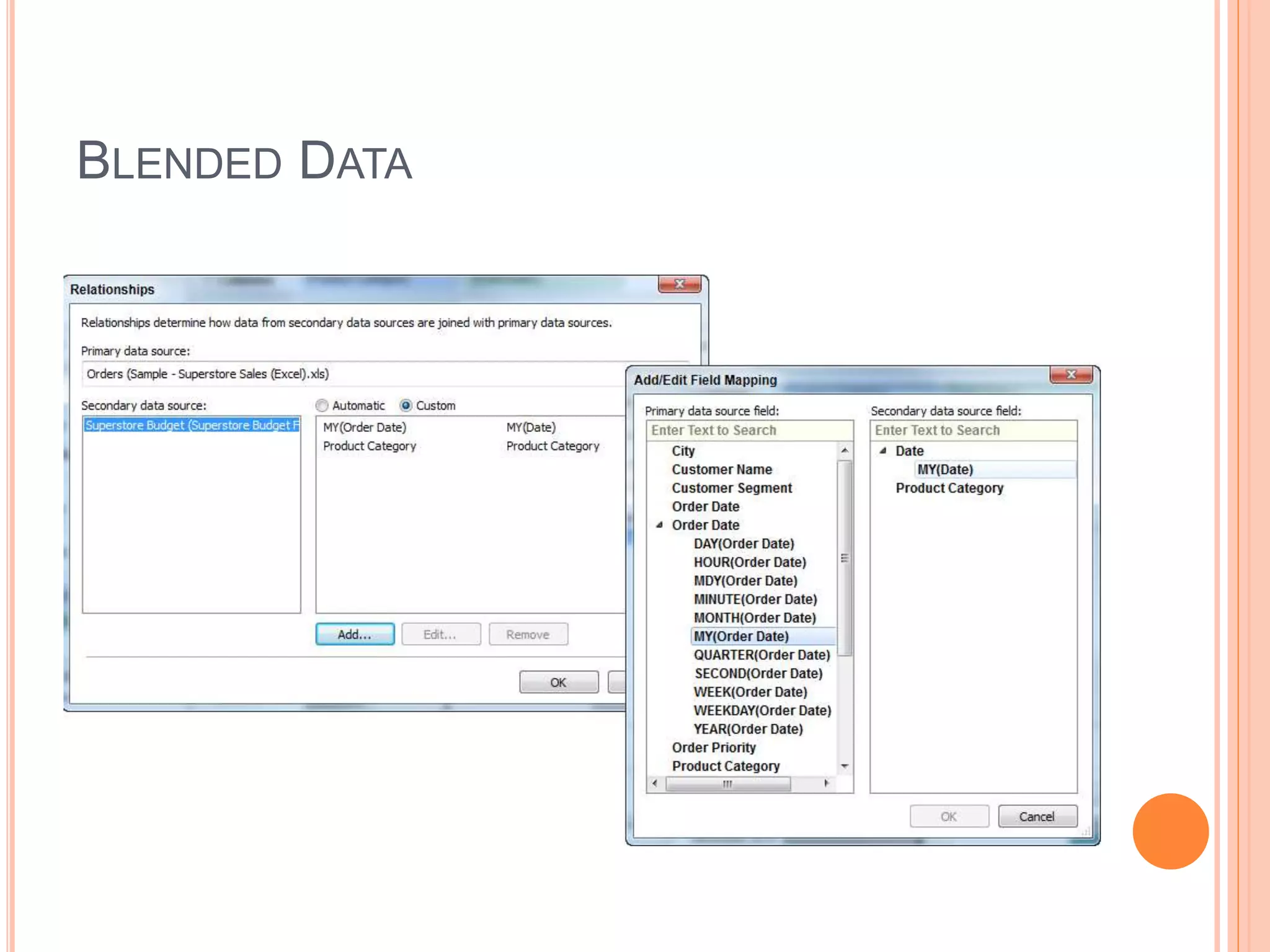
This document discusses data visualization in Tableau. It covers how to connect to different data sources like databases, files, and public data. It describes generated fields, data extracts, and how to join and blend multiple data sources. The document also discusses factors that affect data connection speed and how to deal with common data quality issues like renaming fields, grouping values, handling nulls, and geographic errors.