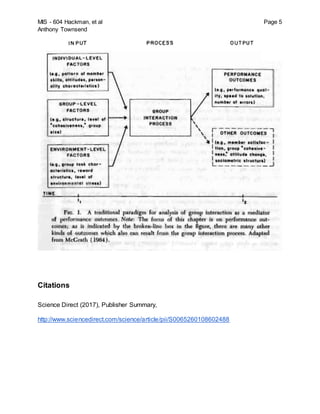
This study examines the relationship between group interaction processes and task performance effectiveness. The researchers analyzed how process variables like agreeing, optimism, and giving opinions correlated with outcomes for an unstructured case study task and a structured ranking task. For the unstructured task, they found positive relationships between several process and output variables. The structured task results showed task products were positively associated with messages of positive regard and requests for opinions, and negatively associated with personally disconfirmatory messages. The researchers conclude that examining group communication processes could help identify impediments and lead to performance improvements by altering inputs and influencing the group interaction process.