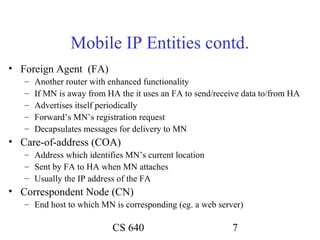
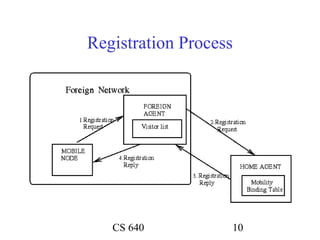
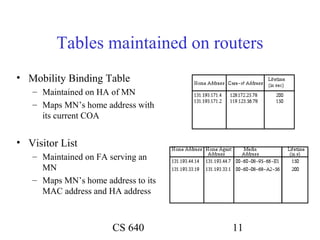
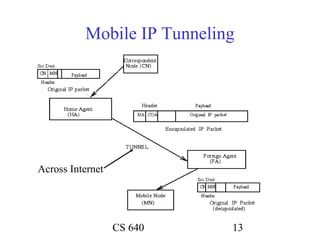
Mobile IP allows mobile nodes to roam between networks while maintaining ongoing connections. It uses home agents, foreign agents, and care-of addresses to transparently route packets to the mobile node's changing locations. When away from its home network, a mobile node registers its current care-of address with its home agent, which then tunnels packets to the mobile node's foreign agent for delivery. This allows the mobile node to maintain its permanent home address no matter where it connects.