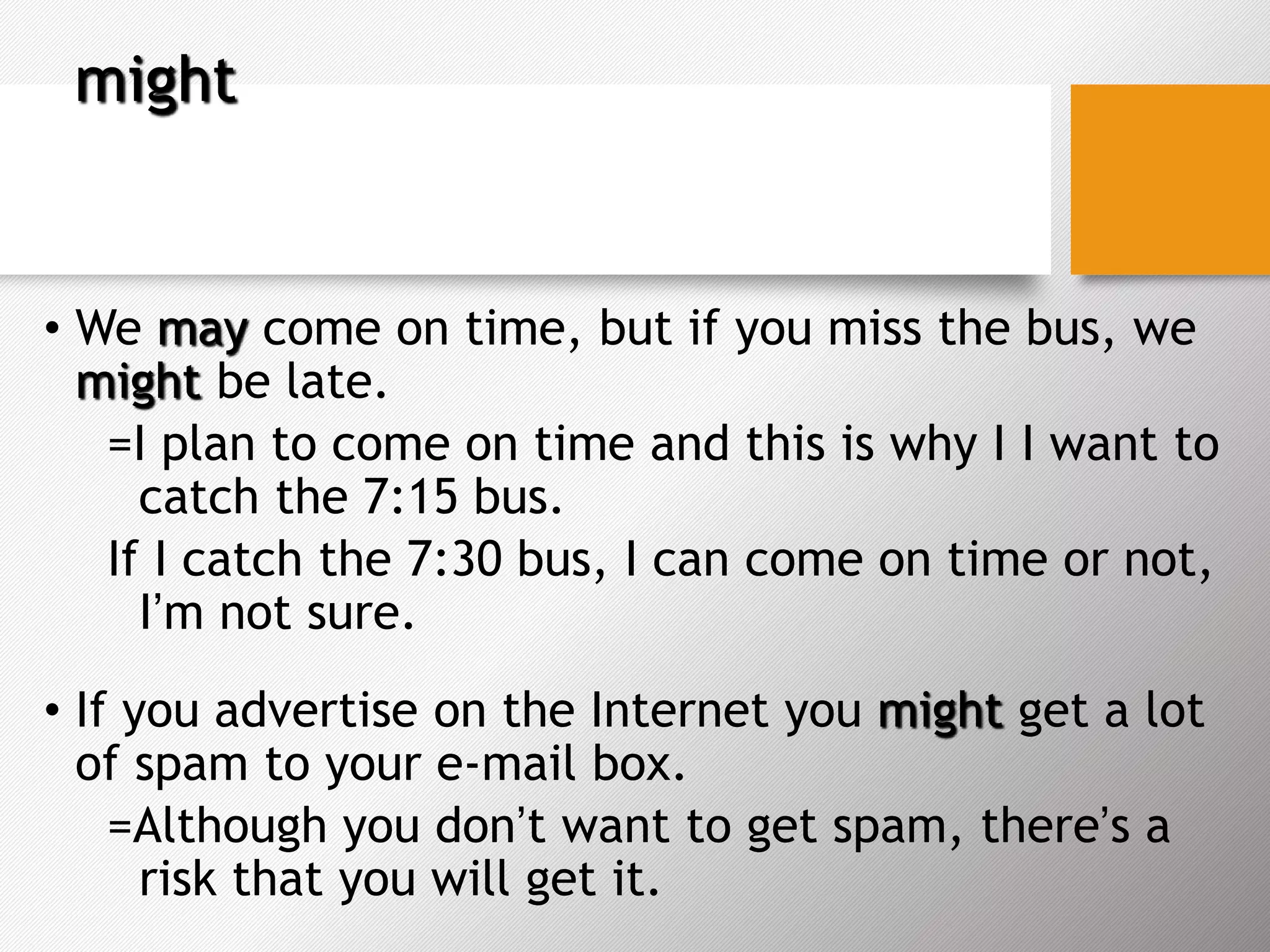
Modal verbs are used to express abilities, possibilities, permissions, obligations, and other auxiliary meanings. They behave differently than normal verbs in that they are always followed by a base verb form and do not take an 's' in the third person present simple. Different modal verbs express different meanings, such as can/could for ability, may for permission or possibility, might for lesser possibility, should for advice or suggestion, must for strong obligation, and mustn't for prohibition. Their meanings and substitutes, like will for future certainty, are important to understand as modal verbs cannot be used in all tenses.