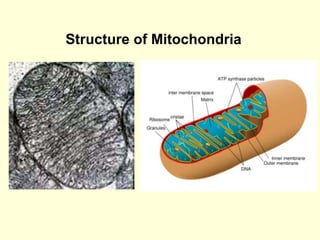
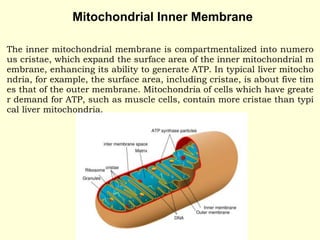
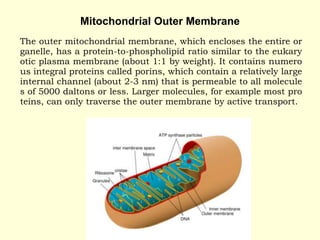
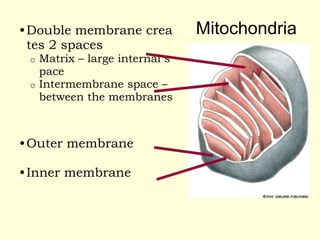
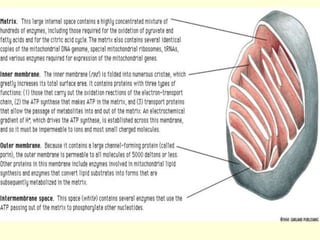
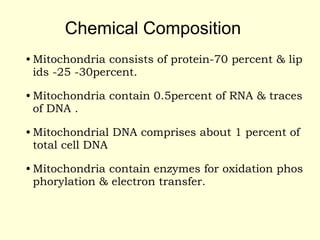
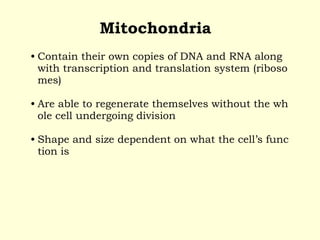
Mitochondria are double-membrane organelles found in eukaryotic cells that generate most of a cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through oxidative phosphorylation. The inner mitochondrial membrane is highly folded into cristae which contain the enzymes and transport chains that generate ATP from nutrients, while the outer membrane encloses the entire organelle and is more permeable. Mitochondria contain their own DNA and can replicate independently of the cell, playing a key role in cellular energy production.