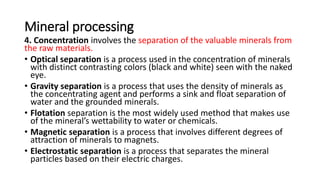
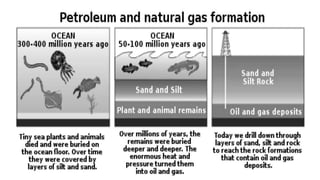
Ore minerals are found through geological studies and testing of soil and rocks. They are mined through surface or underground mining methods then processed. Processing involves sampling, analysis, crushing, separating minerals from waste through techniques like gravity or magnetic separation, and dewatering the concentrates. Fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas were formed from the remains of ancient organisms buried underground. Coal formed from decayed plants, while oil and gas formed from marine organisms. They are non-renewable and contribute to environmental issues when burned.