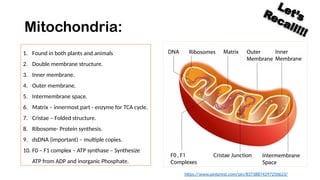
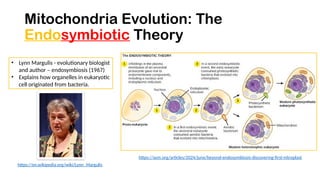
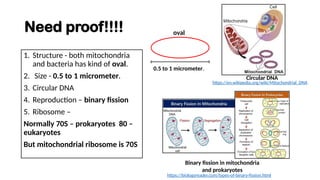
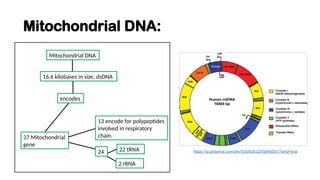
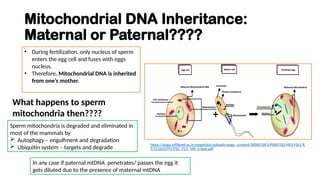
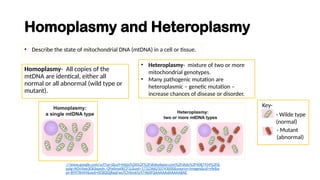
The document discusses mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and its inheritance, highlighting that mtDNA is maternally inherited as paternal mtDNA is degraded during fertilization. It explains the structure and function of mitochondria, the endosymbiotic theory of their evolution, and the high mutation rates associated with mtDNA, which contribute to various mitochondrial diseases. Key diseases mentioned include Leber hereditary optic neuropathy, Kearns-Sayre syndrome, and MELAS, emphasizing the clinical implications of mtDNA mutations.