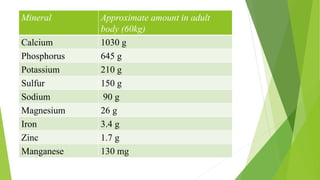
This document discusses minerals in the human body. It notes that minerals are inorganic substances found in all body tissues and fluids, and serve important functions. The major minerals found in the body are calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, sodium, chloride and magnesium, comprising 90% of total mineral content. Minerals are absorbed from foods and their levels regulated by hormones and excretion to maintain dynamic equilibrium. The document lists the approximate amounts of various minerals in the adult body and their general functions.