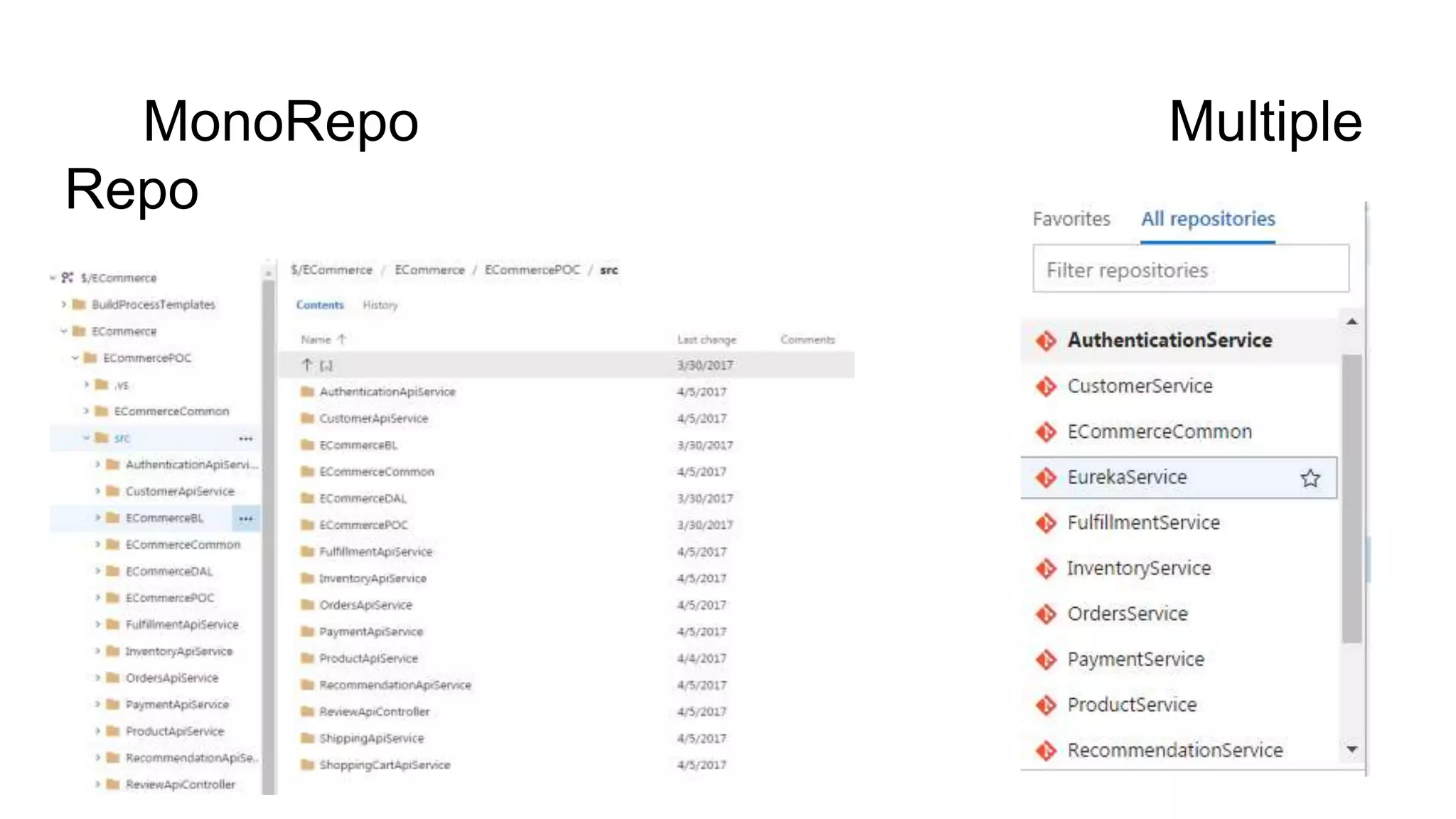
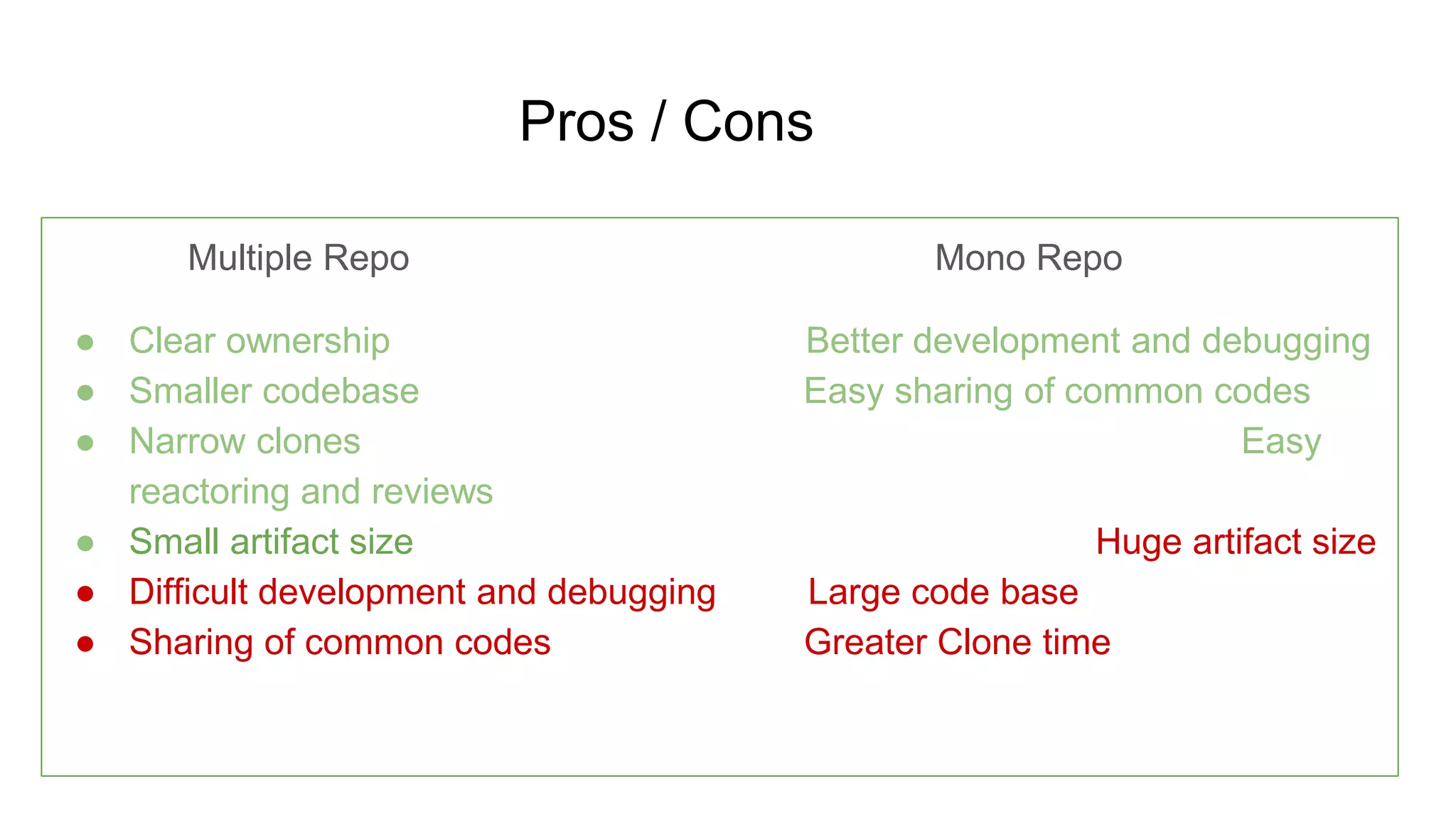
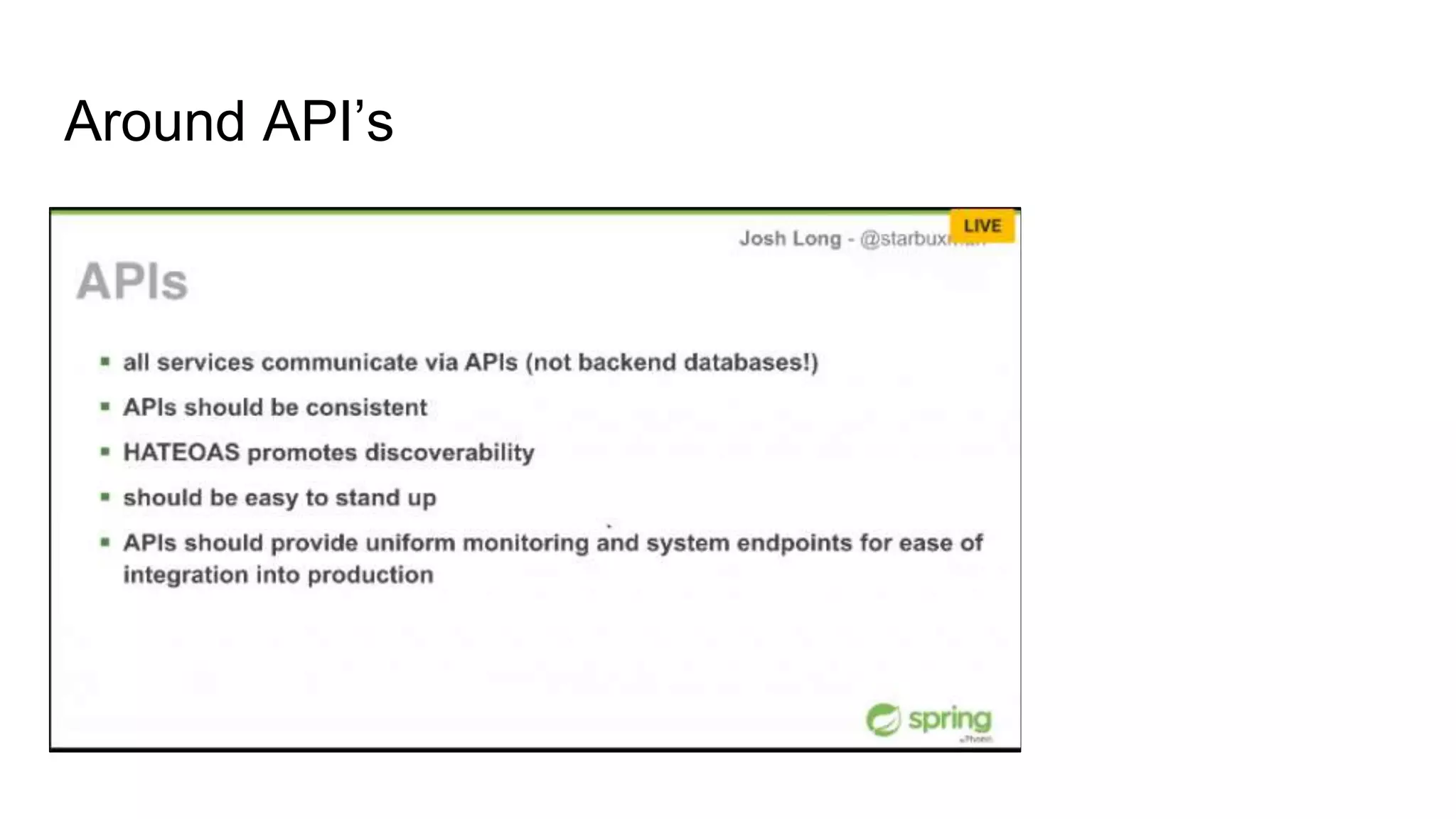
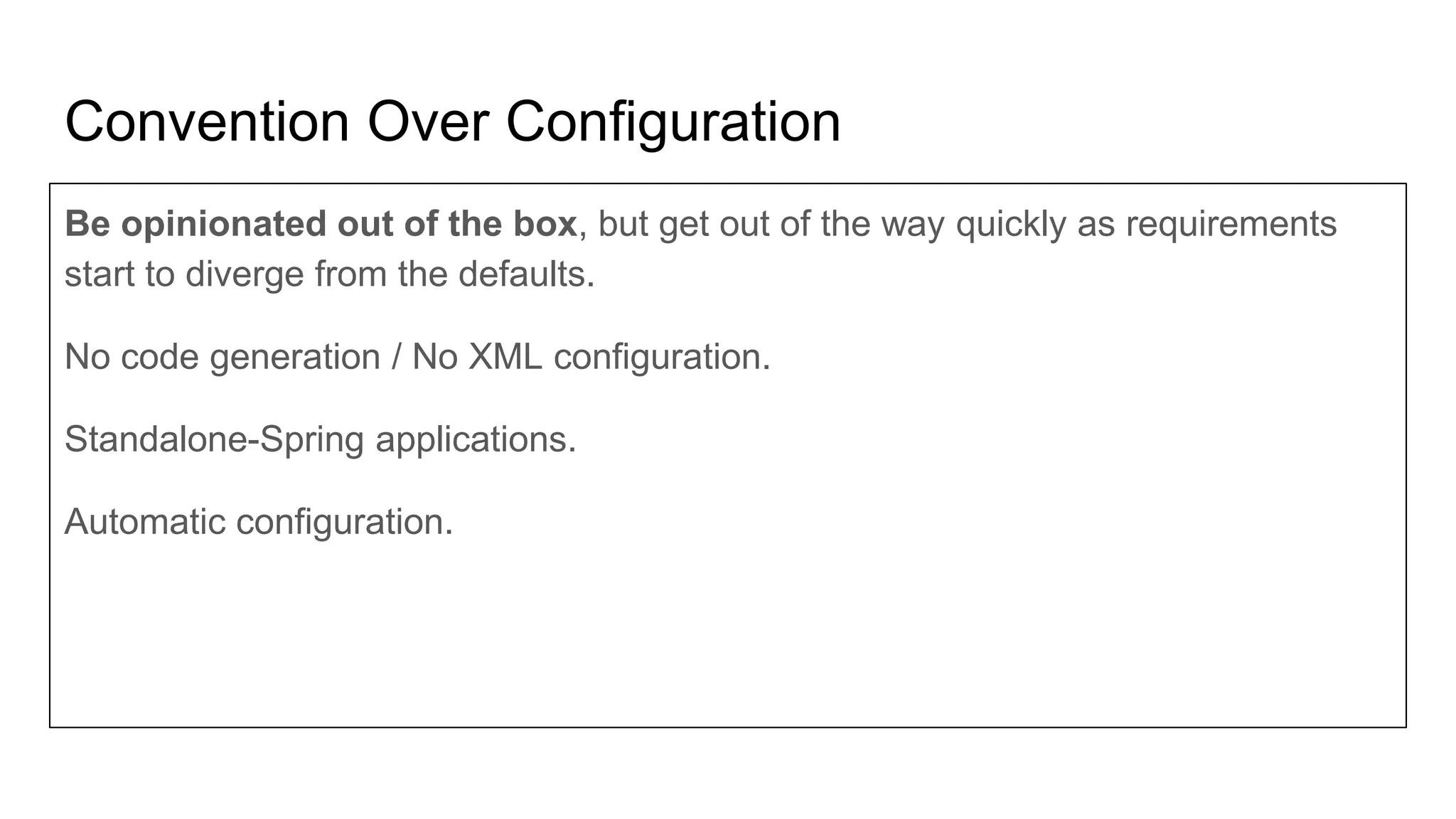
