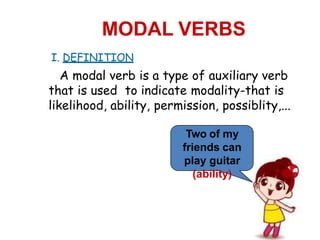
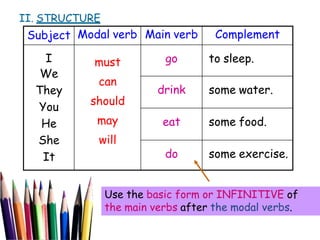
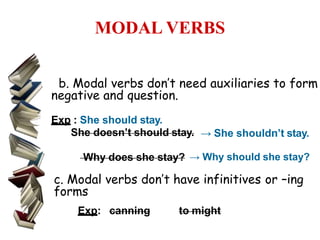
The document defines modal verbs as auxiliary verbs that indicate modality or likelihood, ability, permission, or possibility. It provides a list of common modal verbs such as can, could, may, might, will, would, shall, should, ought to, and must. The document discusses the structure of modal verbs, stating that they do not add 's' or 'es' in third person singular and do not require auxiliaries to form negatives or questions. It also notes that modal verbs do not have infinitives or '-ing' forms. Various uses of specific modal verbs are described through examples, such as using 'can' to express ability or permission and 'should' to say what is right or correct.