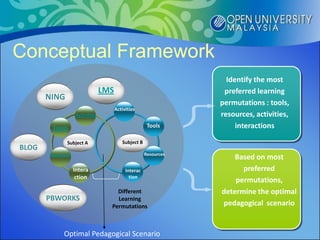
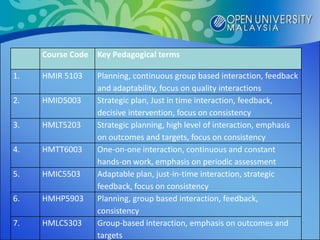
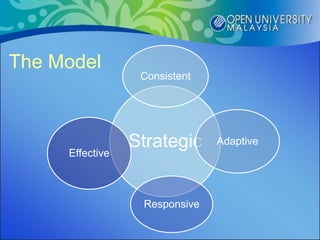
The document proposes the S-CARE pedagogical model for online teaching and learning. It conducted research to understand different pedagogical scenarios used by facilitators and factors preferred by students. The research found that planning, interaction, feedback and resources were important aspects. From these findings, the S-CARE model is proposed which emphasizes being strategic, consistent, adaptive, responsive and effective. The conclusion is that the S-CARE model provides a structure for teaching and learning in the online environment.