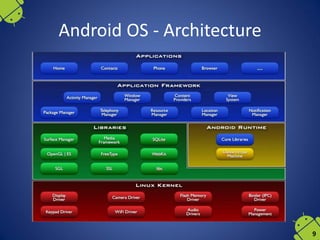
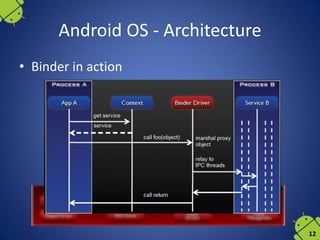
The document outlines the historical development and architecture of mobile operating systems, focusing primarily on Android. It discusses major milestones in mobile technology, from Motorola's first mobile phone in 1973 to the introduction of Android OS in 2008 by Google. The document further details Android's architecture, application development, file systems, and hardware requirements.