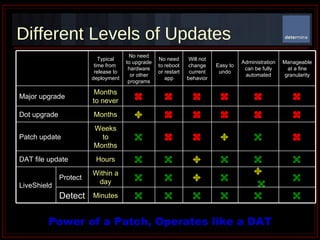
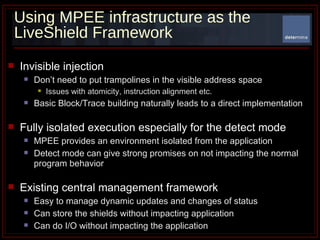
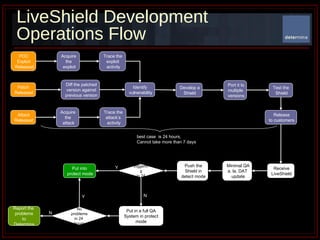
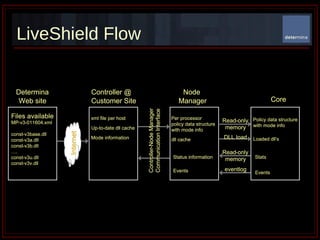
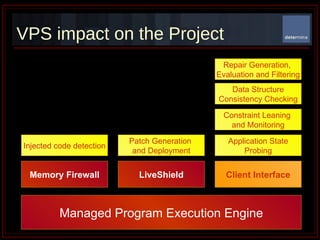
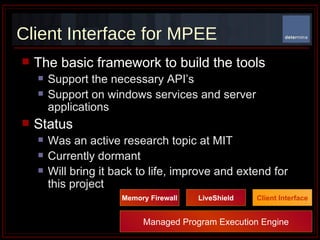
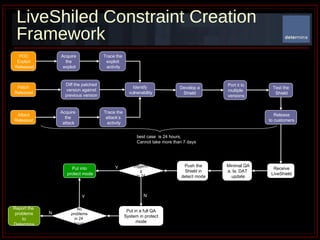
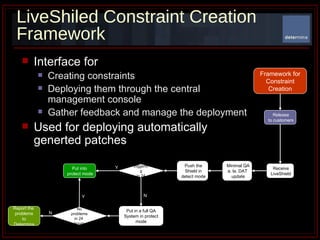
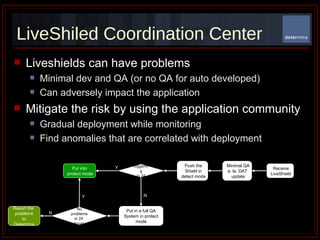
The document summarizes Determina's Vulnerability Protection Suite, which uses patented technology to stop both known and unknown (zero-day) attacks without needing updates, signatures, or behavior modeling. It focuses on vulnerability prevention rather than attack detection. The core technologies include the Managed Program Execution Engine, Memory Firewall, and LiveShield, which provide zero-day endpoint protection.









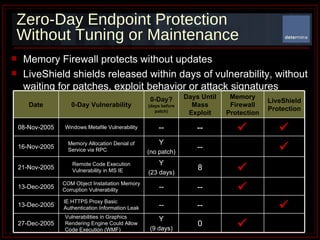






![An Example: Chained Call Attack Local Variables: URL Local Variables: tmp Return Address Argument: h Local Variables: … Return Address Arguments: … Stack http://001110110110111011010001010110101101010110 10110110110110101011010101010110101011010101... URL: 0x7F8B0 Fake arguments handle_URL(handle * h) { char url[64]; … char * tmp =geturl(h) strcpy(url, tmp); … } Code 0x8A234 Fake arguments Libraries setuid() … unlink() … 0x7F8B0 0x8A234](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mit6determinavpsppt2571/85/MIT-6-determina-vps-ppt-20-320.jpg)