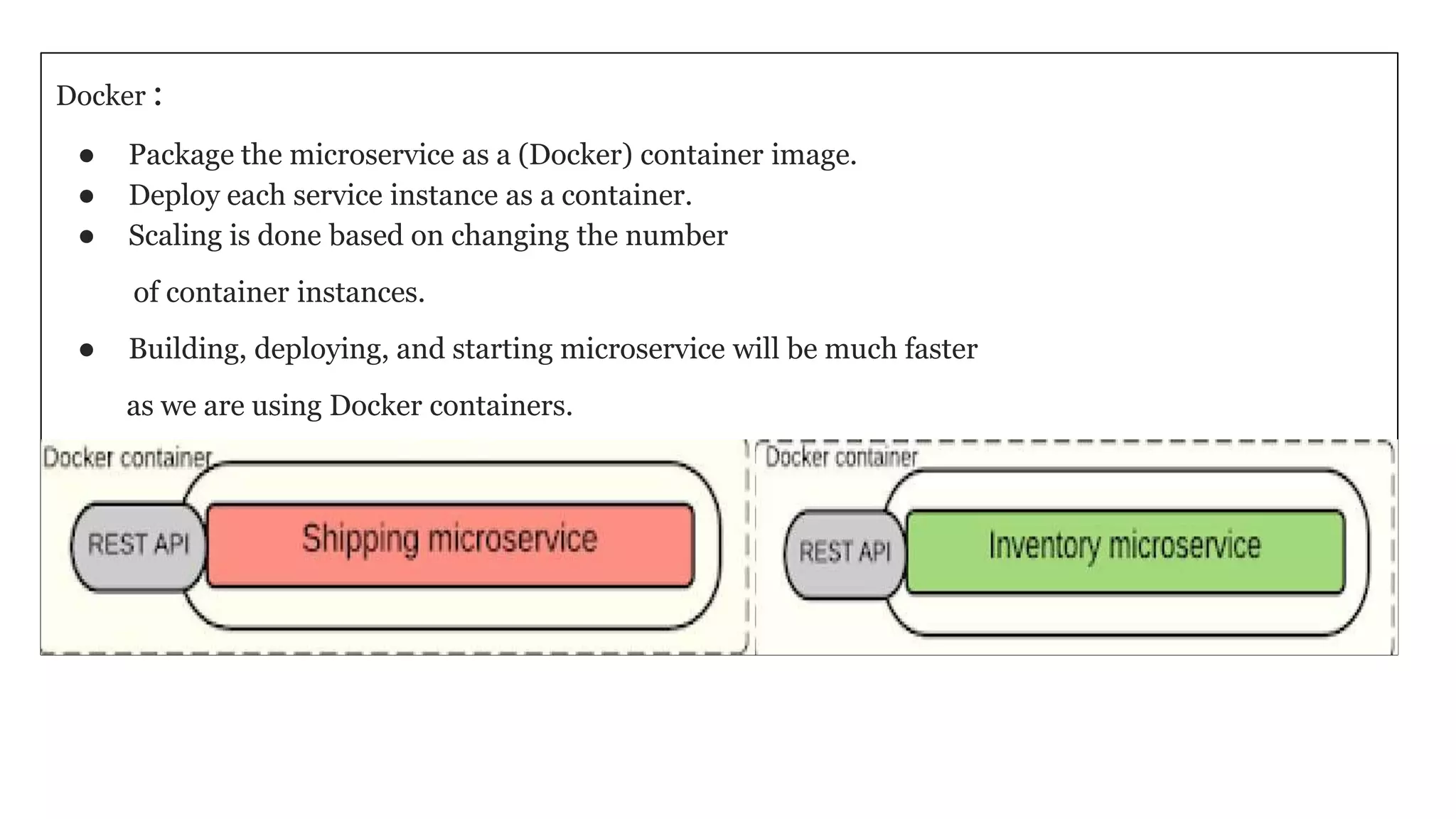
This document provides an agenda and overview for a microservices workshop focusing on hands-on experience. The agenda includes discussing code repository styles, API design with Spring Boot, microservice deployment, and hands-on breakout sessions to build sample microservices. Repository options like mono vs multiple are presented along with pros and cons. Spring Boot basics are explained including conventions, non-functional features, and packaging. Microservice deployment considerations and using Docker are also covered. Participants will then work in teams to build microservices for an e-commerce application.