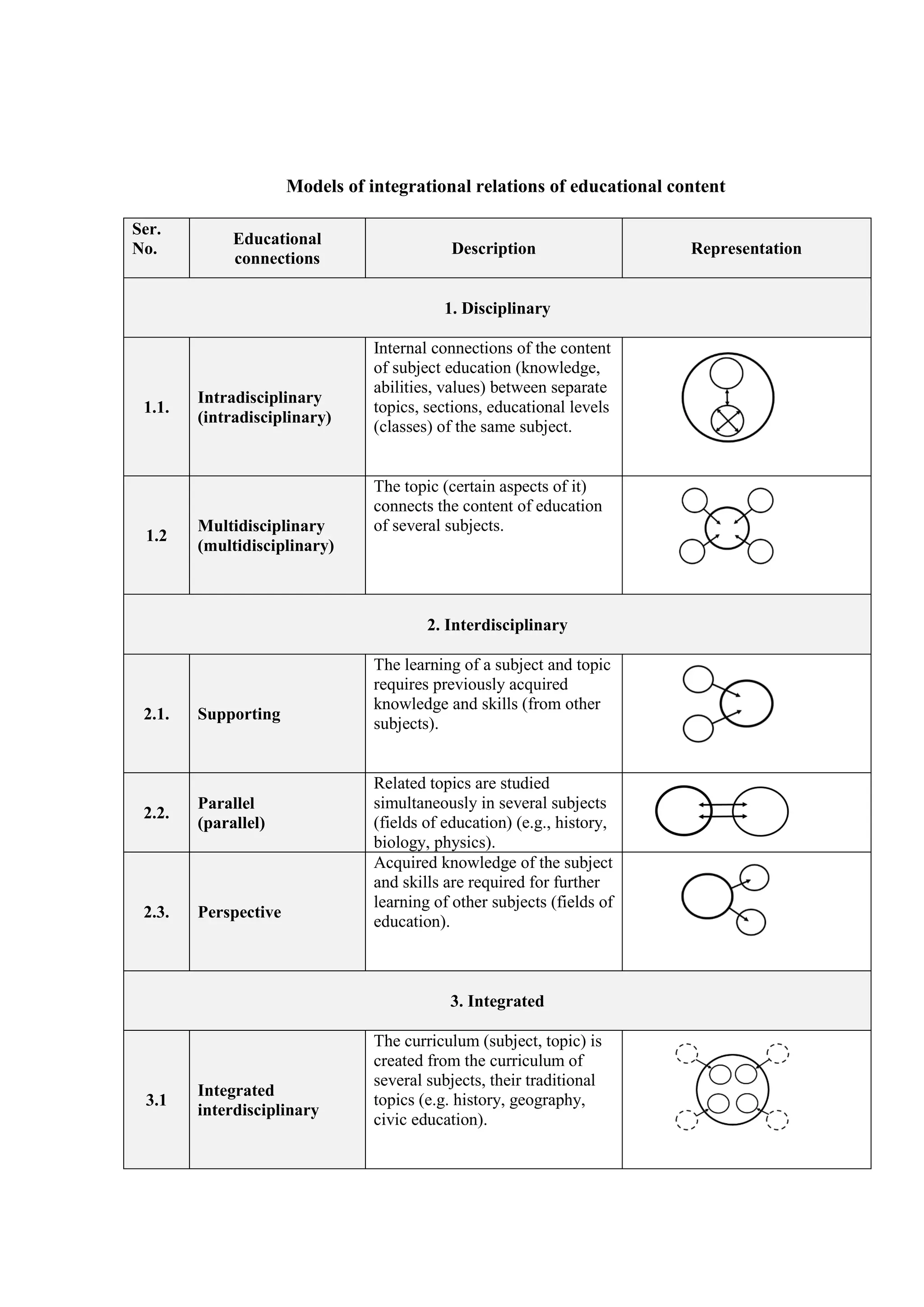
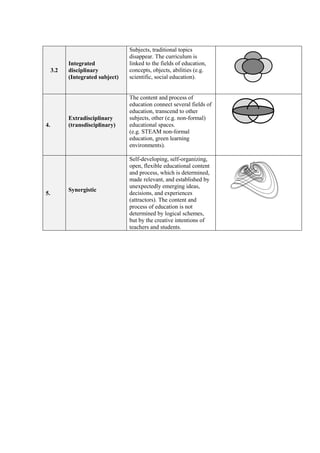
This document outlines 5 models of integrational relations in educational content:
1. Disciplinary models include intradisciplinary connections within a subject and multidisciplinary connections between topics across subjects.
2. Interdisciplinary models involve supporting knowledge from other subjects, parallel study of related topics, and applying knowledge from one subject to another.
3. Integrated models combine curricula from multiple subjects or do away with traditional subjects altogether.
4. Extradisciplinary models connect fields of education and transcend subjects into other learning spaces like STEAM or green environments.
5. Synergistic models are self-developing, open processes determined by emerging ideas rather than logical schemes.