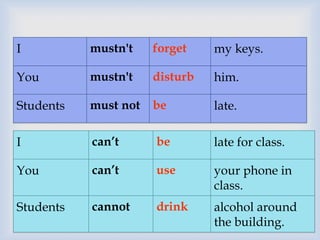
Modal verbs like may, might, must, have to, and can are used to modify other verbs to express meanings like possibility, obligation, permission, and prohibition. May and might are used to talk about possible future actions and can take negative forms with "not". May is also used to ask for or give permission. Have to expresses obligation, while must refers to duties and rules. Mustn't, can't, and cannot are used to express prohibition. A base verb form follows modal verbs.